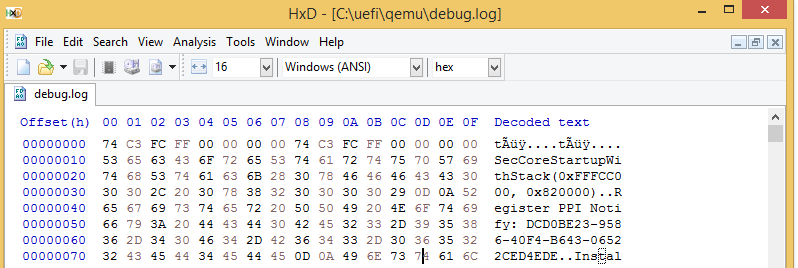
前面提到,Debug Log 中的第一条信息位于 SecMain.c 中的 SecCoreStartupWithStack() 函数中:
DEBUG ((DEBUG_INFO,
"SecCoreStartupWithStack(0x%x, 0x%x)\n",
(UINT32)(UINTN)BootFv,
(UINT32)(UINTN)TopOfCurrentStack
));
这次就分析一下 OVMF 这段代码的具体实现方式。DEBUG 这个宏,之前我们有分析过,有兴趣的读者可以在【参考1】看到之前的文章。
1.这里的 DEBUG 宏可以在 \MdePkg\Include\Library/DebugLib.h 看到,这个和我们之前遇到的是完全相同的定义:
/**
Macro that calls DebugPrint().
If MDEPKG_NDEBUG is not defined and the DEBUG_PROPERTY_DEBUG_PRINT_ENABLED
bit of PcdDebugProperyMask is set, then this macro passes Expression to
DebugPrint().
@param Expression Expression containing an error level, a format string,
and a variable argument list based on the format string.
**/
#if !defined(MDEPKG_NDEBUG)
#define DEBUG(Expression) \
do { \
if (DebugPrintEnabled ()) { \
_DEBUG (Expression); \
} \
} while (FALSE)
#else
#define DEBUG(Expression)
#endif
1.1 其中的 DebugPrintEnabled () 定义在 \OvmfPkg\Library\PlatformDebugLibIoPort\DebugLib.c 文件中,OVMF 这个函数是检查编译期定义
/**
Returns TRUE if DEBUG() macros are enabled.
This function returns TRUE if the DEBUG_PROPERTY_DEBUG_PRINT_ENABLED bit of
PcdDebugProperyMask is set. Otherwise FALSE is returned.
@retval TRUE The DEBUG_PROPERTY_DEBUG_PRINT_ENABLED bit of PcdDebugProperyMask is set.
@retval FALSE The DEBUG_PROPERTY_DEBUG_PRINT_ENABLED bit of PcdDebugProperyMask is clear.
**/
BOOLEAN
EFIAPI
DebugPrintEnabled (
VOID
)
{
return (BOOLEAN) ((PcdGet8(PcdDebugPropertyMask) & DEBUG_PROPERTY_DEBUG_PRINT_ENABLED) != 0);
}
1.2 _DEBUG 的定义在 DebugLib.h 文件中,其中 DebugPrint() 是真正实现功能的函数
/**
Internal worker macro that calls DebugPrint().
This macro calls DebugPrint() passing in the debug error level, a format
string, and a variable argument list.
__VA_ARGS__ is not supported by EBC compiler, Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 2003
and Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Driver Development Kit (Microsoft WINDDK) version 3790.1830.
@param Expression Expression containing an error level, a format string,
and a variable argument list based on the format string.
**/
#if !defined(MDE_CPU_EBC) && (!defined (_MSC_VER) || _MSC_VER > 1400)
#define _DEBUG_PRINT(PrintLevel, ...) \
do { \
if (DebugPrintLevelEnabled (PrintLevel)) { \
DebugPrint (PrintLevel, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} \
} while (FALSE)
#define _DEBUG(Expression) _DEBUG_PRINT Expression
#else
#define _DEBUG(Expression) DebugPrint Expression
#endif
1.2.1 \OvmfPkg\Library\PlatformDebugLibIoPort\DebugLib.c 中定义了 DebugPrint() 函数:
/**
Prints a debug message to the debug output device if the specified error level is enabled.
If any bit in ErrorLevel is also set in DebugPrintErrorLevelLib function
GetDebugPrintErrorLevel (), then print the message specified by Format and the
associated variable argument list to the debug output device.
If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
@param ErrorLevel The error level of the debug message.
@param Format Format string for the debug message to print.
@param ... Variable argument list whose contents are accessed
based on the format string specified by Format.
**/
VOID
EFIAPI
DebugPrint (
IN UINTN ErrorLevel,
IN CONST CHAR8 *Format,
...
)
{
VA_LIST Marker;
VA_START (Marker, Format);
DebugVPrint (ErrorLevel, Format, Marker);
VA_END (Marker);
}
1.2.2 同一个文件中,定义了函数DebugVPrint()
/**
Prints a debug message to the debug output device if the specified
error level is enabled.
If any bit in ErrorLevel is also set in DebugPrintErrorLevelLib function
GetDebugPrintErrorLevel (), then print the message specified by Format and
the associated variable argument list to the debug output device.
If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
@param ErrorLevel The error level of the debug message.
@param Format Format string for the debug message to print.
@param VaListMarker VA_LIST marker for the variable argument list.
**/
VOID
EFIAPI
DebugVPrint (
IN UINTN ErrorLevel,
IN CONST CHAR8 *Format,
IN VA_LIST VaListMarker
)
{
DebugPrintMarker (ErrorLevel, Format, VaListMarker, NULL);
}
1.2.3 同一个文件中 DebugPrintMarker() 代码如下:
/**
Prints a debug message to the debug output device if the specified
error level is enabled base on Null-terminated format string and a
VA_LIST argument list or a BASE_LIST argument list.
If any bit in ErrorLevel is also set in DebugPrintErrorLevelLib function
GetDebugPrintErrorLevel (), then print the message specified by Format and
the associated variable argument list to the debug output device.
If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
@param ErrorLevel The error level of the debug message.
@param Format Format string for the debug message to print.
@param VaListMarker VA_LIST marker for the variable argument list.
@param BaseListMarker BASE_LIST marker for the variable argument list.
**/
VOID
DebugPrintMarker (
IN UINTN ErrorLevel,
IN CONST CHAR8 *Format,
IN VA_LIST VaListMarker,
IN BASE_LIST BaseListMarker
)
{
CHAR8 Buffer[MAX_DEBUG_MESSAGE_LENGTH];
UINTN Length;
//
// If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
//
ASSERT (Format != NULL);
//
// Check if the global mask disables this message or the device is inactive
//
if ((ErrorLevel & GetDebugPrintErrorLevel ()) == 0 ||
!PlatformDebugLibIoPortFound ()) {
return;
}
//
// Convert the DEBUG() message to an ASCII String
//
if (BaseListMarker == NULL) {
Length = AsciiVSPrint (Buffer, sizeof (Buffer), Format, VaListMarker);
} else {
Length = AsciiBSPrint (Buffer, sizeof (Buffer), Format, BaseListMarker);
}
//
// Send the print string to the debug I/O port
//
IoWriteFifo8 (PcdGet16 (PcdDebugIoPort), Length, Buffer);
}
其中PcdDebugIoPort定义在 \OvmfPkg\OvmfPkg.dec文件中:
## This flag is used to control the destination port for PlatformDebugLibIoPort
gUefiOvmfPkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdDebugIoPort|0x402|UINT16|4
因此,就是说这里的DEBUG 是通过向 0x402 直接写入 ASCII 来实现的。
参考:
1. https://www.lab-z.com/stu170dbg/