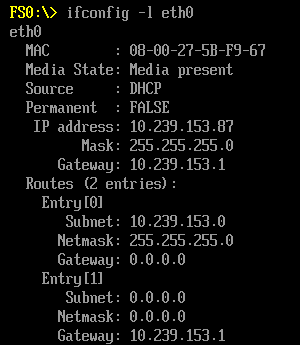
以前设置BIOS的门槛挺高,至少对于不熟悉英文的人进入满屏英文的Setup界面很容易变成丈二和尚———摸不着头脑。但是随着时代的进步,汉化Setup界面并不复杂,在 EDK2 上已经加入了多语言支持功能。但是,某些情况下,Setup中的选项不是来自BIOS Source Code 而是第三方的UEFI ROM,遇到这样的情况,经常会出现一片中文夹杂了一行英文的情况。为了更详细的描述这样的情况,用下面的例子来进行说明。在UDK2017中,有一个 RAM Disk 功能,这个功能在之前的系列文章中有介绍过。默认情况下,NT32Pkg 没有加载这个功能,但是编译过程中会生成 RamDiskDxe.efi。实验如下:
1. 先进入 Setup ,可以看到目前是没有相关选项的
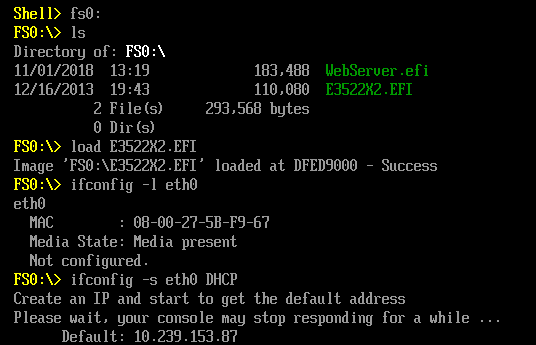
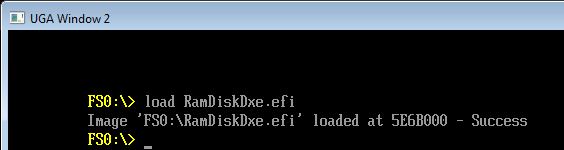
2. 进入 Shell 之后,加载 RamDiskDxe.efi
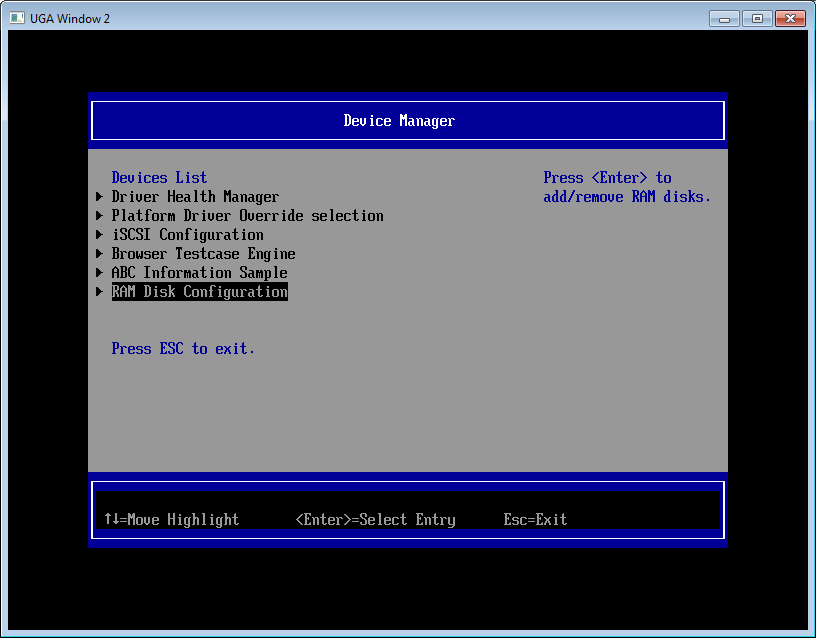
3. 再进入 Setup,可以看到已经出现了 Ram Disk 的选项
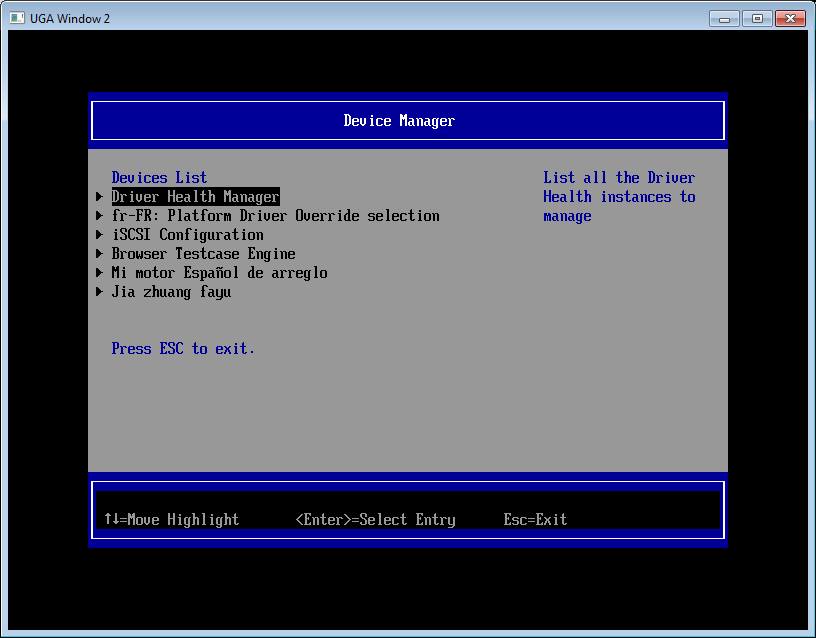
这里,实验的目标就是在不修改 RamDiskDxe.efi 的情况下,当语言选择为法语时,修改 Ram Disk 的名称。
首先研究一下 Setup 的选项,经过研究发现在\MdeModulePkg\Library\UefiHiiLib\HiiString.c中有一个HiiGetString的函数。从注释可以看出,这个函数负责返回 Hii Package中的字符串,因此,我们在其中添加代码,当发现语言设置为法语时,并且取得 Ram Disk 相关的String后,用我们定义的 String 替换掉正常的返回值从而实现“翻译”的动作。
/**
Retrieves a string from a string package in a specific language. If the language
is not specified, then a string from a string package in the current platform
language is retrieved. If the string can not be retrieved using the specified
language or the current platform language, then the string is retrieved from
the string package in the first language the string package supports. The
returned string is allocated using AllocatePool(). The caller is responsible
for freeing the allocated buffer using FreePool().
If HiiHandle is NULL, then ASSERT().
If StringId is 0, then ASSET.
@param[in] HiiHandle A handle that was previously registered in the HII Database.
@param[in] StringId The identifier of the string to retrieved from the string
package associated with HiiHandle.
@param[in] Language The language of the string to retrieve. If this parameter
is NULL, then the current platform language is used. The
format of Language must follow the language format assumed
the HII Database.
@retval NULL The string specified by StringId is not present in the string package.
@retval Other The string was returned.
**/
EFI_STRING
EFIAPI
HiiGetString (
IN EFI_HII_HANDLE HiiHandle,
IN EFI_STRING_ID StringId,
IN CONST CHAR8 *Language OPTIONAL
)
最终代码如下:
//
// Return the Null-terminated Unicode string
//
//LABZ_Start
if (String!=NULL) {
DEBUG((DEBUG_INFO, "Get [%s]\n",String));
if (StrCmp(String,L"Choisir la Langue")==0) { //这里判断一下语言是否已经选择为法语
DEBUG((DEBUG_INFO, "Let's speek French\n"));
FrenchX=TRUE; //做一个标记
}
//只有在切换为法语以及发现需要替换的字符串时再下手
if ((FrenchX)&&(StrCmp(String,L"RAM Disk Configuration")==0)) {
DEBUG((DEBUG_INFO, "Replace item string\n"));
//"RAM Disk Configuration"
//"Jia zhuang fayu "
StrCpy(String,L"Jia zhuang fayu ");
}
}
//LABZ_End
需要特别注意的是:返回值是放在 String 中的,它是由HiiGetString()函数进行空间分配,然后由调用者负责分配。因此,我们需要在 String 中修改,而不能简单的用另外一个变量来赋值给 String,否则在运行时会出现不可预料的错误。
重新实验,加载 RamDiskDxe.efi ,再选择法语后运行结果:
在 Log 中我们可以看到下面的 Debug Message:
1.发现语言选项切换为法语
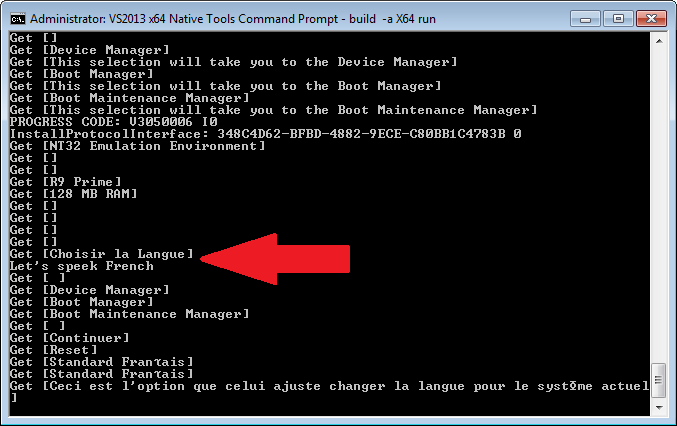
2.发现选项,替换之。
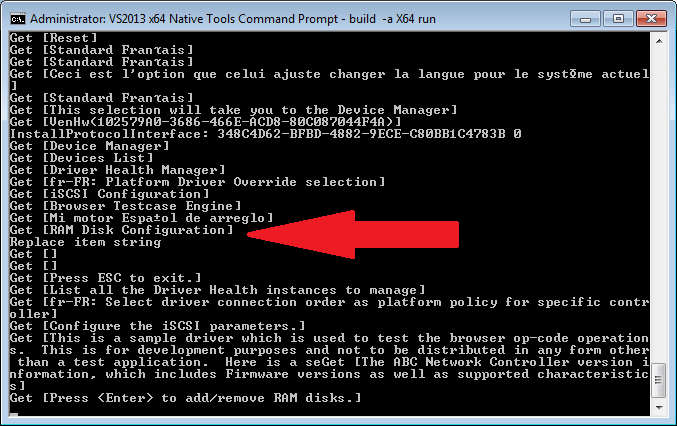
上面的实验都是在 UDK2017 NT32中进行的。完整的代码和 RamDiskDxe.efi 可以在这里下载:
额外说两句,法国是非常有名的老牌资本主义国家,譬如每个人耳熟能详的名言“知识就是力量,法国就是培根”。

不过从目前的新闻来看,这个国家正在一步步走向衰落。
纵观历史,我们所处的时代正是国运上升的时期,也许是我们的幸运吧。希望通过我们的努力能让我们的后辈有着更多的选择。