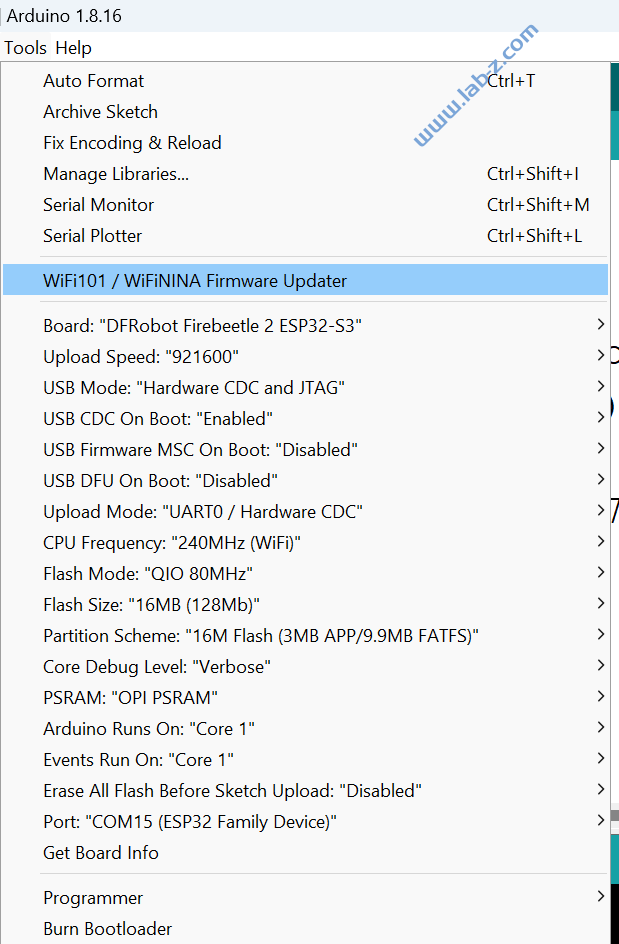
#include "VGA.h"
#include <FONT_9x16.h>
VGA vga;
int scale = 2;
void setup()
{
// r,r,r,r,r, g,g, g, g, g, g, b, b, b, b, b, h,v
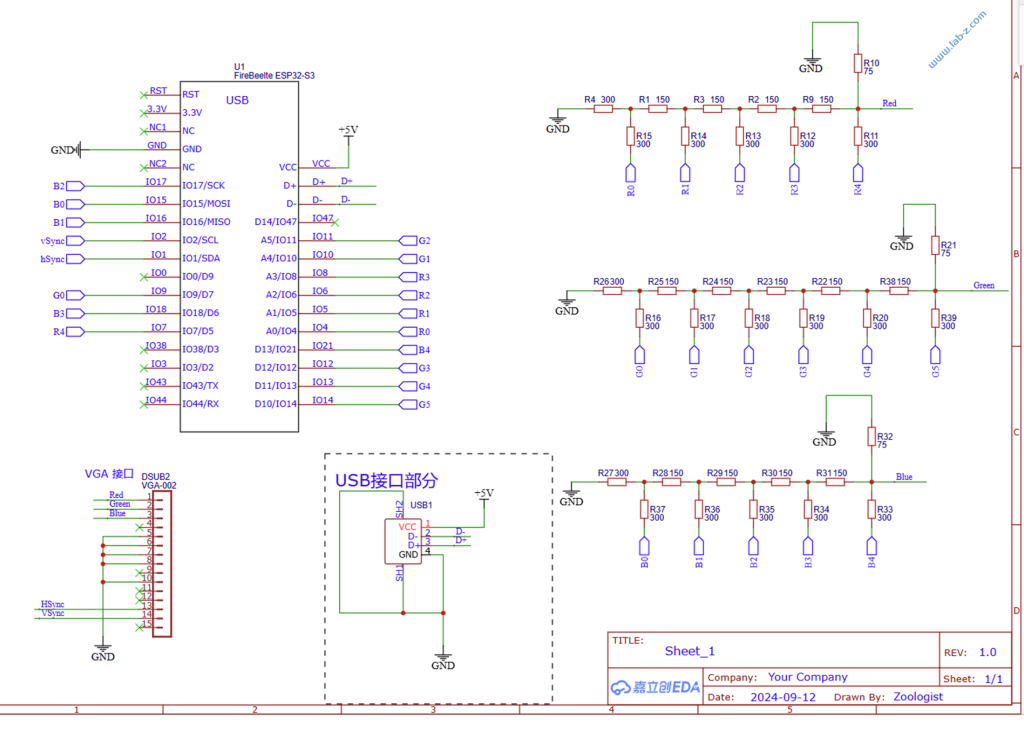
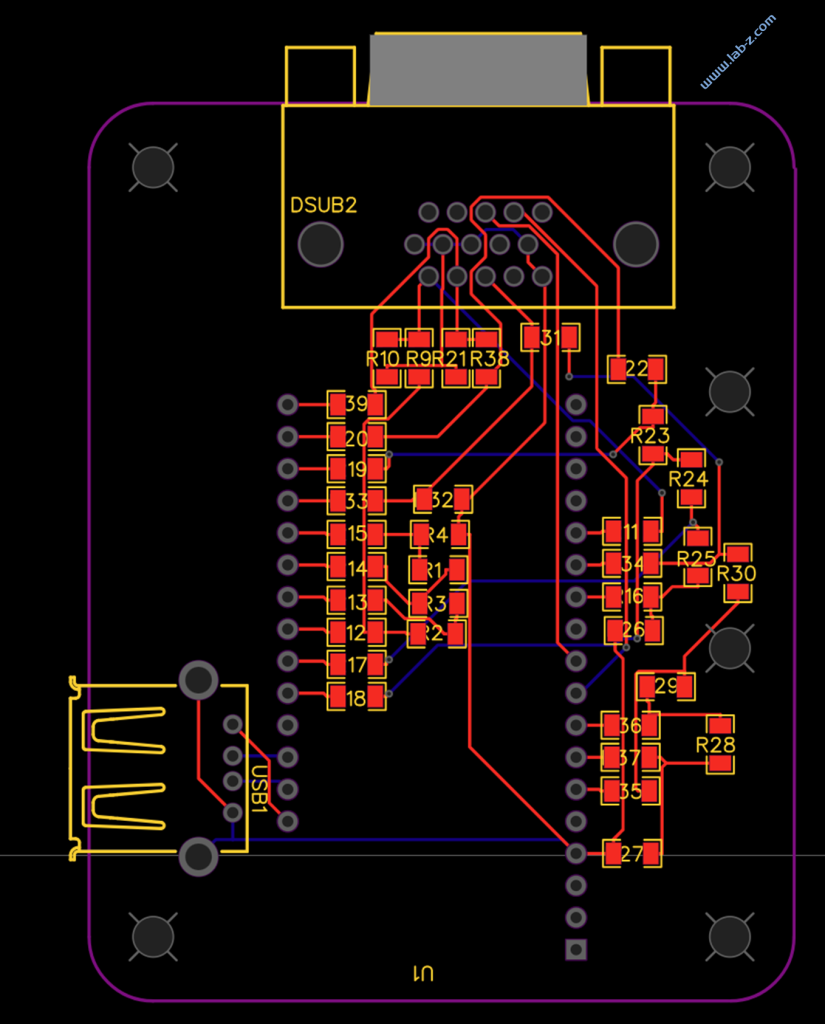
const PinConfig pins(4,5,6,7,8, 9,10,11,12,13,14, 15,16,17,18,21, 1,2);
Mode mode = Mode::MODE_640x480x60;
if(!vga.init(pins, mode, 8, 3)) while(1) delay(1);
vga.start();
for(int y = 0; y < 480; y++)
for(int x = 0; x < 640; x++)
vga.dotdit(x, y, x, y, 255-x);
vga.setFont(FONT_9x16);
vga.start();
delay(5000);
}
void loop()
{
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 100000; count++)
vga.dot(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 10000; count++)
vga.line(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 10000; count++)
vga.tri(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 1000; count++)
vga.fillTri(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 10000; count++)
vga.rect(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 1000; count++)
vga.fillRect(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 10000; count++)
vga.circle(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%100, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 5000; count++)
vga.fillCircle(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%50, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 10000; count++)
vga.ellipse(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%100, rand()%100, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 1000; count++)
vga.fillEllipse(rand()%640, rand()%480, rand()%100, rand()%100, rand()%255);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 100000; count++)
vga.mouse(rand()%640, rand()%480);
vga.clear(0);
delay(1000);
for(int count = 0; count < 1000; count++)
{
static int c = 0;
static int d = 1;
c += d;
if (c == 0 || c == 255)
d = -d;
char text[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
};
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
text[i] = 33 + (i + (c >> 2));
vga.setCursor(8, 48);
vga.setTextColor(vga.rgb(c, 255 - c, 255), vga.rgb(0, c / 2, 127 - c / 2));
vga.print(text);
vga.setCursor(8, 148);
vga.print(text);
vga.setCursor(8, 248);
vga.print(text);
vga.setCursor(8, 348);
vga.print(text);
}
delay(4000);
}
工作的测试视频【FireBeelte 2 ESP32-S3 VGA 输出测试】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1yrzjY4EmG/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=5ca375392c3dd819bfc37d4672cb6d54