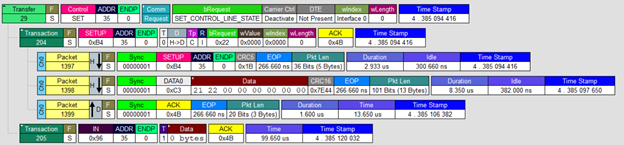
这次介绍的是ESP32 Arduino 直接读取蓝牙键盘的输入。特别需要注意的是蓝牙键盘有两种,Classical 和 BLE。我测试过罗技的 K480 是Classical蓝牙键盘:
/** NimBLE_Server Demo:
*
* Demonstrates many of the available features of the NimBLE client library.
*
* Created: on March 24 2020
* Author: H2zero
*
*/
/*
* This program is based on https://github.com/h2zero/NimBLE-Arduino/tree/master/examples/NimBLE_Client.
* My changes are covered by the MIT license.
*/
/*
* MIT License
*
* Copyright (c) 2022 esp32beans@gmail.com
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
* copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
* SOFTWARE.
*/
// Install NimBLE-Arduino by h2zero using the IDE library manager.
#include <NimBLEDevice.h>
const char HID_SERVICE[] = "1812";
const char HID_INFORMATION[] = "2A4A";
const char HID_REPORT_MAP[] = "2A4B";
const char HID_CONTROL_POINT[] = "2A4C";
const char HID_REPORT_DATA[] = "2A4D";
void scanEndedCB(NimBLEScanResults results);
static NimBLEAdvertisedDevice* advDevice;
static bool doConnect = false;
static uint32_t scanTime = 0; /** 0 = scan forever */
/** None of these are required as they will be handled by the library with defaults. **
** Remove as you see fit for your needs */
class ClientCallbacks : public NimBLEClientCallbacks {
void onConnect(NimBLEClient* pClient) {
Serial.println("Connected");
/** After connection we should change the parameters if we don't need fast response times.
* These settings are 150ms interval, 0 latency, 450ms timout.
* Timeout should be a multiple of the interval, minimum is 100ms.
* I find a multiple of 3-5 * the interval works best for quick response/reconnect.
* Min interval: 120 * 1.25ms = 150, Max interval: 120 * 1.25ms = 150, 0 latency, 60 * 10ms = 600ms timeout
*/
pClient->updateConnParams(120,120,0,60);
};
void onDisconnect(NimBLEClient* pClient) {
Serial.print(pClient->getPeerAddress().toString().c_str());
Serial.println(" Disconnected - Starting scan");
NimBLEDevice::getScan()->start(scanTime, scanEndedCB);
};
/** Called when the peripheral requests a change to the connection parameters.
* Return true to accept and apply them or false to reject and keep
* the currently used parameters. Default will return true.
*/
bool onConnParamsUpdateRequest(NimBLEClient* pClient, const ble_gap_upd_params* params) {
// Failing to accepts parameters may result in the remote device
// disconnecting.
return true;
};
/********************* Security handled here **********************
****** Note: these are the same return values as defaults ********/
uint32_t onPassKeyRequest(){
Serial.println("Client Passkey Request");
/** return the passkey to send to the server */
return 123456;
};
bool onConfirmPIN(uint32_t pass_key){
Serial.print("The passkey YES/NO number: ");
Serial.println(pass_key);
/** Return false if passkeys don't match. */
return true;
};
/** Pairing process complete, we can check the results in ble_gap_conn_desc */
void onAuthenticationComplete(ble_gap_conn_desc* desc){
if(!desc->sec_state.encrypted) {
Serial.println("Encrypt connection failed - disconnecting");
/** Find the client with the connection handle provided in desc */
NimBLEDevice::getClientByID(desc->conn_handle)->disconnect();
return;
}
};
};
/** Define a class to handle the callbacks when advertisments are received */
class AdvertisedDeviceCallbacks: public NimBLEAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks {
void onResult(NimBLEAdvertisedDevice* advertisedDevice) {
if ((advertisedDevice->getAdvType() == BLE_HCI_ADV_TYPE_ADV_DIRECT_IND_HD)
|| (advertisedDevice->getAdvType() == BLE_HCI_ADV_TYPE_ADV_DIRECT_IND_LD)
|| (advertisedDevice->haveServiceUUID() && advertisedDevice->isAdvertisingService(NimBLEUUID(HID_SERVICE))))
{
Serial.print("Advertised HID Device found: ");
Serial.println(advertisedDevice->toString().c_str());
/** stop scan before connecting */
NimBLEDevice::getScan()->stop();
/** Save the device reference in a global for the client to use*/
advDevice = advertisedDevice;
/** Ready to connect now */
doConnect = true;
}
};
};
/** Notification / Indication receiving handler callback */
// Notification from 4c:75:25:xx:yy:zz: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 1,0,0,0,0,
void notifyCB(NimBLERemoteCharacteristic* pRemoteCharacteristic, uint8_t* pData, size_t length, bool isNotify){
std::string str = (isNotify == true) ? "Notification" : "Indication";
str += " from ";
/** NimBLEAddress and NimBLEUUID have std::string operators */
str += std::string(pRemoteCharacteristic->getRemoteService()->getClient()->getPeerAddress());
str += ": Service = " + std::string(pRemoteCharacteristic->getRemoteService()->getUUID());
str += ", Characteristic = " + std::string(pRemoteCharacteristic->getUUID());
str += ", Value = ";
Serial.print(str.c_str());
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Serial.print(pData[i], HEX);
Serial.print(',');
}
Serial.print(' ');
if (length == 6) {
// BLE Trackball Mouse from Amazon returns 6 bytes per HID report
Serial.printf("buttons: %02x, x: %d, y: %d, wheel: %d",
pData[0], *(int16_t *)&pData[1], *(int16_t *)&pData[3], (int8_t)pData[5]);
}
else if (length == 5) {
// https://github.com/wakwak-koba/ESP32-NimBLE-Mouse
// returns 5 bytes per HID report
Serial.printf("buttons: %02x, x: %d, y: %d, wheel: %d hwheel: %d",
pData[0], (int8_t)pData[1], (int8_t)pData[2], (int8_t)pData[3], (int8_t)pData[4]);
}
Serial.println();
}
/** Callback to process the results of the last scan or restart it */
void scanEndedCB(NimBLEScanResults results){
Serial.println("Scan Ended");
}
/** Create a single global instance of the callback class to be used by all clients */
static ClientCallbacks clientCB;
/** Handles the provisioning of clients and connects / interfaces with the server */
bool connectToServer()
{
NimBLEClient* pClient = nullptr;
/** Check if we have a client we should reuse first **/
if(NimBLEDevice::getClientListSize()) {
/** Special case when we already know this device, we send false as the
* second argument in connect() to prevent refreshing the service database.
* This saves considerable time and power.
*/
pClient = NimBLEDevice::getClientByPeerAddress(advDevice->getAddress());
if(pClient){
if(!pClient->connect(advDevice, false)) {
Serial.println("Reconnect failed");
return false;
}
Serial.println("Reconnected client");
}
/** We don't already have a client that knows this device,
* we will check for a client that is disconnected that we can use.
*/
else {
pClient = NimBLEDevice::getDisconnectedClient();
}
}
/** No client to reuse? Create a new one. */
if(!pClient) {
if(NimBLEDevice::getClientListSize() >= NIMBLE_MAX_CONNECTIONS) {
Serial.println("Max clients reached - no more connections available");
return false;
}
pClient = NimBLEDevice::createClient();
Serial.println("New client created");
pClient->setClientCallbacks(&clientCB, false);
/** Set initial connection parameters: These settings are 15ms interval, 0 latency, 120ms timout.
* These settings are safe for 3 clients to connect reliably, can go faster if you have less
* connections. Timeout should be a multiple of the interval, minimum is 100ms.
* Min interval: 12 * 1.25ms = 15, Max interval: 12 * 1.25ms = 15, 0 latency, 51 * 10ms = 510ms timeout
*/
pClient->setConnectionParams(12,12,0,51);
/** Set how long we are willing to wait for the connection to complete (seconds), default is 30. */
pClient->setConnectTimeout(5);
if (!pClient->connect(advDevice)) {
/** Created a client but failed to connect, don't need to keep it as it has no data */
NimBLEDevice::deleteClient(pClient);
Serial.println("Failed to connect, deleted client");
return false;
}
}
if(!pClient->isConnected()) {
if (!pClient->connect(advDevice)) {
Serial.println("Failed to connect");
return false;
}
}
Serial.print("Connected to: ");
Serial.println(pClient->getPeerAddress().toString().c_str());
Serial.print("RSSI: ");
Serial.println(pClient->getRssi());
/** Now we can read/write/subscribe the charateristics of the services we are interested in */
NimBLERemoteService* pSvc = nullptr;
NimBLERemoteCharacteristic* pChr = nullptr;
NimBLERemoteDescriptor* pDsc = nullptr;
pSvc = pClient->getService(HID_SERVICE);
if(pSvc) { /** make sure it's not null */
// This returns the HID report descriptor like this
// HID_REPORT_MAP 0x2a4b Value: 5,1,9,2,A1,1,9,1,A1,0,5,9,19,1,29,5,15,0,25,1,75,1,
// Copy and paste the value digits to http://eleccelerator.com/usbdescreqparser/
// to see the decoded report descriptor.
pChr = pSvc->getCharacteristic(HID_REPORT_MAP);
if(pChr) { /** make sure it's not null */
Serial.print("HID_REPORT_MAP ");
if(pChr->canRead()) {
std::string value = pChr->readValue();
Serial.print(pChr->getUUID().toString().c_str());
Serial.print(" Value: ");
uint8_t *p = (uint8_t *)value.data();
for (size_t i = 0; i < value.length(); i++) {
Serial.print(p[i], HEX);
Serial.print(',');
}
Serial.println();
}
}
else {
Serial.println("HID REPORT MAP char not found.");
}
// Subscribe to characteristics HID_REPORT_DATA.
// One real device reports 2 with the same UUID but
// different handles. Using getCharacteristic() results
// in subscribing to only one.
std::vector<NimBLERemoteCharacteristic*>*charvector;
charvector = pSvc->getCharacteristics(true);
for (auto &it: *charvector) {
if (it->getUUID() == NimBLEUUID(HID_REPORT_DATA)) {
Serial.println(it->toString().c_str());
if (it->canNotify()) {
if(!it->subscribe(true, notifyCB)) {
/** Disconnect if subscribe failed */
Serial.println("subscribe notification failed");
pClient->disconnect();
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
Serial.println("Done with this device!");
return true;
}
void setup ()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting NimBLE HID Client");
/** Initialize NimBLE, no device name spcified as we are not advertising */
NimBLEDevice::init("");
/** Set the IO capabilities of the device, each option will trigger a different pairing method.
* BLE_HS_IO_KEYBOARD_ONLY - Passkey pairing
* BLE_HS_IO_DISPLAY_YESNO - Numeric comparison pairing
* BLE_HS_IO_NO_INPUT_OUTPUT - DEFAULT setting - just works pairing
*/
//NimBLEDevice::setSecurityIOCap(BLE_HS_IO_KEYBOARD_ONLY); // use passkey
//NimBLEDevice::setSecurityIOCap(BLE_HS_IO_DISPLAY_YESNO); //use numeric comparison
/** 2 different ways to set security - both calls achieve the same result.
* no bonding, no man in the middle protection, secure connections.
*
* These are the default values, only shown here for demonstration.
*/
NimBLEDevice::setSecurityAuth(true, false, true);
//NimBLEDevice::setSecurityAuth(/*BLE_SM_PAIR_AUTHREQ_BOND | BLE_SM_PAIR_AUTHREQ_MITM |*/ BLE_SM_PAIR_AUTHREQ_SC);
/** Optional: set the transmit power, default is 3db */
NimBLEDevice::setPower(ESP_PWR_LVL_P9); /** +9db */
/** Optional: set any devices you don't want to get advertisments from */
// NimBLEDevice::addIgnored(NimBLEAddress ("aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff"));
/** create new scan */
NimBLEScan* pScan = NimBLEDevice::getScan();
/** create a callback that gets called when advertisers are found */
pScan->setAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks(new AdvertisedDeviceCallbacks());
/** Set scan interval (how often) and window (how long) in milliseconds */
pScan->setInterval(45);
pScan->setWindow(15);
/** Active scan will gather scan response data from advertisers
* but will use more energy from both devices
*/
pScan->setActiveScan(true);
/** Start scanning for advertisers for the scan time specified (in seconds) 0 = forever
* Optional callback for when scanning stops.
*/
pScan->start(scanTime, scanEndedCB);
}
void loop ()
{
/** Loop here until we find a device we want to connect to */
if (!doConnect) return;
doConnect = false;
/** Found a device we want to connect to, do it now */
if(connectToServer()) {
Serial.println("Success! we should now be getting notifications!");
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to connect, starting scan");
NimBLEDevice::getScan()->start(scanTime,scanEndedCB);
}
}
Starting NimBLE HID Client
Advertised HID Device found: Name: RAPOO BT4.0 KB, Address: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99, appearance: 961, serviceUUID: 0x1812
Scan Ended
New client created
Connected
Connected to: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99
RSSI: -64
HID_REPORT_MAP 0x2a4b Value:
Done with this device!
Success! we should now be getting notifications!
b4:ee:25:f3:86:99 Disconnected - Starting scan
Advertised HID Device found: Name: RAPOO BT4.0 KB, Address: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99, appearance: 961, serviceUUID: 0x1812
Scan Ended
Connected
Reconnected client
Connected to: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99
RSSI: -43
HID_REPORT_MAP 0x2a4b Value:
Done with this device!
Success! we should now be getting notifications!
b4:ee:25:f3:86:99 Disconnected - Starting scan
Advertised HID Device found: Name: RAPOO BT4.0 KB, Address: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99, appearance: 961, serviceUUID: 0x1812
Scan Ended
Connected
Reconnected client
Connected to: b4:ee:25:f3:86:99
RSSI: -42
HID_REPORT_MAP 0x2a4b Value: 5,1,9,6,A1,1,85,1,5,7,19,E0,29,E7,15,0,25,1,75,1,95,8,81,2,95,1,75,8,81,3,95,5,75,1,5,8,19,1,29,5,91,2,95,1,75,3,91,3,95,6,75,8,15,0,26,FF,0,5,7,19,0,29,FF,81,0,C0,5,C,9,1,A1,1,85,2,15,0,25,1,75,1,95,1E,A,24,2,A,25,2,A,26,2,A,27,2,A,21,2,A,2A,2,A,23,2,A,8A,1,9,E2,9,EA,9,E9,9,CD,9,B7,9,B6,9,B5,A,83,1,A,94,1,A,92,1,A,9,2,9,B2,9,B3,9,B4,9,8D,9,4,9,30,A,7,3,A,A,3,A,B,3,A,B1,1,9,B8,81,2,95,1,75,2,81,3,C0,
Characteristic: uuid: 0x2a4d, handle: 27 0x001b, props: 0x1a
Characteristic: uuid: 0x2a4d, handle: 31 0x001f, props: 0x1a
Characteristic: uuid: 0x2a4d, handle: 35 0x0023, props: 0x0e
Done with this device!
Success! we should now be getting notifications!
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,14,2B,0,0,0,0,
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,2B,0,0,0,0,0,
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,14,0,0,0,0,0,
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,
Notification from b4:ee:25:f3:86:99: Service = 0x1812, Characteristic = 0x2a4d, Value = 0,0,2C,0,0,0,0,0,