最近写程序遇到了一个非常奇怪的问题,化简问题如下:
1. 定义 CHAR8 大小的 Buffer[4]
2. 其中赋值为 128 82 0 0
3. 将他们通过下面的公式合成为一个 INT32
Buffer[0]+(Buffer[1]<<8) +(Buffer[2]<<16)+ (Buffer[3]<<24);
4. 我们期望得到 0x5280=21120, 但是给出来的结果却是 20864
编写程序如下,我们从命令行接收参数,然后转换为数值。
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR8 Buffer[4];
UINTN FileSize=0;
Print(L"Argv [%s %s %s %s]\n",
Argv[1],Argv[2],Argv[3],Argv[4]);
#pragma warning(disable:4244)
Buffer[0]=StrDecimalToUintn(Argv[1]);
Buffer[1]=StrDecimalToUintn(Argv[2]);
Buffer[2]=StrDecimalToUintn(Argv[3]);
Buffer[3]=StrDecimalToUintn(Argv[4]);
Print(L"Buffer [%x %x %x %x]\n",
Buffer[0],Buffer[1],Buffer[2],Buffer[3]);
FileSize=Buffer[0]+
(Buffer[1]<<8)+
(Buffer[2]<<16)+
(Buffer[3]<<24);
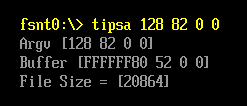
Print(L"File Size = [%d]\n",FileSize);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
为了Debug,需要打开生成汇编代码的功能,方法是在工程的 inf 文件 [BuildOptions] 下面加入如下语句:
[BuildOptions]
MSFT:*_*_IA32_CC_FLAGS = /FAsc
再次编译即可在Build目录下看到生成的 cod 文件
关键代码部分:
; 28 :
; 29 : Print(L"Buffer [%x %x %x %x]\n",
; 30 : Buffer[0],Buffer[1],Buffer[2],Buffer[3]);
00048 0f be 7c 24 3e movsx edi, BYTE PTR _Buffer$[esp+50]
0004d 0f be 6c 24 3d movsx ebp, BYTE PTR _Buffer$[esp+49]
00052 0f be f0 movsx esi, al
00055 56 push esi
00056 57 push edi
00057 0f be db movsx ebx, bl
0005a 55 push ebp
0005b 53 push ebx
0005c 68 00 00 00 00 push OFFSET ??_C@_1CM@LIBNEIP@?$AAB?$AAu?$AAf?$AAf?$AAe?$AAr?$AA?5?$AA?$FL?$AA?$CF?$AAx?$AA?5?$AA?$CF?$AAx?$AA?5?$AA?$CF?$AAx?$AA?5?$AA?$CF?$AAx?$AA?$FN?$AA?6?$AA?$AA@
00061 e8 00 00 00 00 call _Print
其中 push esi是 Buffer[3], push edi是 Buffer[2], push ebp 是 Buffer[1] , push ebx 是 Buffer[0],看起来一切正常。我们根据简单的结果进行计算0xFFFFFF80+0x5200+0x00+0x00=0x5180 就是说出现问题出在运行期的取值,和 Printf函数 没有关系。所以,关注点在为什么 1byte的0x80被定义成了 0xFFFFFF80。之后,我尝试化简程序,直接定义变量输出查看。我们定义三个变量 a b c用 printf 输出之:
CHAR8 a=129;
UINT8 b=130;
unsigned char c=131;
Print(L"A= [%x]\n",a);
Print(L"B= [%x]\n",b);
Print(L"C= [%x]\n",c);
运行结果:
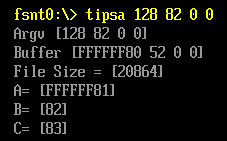
可以看到,如同我们的假设的, CHAR8 的 128被定义为 -127.
具体的 CHAR8定义可以在 MdePkg 中的 ProcessorBind.h 中找到:
///
/// 1-byte Character.
///
typedef char CHAR8;
CHAR 本身是一种有符号的整数(所以才会有 unsigned char)。因此,这就是一个错误的定义数据类型而导致的问题,解决方法很简单,用 UINT8 做定义就好了(从ProcessorBind.h可以看出,UINT8是 unsigned char)。
最后,贴一下修改后的完整INF 文件以便参考:
## @file
# A simple, basic, application showing how the Hello application could be
# built using the "Standard C Libraries" from StdLib.
#
# Copyright (c) 2010 - 2011, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.<BR>
# This program and the accompanying materials
# are licensed and made available under the terms and conditions of the BSD License
# which accompanies this distribution. The full text of the license may be found at
# http://opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.
#
# THE PROGRAM IS DISTRIBUTED UNDER THE BSD LICENSE ON AN "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
##
[Defines]
INF_VERSION = 0x00010006
BASE_NAME = tipsa
FILE_GUID = 4ea97c46-7491-4dfd-0064-747010f3ce5f
MODULE_TYPE = UEFI_APPLICATION
VERSION_STRING = 0.1
ENTRY_POINT = ShellCEntryLib
#
# VALID_ARCHITECTURES = IA32 X64 IPF
#
[Sources]
tipsa.c
[Packages]
StdLib/StdLib.dec
MdePkg/MdePkg.dec
ShellPkg/ShellPkg.dec
[LibraryClasses]
LibC
ShellCEntryLib
ShellLib
[Protocols]
[BuildOptions]
MSFT:*_*_IA32_CC_FLAGS = /FAsc