这里介绍一下解压缩 EFI_DECOMPRESS_PROTOCOL 的使用。
首先是 GetInfo 函数【参考1】。通过它我们能够获得压缩文件的一些基本信息,比如:解压后的大小,解压过程需要的临时内存空间的大小。
之后就是具体的解压函数 Decompress 【参考2】
根据上面的信息,编写一个简单的测试程序,首先将压缩格式的文件读取到内存中,再使用 GetInfo 取得必要的信息,最后,根据必须要的信息创建内存 Buffer ,使用 Decompress 解压即可。
代码如下
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/Decompress.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_DECOMPRESS_PROTOCOL *Decompress;
VOID *ImageBuffer=NULL;
UINT32 ImageLength=0;
UINT32 DestinationSize;
UINT8 *Scratch;
UINT32 ScratchSize;
VOID *DecompressedImageBuffer=NULL;
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
EFI_FILE_INFO *FileInfo = NULL;
UINTN ReadSize;
EFI_HANDLE *HandleBuffer=NULL;
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol (&gEfiDecompressProtocolGuid,
NULL, (VOID**)&Decompress);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"Can't find Decompress Protocol! \n");
} else {
//Open the file given by the parameter
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(
Argv[1],
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}//if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
//Get file size
FileInfo = ShellGetFileInfo((SHELL_FILE_HANDLE)FileHandle);
//Allocate a memory buffer
HandleBuffer = AllocateZeroPool((UINTN) FileInfo->FileSize);
if (HandleBuffer == NULL) {
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES); }
ReadSize=(UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize;
//Load the whole file to the buffer
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&ReadSize,HandleBuffer);
//Close the source file
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
Status = Decompress->GetInfo (
Decompress,
HandleBuffer,
ReadSize,
&DestinationSize,
&ScratchSize
);
if (!EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Print(L"[GetInfo] Destination Size %d\n",DestinationSize);
Print(L"[GetInfo] Scratch Size %d\n",ScratchSize);
DecompressedImageBuffer = AllocateZeroPool (DestinationSize);
if (DecompressedImageBuffer != NULL) {
Scratch = AllocateZeroPool (ScratchSize);
if (Scratch != NULL) {
Status = Decompress->Decompress(
Decompress,
HandleBuffer, //Source
ReadSize, //Source Size
DecompressedImageBuffer,//Destination
DestinationSize, //DestinationSize
Scratch,
ScratchSize
);
if (!EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
ImageBuffer = DecompressedImageBuffer;
ImageLength = DestinationSize;
//Create a new file
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(L"decomp.bmp",
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ |
EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"CreatFile failed [%r]!\n",Status);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Status = ShellWriteFile(FileHandle,
&DestinationSize,
ImageBuffer
);
//Close the source file
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
} //if (!EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
else
{
Print(L"Decompress error [%r] \n",Status);
}
FreePool (Scratch);
} // if (Scratch != NULL) {
} //if (ImageBuffer != NULL) {
} //if (!EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
else {
Print(L"Read compressed file error!\n",ScratchSize);
}
} //if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
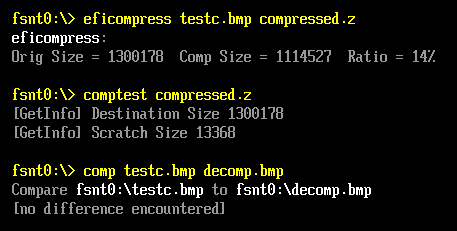
运行结果
完整程序下载
特别注意:
1.本文测试使用的压缩文件是 UEFI 下面生成的,具体命令是
eficompress testc.bmp compressed.z
我尝试使用 BaseTools 里面的压缩工具,生成的文件格式会出现不兼容,无法正常解压的情况。
2.根据我自己的理解 Scratch Buffer 是解压过程中解压算法使用的内存区域,不同压缩文件对于这片区域的大小要求不同。
参考:
1. UEFI Spec 2.4 P883
2. UEFI Spec 2.4 P885
3. ShellPkg 中的 EfiDecompress 程序是非常好的参考例子。


可以用edk2的BaseTools\Source\C\Common\EfiCompress.c压缩,压缩后的文件可以用EFI_DECOMPRESS_PROTOCOL 解压。