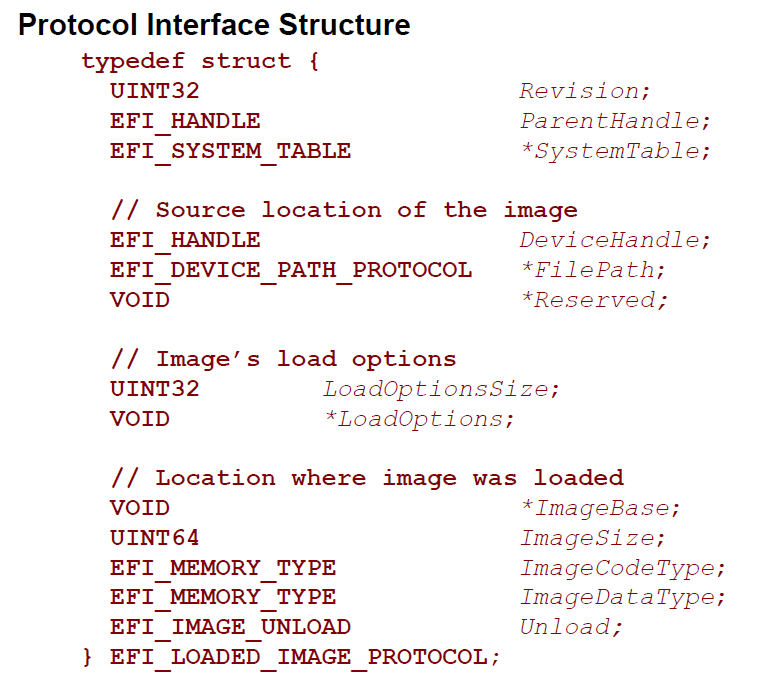
上次介绍了如何在一个程序中直接调用另外的程序,那么在调用过程中是否有机会获得一些加载起来的EFI的信息呢?经过一番搜索,发现EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL【参考1】。这个protocol的作用就是 “Can be used on any image handle to obtain information about the loaded image.”
从定义上看,我们能够得到加载的Image的一些基本信息。在上次程序的基础上,添加一些代码来实验。
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
extern EFI_SHELL_PROTOCOL *gEfiShellProtocol;
extern EFI_SHELL_ENVIRONMENT2 *mEfiShellEnvironment2;
extern EFI_HANDLE gImageHandle;
/**
GET DEVICEPATH
**/
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *
EFIAPI
ShellGetDevicePath (
IN CHAR16 * CONST DeviceName OPTIONAL
)
{
//
// Check for UEFI Shell 2.0 protocols
//
if (gEfiShellProtocol != NULL) {
return (gEfiShellProtocol->GetDevicePathFromFilePath(DeviceName));
}
//
// Check for EFI shell
//
if (mEfiShellEnvironment2 != NULL) {
return (mEfiShellEnvironment2->NameToPath(DeviceName));
}
return (NULL);
}
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN char **Argv
)
{
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *DevicePath;
EFI_HANDLE NewHandle;
EFI_STATUS Status;
UINTN ExitDataSizePtr;
CHAR16 *R=L"HelloWorld.efi";
EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL *ImageInfo = NULL;
Print(L"File [%s]\n",R);
DevicePath=ShellGetDevicePath(R);
//
// Load the image with:
// FALSE - not from boot manager and NULL, 0 being not already in memory
//
Status = gBS->LoadImage(
FALSE,
gImageHandle,
DevicePath,
NULL,
0,
&NewHandle);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (NewHandle != NULL) {
gBS->UnloadImage(NewHandle);
}
Print(L"Error during LoadImage [%X]\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
Status = gBS -> HandleProtocol (
NewHandle,
&gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid,
&ImageInfo
);
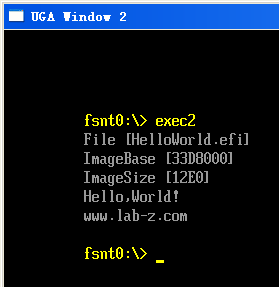
Print(L"ImageBase [%lX]\n",ImageInfo->ImageBase);
Print(L"ImageSize [%lX]\n",ImageInfo->ImageSize);
//
// now start the image, passing up exit data if the caller requested it
//
Status = gBS->StartImage(
NewHandle,
&ExitDataSizePtr,
NULL
);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (NewHandle != NULL) {
gBS->UnloadImage(NewHandle);
}
Print(L"Error during StartImage [%X]\n",Status);
return (Status);
}
gBS->UnloadImage (NewHandle);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
特别注意,我们代码中需要使用这个Protocol的GUID,在INF中添加下面的引用即可。
[Protocols] gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid
运行结果
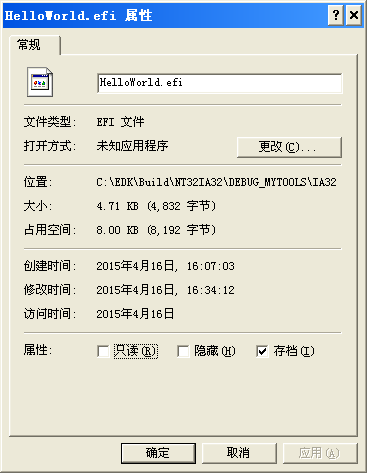
可以看到显示的ImageSize就是 HelloWorld.efi的大小。
实验调用的代码比较特殊,如果直接调用CLIB编写的程序会导致错误。至于具体的原因,后续再进行研究。
实验的 HelloWorld.EFI 的代码在下面
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/PcdLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
/**
The user Entry Point for Application. The user code starts with this function
as the real entry point for the application.
@param[in] ImageHandle The firmware allocated handle for the EFI image.
@param[in] SystemTable A pointer to the EFI System Table.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The entry point is executed successfully.
@retval other Some error occurs when executing this entry point.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
UefiMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
Print(L"Hello,World! \r\n");
Print(L"www.lab-z.com \r\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
对应的INF
[Defines] INF_VERSION = 0x00010005 BASE_NAME = HelloWorld FILE_GUID = 6987936E-ED34-44db-AE97-1FA5E4ED2116 MODULE_TYPE = UEFI_APPLICATION VERSION_STRING = 1.0 ENTRY_POINT = UefiMain # # The following information is for reference only and not required by the build tools. # # VALID_ARCHITECTURES = IA32 X64 IPF EBC # [Sources] HelloWorld.c [Packages] MdePkg/MdePkg.dec MdeModulePkg/MdeModulePkg.dec [LibraryClasses] UefiApplicationEntryPoint UefiLib PcdLib [FeaturePcd] [Pcd]
实验完整代码下载
exec2
参考:
1.UEFI Spec 2.4 P265