在 EDK2 中有一种比较有趣的定义和初始化Table 的方法,主要是基于 __VA_ARGS__ 这个宏。
“__VA_ARGS__是一个预处理宏,用于表示可变数量的参数。当在宏定义中使用__VA_ARGS__,它会自动展开为传递给宏的实际参数。以下是一个示例使用__VA_ARGS__的宏定义代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#define PRINT_ARGS(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
int main() {
PRINT_ARGS("Hello, %s!\n", "World");
return 0;
}
上述代码中,宏定义PRINT_ARGS使用__VA_ARGS__来表示可变数量的参数,并通过printf函数打印参数。在main函数中,我们调用PRINT_ARGS宏来打印字符串"Hello, World!"。运行结果为输出"Hello, World!"。
总结:__VA_ARGS__是一个用于表示可变数量参数的预处理宏,在宏定义中使用它可以方便地处理不定数量的参数。“----来自百度
很多时候,我们定义一个 Table 用来传递一些常量,Table需要给出具体的长度,通过这个宏可以实现自动给出Table 的长度,避免用户手工计数的麻烦。
下面是一个示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#define MY_TABLE_INIT(Vid,Did,...) \
{ \
{ Vid, Did, (sizeof((UINT32[]){__VA_ARGS__})/sizeof(UINT32)) }, \
{ __VA_ARGS__ } \
}
typedef struct {
UINT16 VendorId;
UINT16 DeviceId;
UINT16 DataDwords;
} MY_TABLE_HEADER;
typedef struct {
MY_TABLE_HEADER Header;
UINT32 Data[];
} ONE_TABLE;
ONE_TABLE Table = MY_TABLE_INIT (
0x1234, 0x5678,
// Raw Data
0x01234567,
0x89ABCDEF,
0xFEDCBA98,
0x76543210
);
INTN
EFIAPI
ShellAppMain (
IN UINTN Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
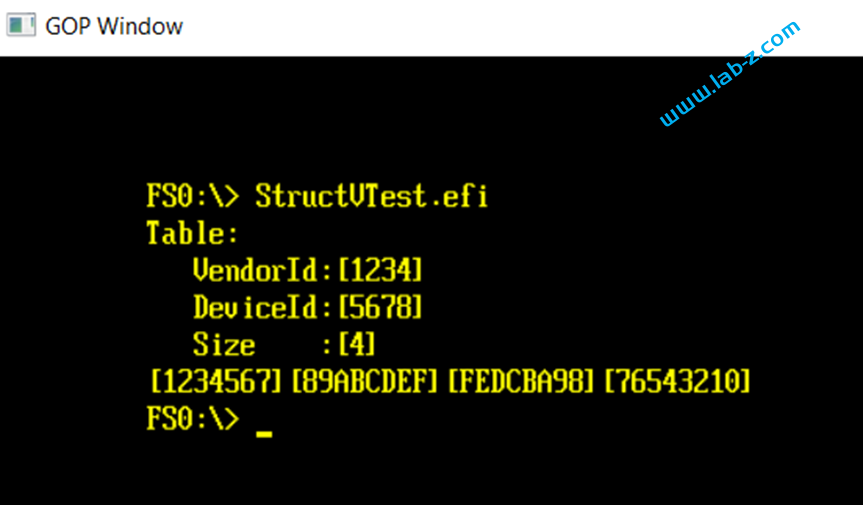
Print(L"Table:\n");
Print(L" VendorId:[%X]\n",Table.Header.VendorId);
Print(L" DeviceId:[%X]\n",Table.Header.DeviceId);
Print(L" Size :[%X]\n",Table.Header.DataDwords);
for (int i=0;i<Table.Header.DataDwords;i++) {
Print(L"[%04X]",Table.Data[i]);
}
Print(L"\n");
return(0);
}
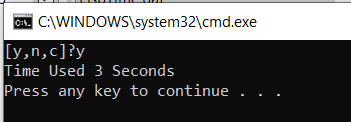
运行结果如下:
上面代码的解释如下:
1.首先我们定义一个 ONE_TABLE 结构体用来“携带”数据。
typedef struct {
MY_TABLE_HEADER Header;
UINT32 Data[];
} ONE_TABLE;
从定义可以看到,这个结构体包含了一个头,还有一个变长的数据段。头可以实现用于识别判断这个Table 是否为我们需要的目的,例如,其中有DID和VID 信息。具体定义如下,特别注意 DataDwords 给出了后面变长数据段的长度:
typedef struct {
UINT16 VendorId;
UINT16 DeviceId;
UINT16 DataDwords;
} MY_TABLE_HEADER;
对于DataDwords 就是我们前面提到的“Table需要给出具体的长度”的问题。
2.为了解决上述问题,通过下面的宏来解决:
#define MY_TABLE_INIT(Vid,Did,...) \
{ \
{ Vid, Did, (sizeof((UINT32[]){__VA_ARGS__})/sizeof(UINT32)) }, \
{ __VA_ARGS__ } \
}
其中(sizeof((UINT32[]){__VA_ARGS__})/sizeof(UINT32)) 就是计算长度的代码。最终的结果是以 UINT32(DWORD)给出的。
3.初始化定义如下,可以看到DataDwords的计算是宏直接完成的,并不需要我们直接提供
ONE_TABLE Table = MY_TABLE_INIT (
0x1234, 0x5678,
// Raw Data
0x01234567,
0x89ABCDEF,
0xFEDCBA98,
0x76543210
);
可以看到,通过上面的方法可以帮助我们方便的实现可变数据的长度定义,有兴趣的朋友不妨尝试一下。
完整的代码下载: