krishnaLee(sssky307)为我们提供了一个解析DevicePath 的例子:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiBootServicesTableLib.h> //global gST gBS gImageHandle
#include <Protocol/LoadedImage.h> //EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL
#include <Protocol/DevicePath.h> //EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL
#include <Protocol/DevicePathToText.h> //EFI_DEVICE_PATH_TO_TEXT_PROTOCOL
#include <Library/DevicePathLib.h> //link
//reference:http://www.cppblog.com/djxzh/archive/2012/03/06/167106.aspx
//reference:http://www.lab-z.com/getcurd/
//My custom struct defined by UEFI 2.6 Spec
typedef struct
{
UINT8 Type;
UINT8 SubType;
UINT16 Length;
UINT32 PartitionNumber;
UINT64 PartitionStart;
UINT64 PartitionSize;
GUID PartitionSig;
UINT8 PartitionFormat;
UINT8 SignatureType;
} HardDriveMediaDevicePath;
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
UefiMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL *LoadedImage;
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *ImageDevicePath=NULL;
UINT8 *path;
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_TO_TEXT_PROTOCOL *Device2TextProtocol;
CHAR16 *TextDevicePath;
Print(L"Print Nodes:\n");
//open the Loaded image protocol,which is binded on the imageHandle,to get the device handle.
Status = gBS->OpenProtocol (
gImageHandle,
&gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid,
(VOID**)&LoadedImage,
gImageHandle,
NULL,
EFI_OPEN_PROTOCOL_GET_PROTOCOL
);
//get the device path protocol for the device handle.
if (!EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
Status = gBS->OpenProtocol (
LoadedImage->DeviceHandle,
&gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid,
(VOID**)&ImageDevicePath, //get the path protocol
gImageHandle,
NULL,
EFI_OPEN_PROTOCOL_GET_PROTOCOL
);
}
//parse the device path
path=(UINT8 *)ImageDevicePath;
while(1)
{
if(((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Type==0x7F||((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->SubType==0xFF)
{
//if it is end node:
Print(L"type:%d,subType:%d,length:%d\n",\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Type,\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->SubType,\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[0]+((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[1]*0xff);
break;
}
else
{
UINT16 len=((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[0]+((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[1]*0xff;
Print(L"type:%d,subType:%d,length:%d\n",\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Type,\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->SubType,\
((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[0]+((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Length[1]*0xff);
//print my concern node
if(((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->Type==0x4&&((EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL *)path)->SubType==0x1)
{
HardDriveMediaDevicePath *path2=(HardDriveMediaDevicePath *)path;
Print(L" PartitionNumber:%d \n PartitionStart:0x%lx \n PartitionSize:0x%lx \n PartitionSig:%g \n PartitionFormat:%d \n SignatureType:%d \n",\
path2->PartitionNumber,path2->PartitionStart,path2->PartitionSize,path2->PartitionSig,path2->PartitionFormat,path2->SignatureType);
}
//go to next node;
path+=len;
}
}//while end
//get a converter.
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(&gEfiDevicePathToTextProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID**)&Device2TextProtocol
);
//convert device path to text.
if (!EFI_ERROR (Status))
{
TextDevicePath= Device2TextProtocol->ConvertDevicePathToText(ImageDevicePath, 1, 1);
Print(L"%s\n",TextDevicePath);
gBS->FreePool(TextDevicePath);
}
//clear
gBS->CloseProtocol(
LoadedImage->DeviceHandle,
&gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid,
gImageHandle,
NULL);
gBS->CloseProtocol(
gImageHandle,
&gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid,
gImageHandle,
NULL);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
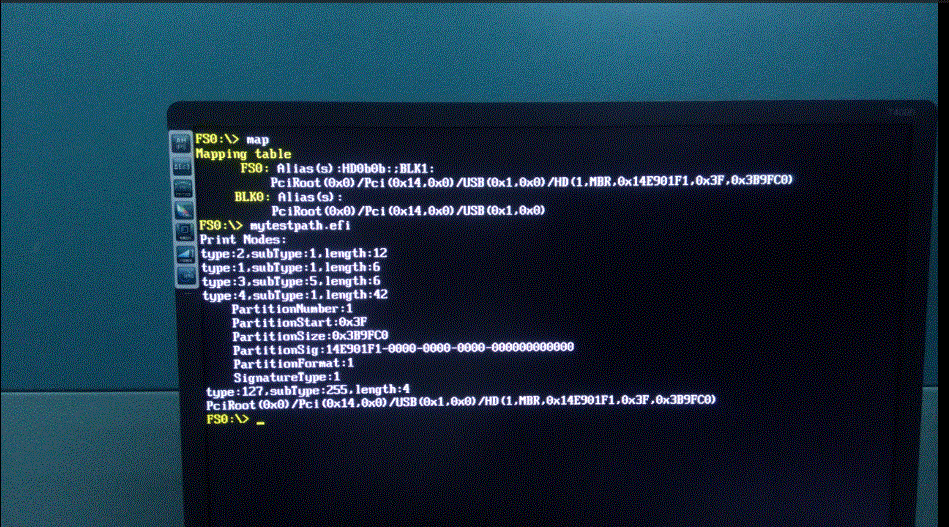
运行结果如下:
X64 的 EFI: mytestpathX64
完整的代码下载: mytestpath
Hi Sir, 請問您是參考哪一份Uefi SPEC. 去解析出這些type and information.我想多了解detail ..感謝!
Best Regards,
Tim
有说明是2.6
博主请问你用的是什么模拟器?或者虚拟机
我基本上用 NT32 模拟器而已。再复杂的只能用实体机了。
还有一个小问题是,我之前练习一直用的QEMU,现在看VirtualBOX也挺好用。博主有用过么?用过的话能请教下将编译好的.efi放到什么位置并进行设置才能让虚拟机在shell里读到呢。在VirtualBOX里不太会。
VirtualBox 的话,我还没有找到好办法直接把外面的东西 copy 到里面去。理论上你可以创建一个虚拟硬盘,然后把外面东西copy到这个硬盘上就可以在 fs0: 下面运行。 可行的接口有:串口, USB ,网卡…….但是目前我还没有找到方便易行的方案。如果你有空不妨研究一下。