随手翻了一下 UEFI Shell 的 Source ,看了一下 Stall 命令觉得挺有意思,研究了一下。
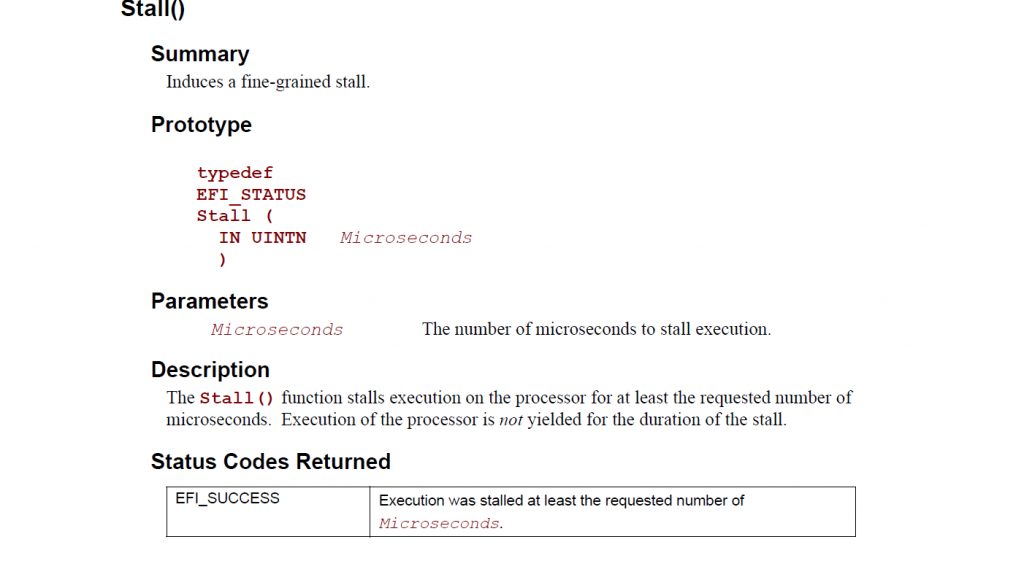
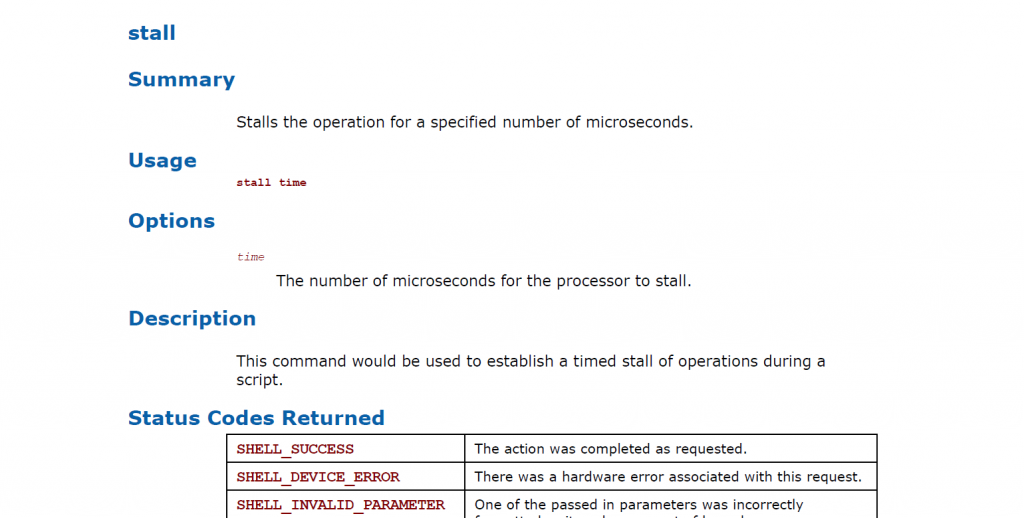
这个命令的介绍如下,实现了一个很简单的功能:暂停 xxx 微妙 (MicroSeconds 百万分之一秒)
对应的代码在 \Shell\stall\stall.c 可以看到
关键部分的代码是:
Microseconds = Atoi (ChkPck.VarList->VarStr); //要暂停的时间 UINTN Microseconds;
PrintToken (STRING_TOKEN (STR_STALL_FOR), HiiStallHandle, Microseconds);
Remaining = Microseconds % 100000;
Status = RT->GetTime (&TmpTime, NULL); //取当前时间
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Status = EFI_ABORTED;
goto Done;
}
MilliSeconds1 = (TmpTime.Hour * 3600 + TmpTime.Minute * 60 + TmpTime.Second) * 1000; //当前时间转化为毫秒
while (Microseconds - Remaining) {
//
// Break the execution?
//
if (GetExecutionBreak ()) { //允许打断
goto Done;
}
BS->Stall (100000); //暂停 1秒
Status = RT->GetTime (&TmpTime, NULL);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Status = EFI_ABORTED;
goto Done;
}
MilliSeconds2 = (TmpTime.Hour * 3600 + TmpTime.Minute * 60 + TmpTime.Second) * 1000;
if (MilliSeconds2 < MilliSeconds1) { //如果发生跨天的情况,算了一下 0xFFFFFFFF 个微秒最多只能跨一天
MilliSeconds2 += (24 * 3600 * 1000);
}
if ((Microseconds - Remaining) / 1000 <= (MilliSeconds2 - MilliSeconds1)) {
break;
}
} // while (Microseconds - Remaining) 结束
BS->Stall (Remaining);
看起来整个过程就是:使用 BS 的 Stall 不断做短时间的暂停,直到完成预订的Stall 时间。不过想不太明白,这样做同直接 BS -> Stall 指定的时间相比能获得什么好处?莫非是给一个能够用 Ctrl-Break 的机会么?
参考:
1. Shell Stall 命令的介绍,来自 UEFI Shell Specification Rev 2.1
2. BS->Stall 的介绍,来自 UEFI Spec 2.4