这次带来的项目是一个能够将两个USB 手柄转为蓝牙手柄的项目,这样玩家可以不受距离的限制使用手柄进行游戏。
项目基于 ESP32 C3 作为主控,使用 Max3421e 芯片作为 USB Host ,经过 WCH 的CH334 USB HUB 芯片扩展出2个USB 接口,这样就能同时连接2个USB手柄(CH334 支持一转四,因此最多同时可以连接4个USB手柄)。获得数据之后, C3 将自身模拟为USB 手柄设备,将按键数据通过蓝牙上传给主机,这样就实现了将两个USB 手柄转为蓝牙手柄。
下面首先介绍硬件设计。
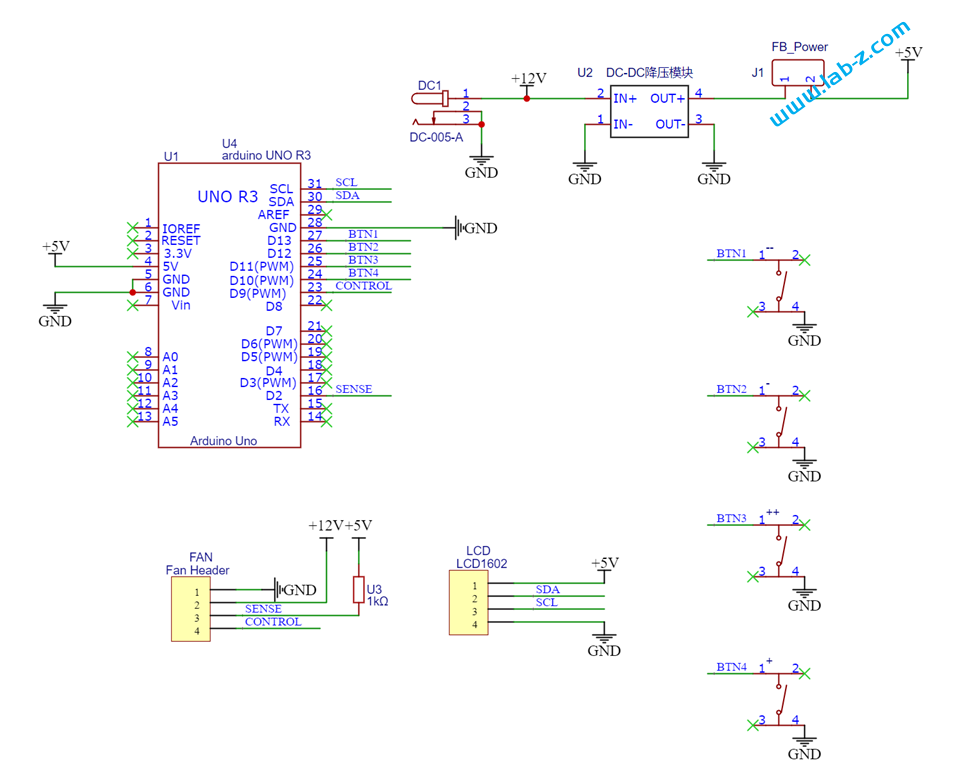
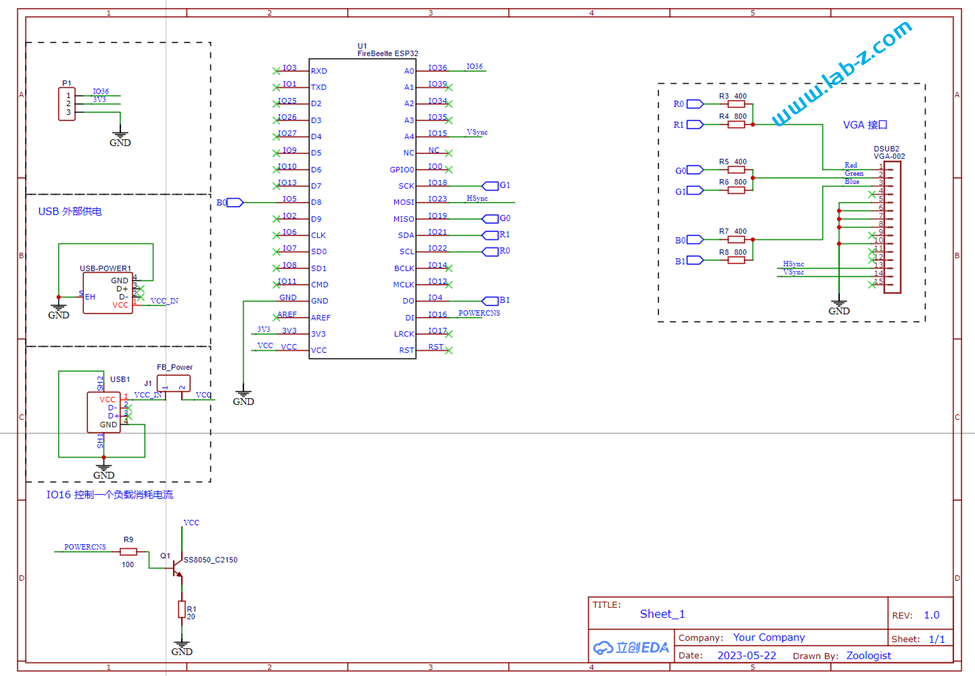
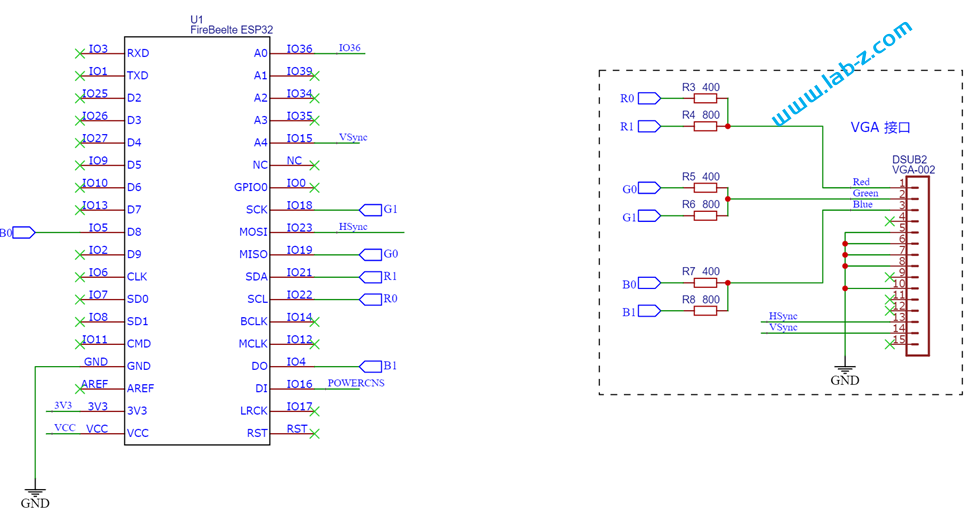
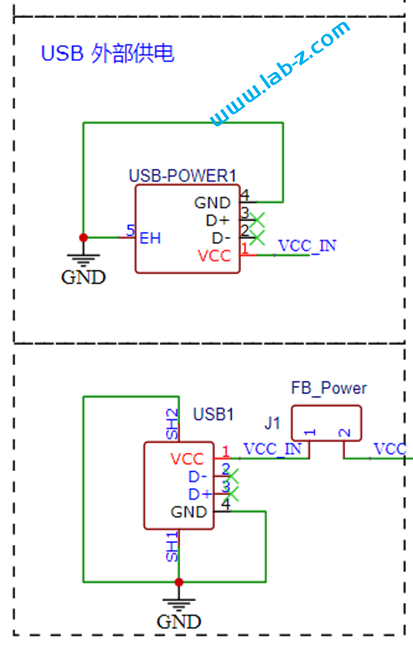
完整电路图如下:
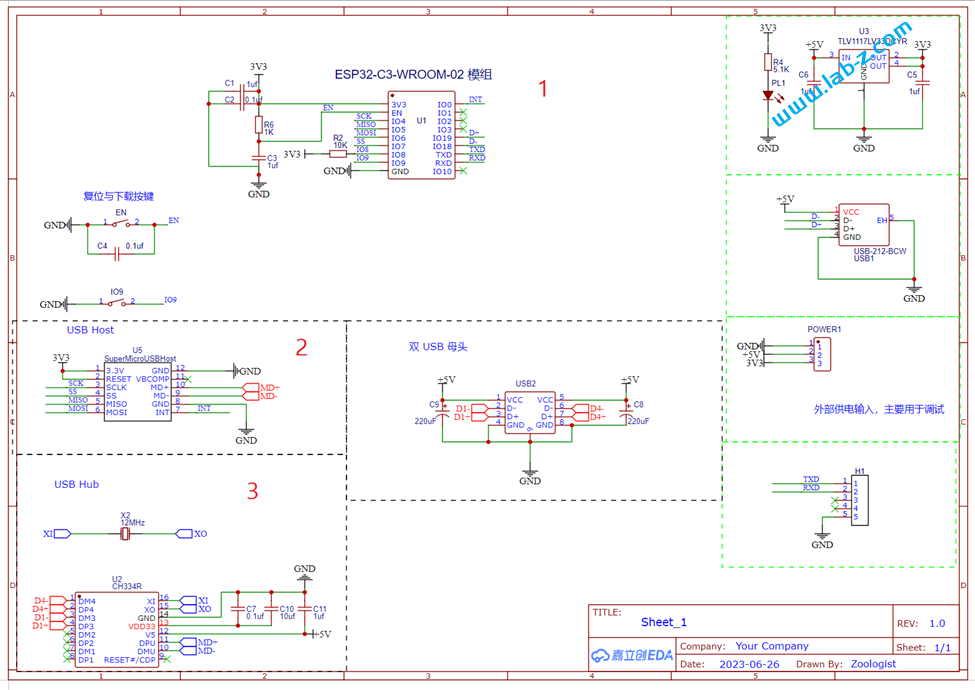
电路1 是 ESP32 C3 模块。ESP32-C3是一款安全稳定、低功耗、低成本的物联网芯片,搭载 RISC-V 32 位单核处理器,时钟频率高达 160 MHz。具有 22 个可编程 GPIO 管脚、内置 400 KB SRA、支持 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi 和 Bluetooth 5 (LE)。从图中也可以看到其所需外围元件很少,方便应用;
电路2是我们之前设计的 Super Micro USB Host,它的核心是 Max3421e 芯片,这个方案我们多次使用,是非常优秀的USB Host 方案;
电路3 是 USB Hub 部分,这里使用了CH334芯片.这款芯片符合 USB2.0 协议规范的4 端口 USB HUB 控制器芯片,上行端口支持 USB2.0高速和全速,下行端口支持 USB2.0 高速480Mbps、全速 12Mbps 和低速1.5Mbps。不但支持低成本的的 STT 模式(单个TT分时调度4个下行端口),还支持高性能的 MTT 模式 (4个TT各对应1个端口,并发处理)。需要注意的是,在此之前我实验过价格低廉的 FE1.2 芯片,但是FE1.2对 Max3421e 存在兼容性问题,无法正常工作。最终选择了CH334这个。如果有需要对 Max3421e 扩展USB 来使用的朋友,请注意USB Hub 这个坑。
上面就是这个设计最主要的三个部分,其他的都是辅助部分。
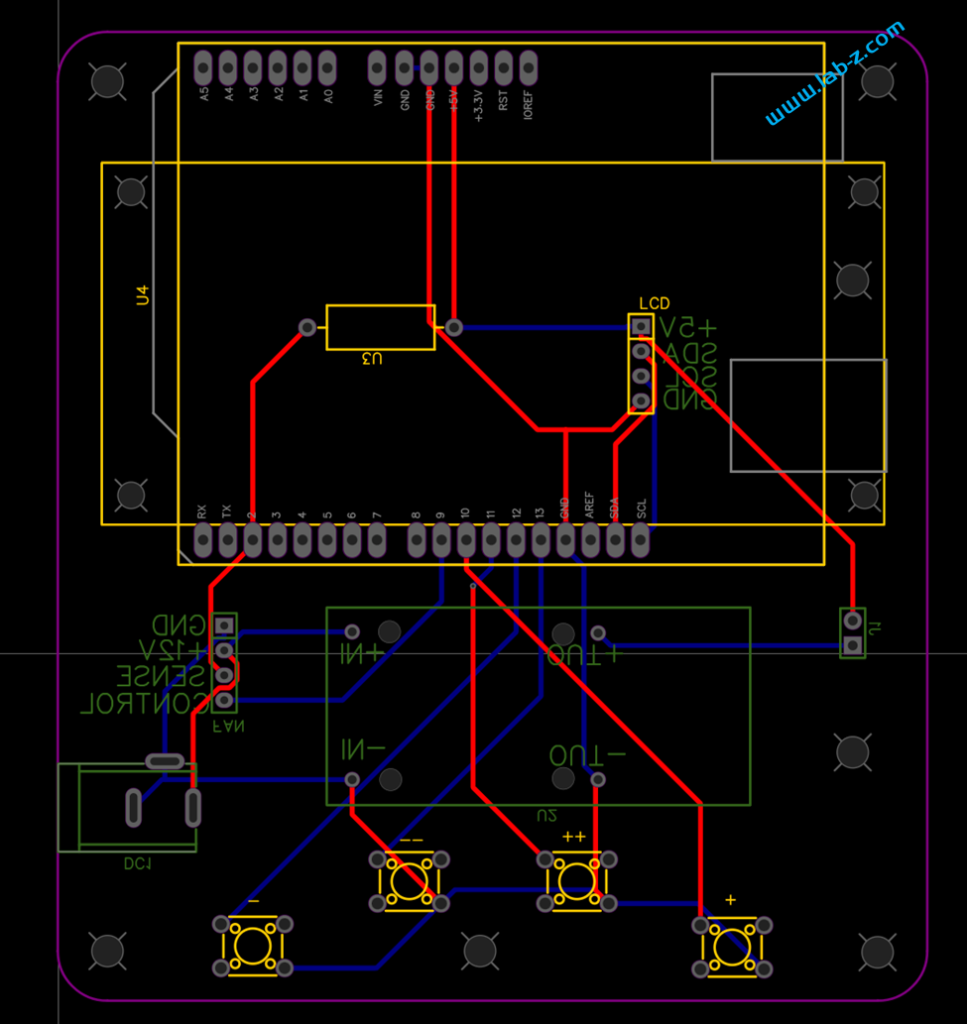
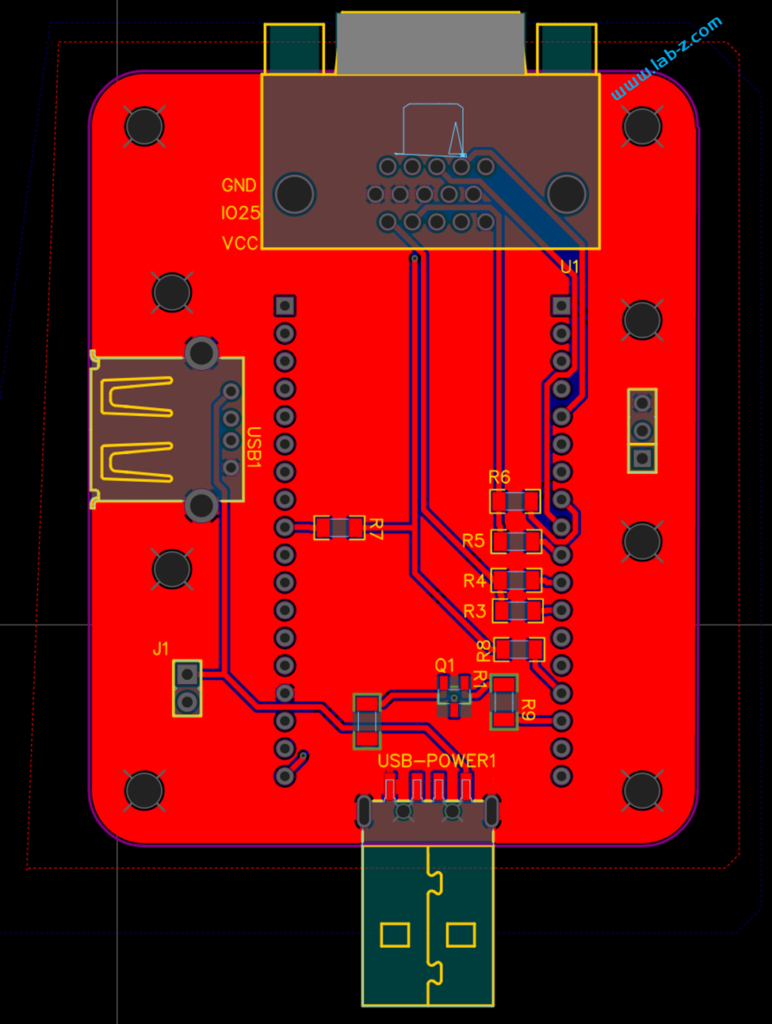
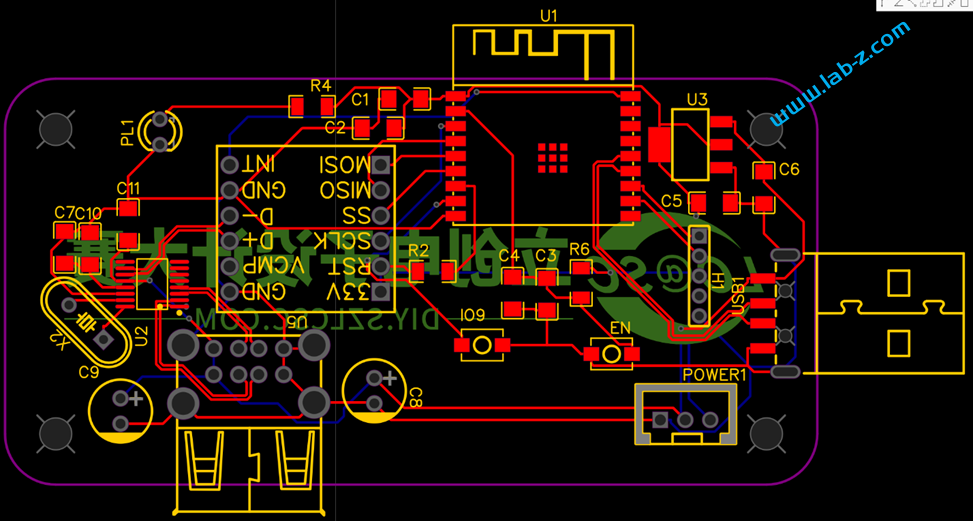
PCB 设计如下:
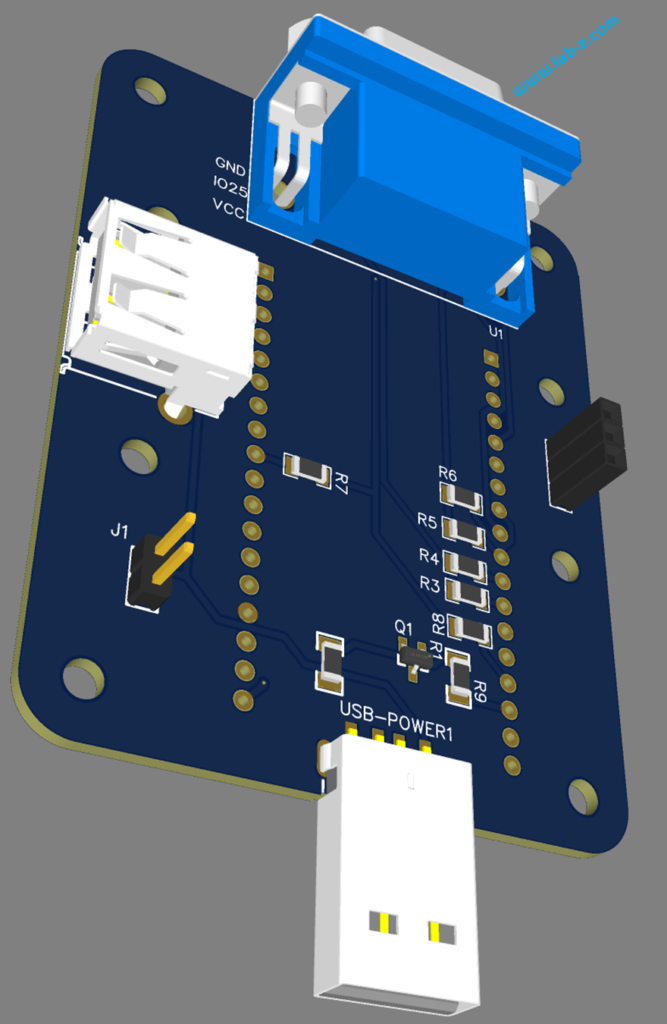
3D 预览如下:
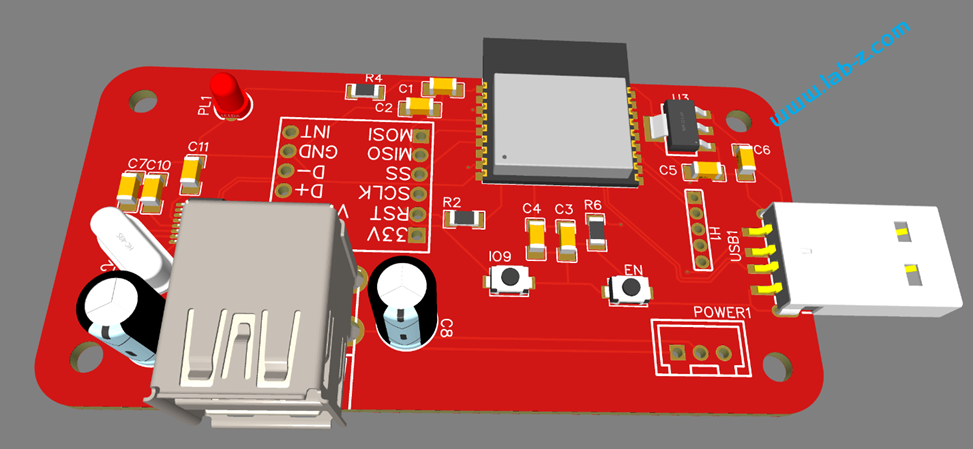
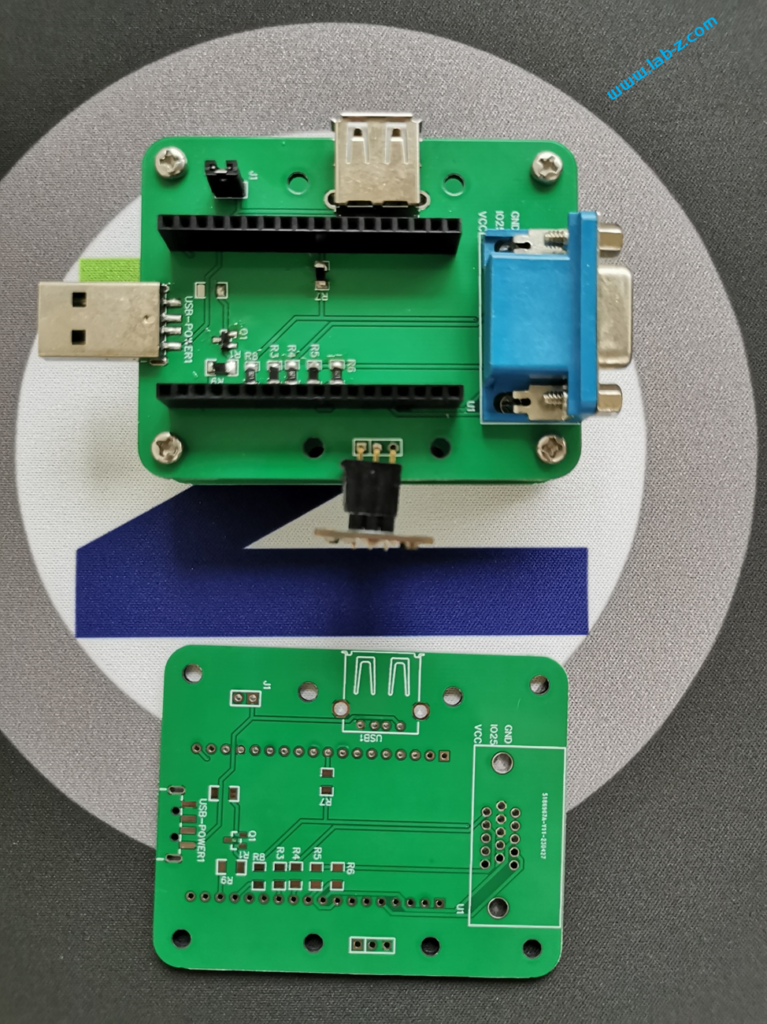
焊接安装之后如下:
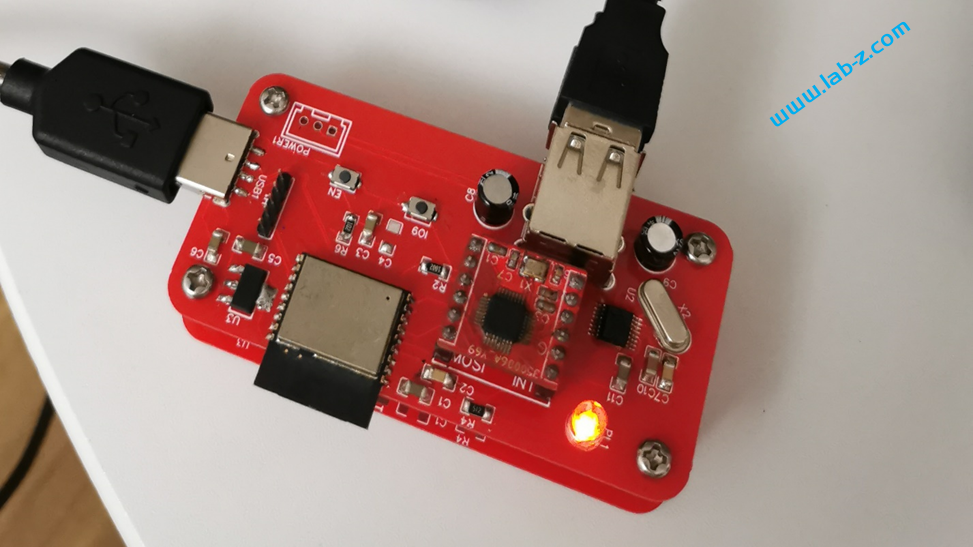

硬件完成后就要开始着手软件的设计了。
中所周知,USB HID的一个特点是:无需驱动即可使用。实现这个功能的秘密在于:在开始工作后设备会对主机发送一个HID Report Descriptor。在这个 Descriptor中描述了数据格式。这样主机收到之后能够清晰的了解收到的数据包中数据的含义,比如:Report Descriptor 内容是第一个字节是按键信息,第二个字节表示 X 坐标,第三个字节表示Y坐标。这样,当主机收到 01 00 00 ,主机知道有按键按下;当主机收到 00 0A 00 ,它能够知道鼠标向右移动了10 像素。蓝牙HID 也有类似的设计,其中的Report Descriptor 在蓝牙上成为Report Map 。其中的条目定义和 USB HID 的完全相同。因此,这里我们通过很小的改动就能将USB 手柄迁移到蓝牙上,他们使用相同的 Report Descriptor也能够避免数据解析的麻烦。仍然以前面的鼠标为例,当蓝牙设备使用和USB 设备相同的Report Descriptor时,主机对于 00 0A 00 这种数据,都能解析为鼠标向右移动了10 像素。
下面是我使用的 USB 手柄的 Report Descriptor:
Interface 0 HID Report Descriptor Joystick
Item Tag (Value) Raw Data
Usage Page (Generic Desktop) 05 01
Usage (Joystick) 09 04
Collection (Application) A1 01
Report ID (1) 85 01
Collection (Logical) A1 02
Report Size (8) 75 08
Report Count (4) 95 04
Logical Minimum (0) 15 00
Logical Maximum (255) 26 FF 00
Physical Minimum (0) 35 00
Physical Maximum (255) 46 FF 00
Usage (Rz) 09 35
Usage (Z) 09 32
Usage (X) 09 30
Usage (Y) 09 31
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,NNul,Bit) 81 02
Report Size (4) 75 04
Report Count (1) 95 01
Logical Maximum (7) 25 07
Physical Maximum (315) 46 3B 01
Unit (Eng Rot: Degree) 65 14
Usage (Hat Switch) 09 39
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,Null,Bit) 81 42
Unit (None) 65 00
Report Size (1) 75 01
Report Count (12) 95 0C
Logical Maximum (1) 25 01
Physical Maximum (1) 45 01
Usage Page (Button) 05 09
Usage Minimum (Button 1) 19 01
Usage Maximum (Button 12) 29 0C
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,NNul,Bit) 81 02
Usage Page (Vendor-Defined 1) 06 00 FF
Report Size (1) 75 01
Report Count (8) 95 08
Logical Maximum (1) 25 01
Physical Maximum (1) 45 01
Usage (Vendor-Defined 1) 09 01
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,NNul,Bit) 81 02
End Collection C0
Collection (Logical) A1 02
Report Size (8) 75 08
Report Count (4) 95 04
Physical Maximum (255) 46 FF 00
Logical Maximum (255) 26 FF 00
Usage (Vendor-Defined 2) 09 02
Output (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,NNul,NVol,Bit) 91 02
End Collection C0
End Collection C0
Usage Page (Generic Desktop) 05 01
Usage (Joystick) 09 04
Collection (Application) A1 01
Report ID (2) 85 02
Collection (Logical) A1 02
Report Size (8) 75 08
Report Count (4) 95 04
Logical Minimum (0) 15 00
Logical Maximum (255) 26 FF 00
Physical Minimum (0) 35 00
Physical Maximum (255) 46 FF 00
Usage (Rz) 09 35
Usage (Z) 09 32
Usage (X) 09 30
Usage (Y) 09 31
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,NNul,Bit) 81 02
Report Size (4) 75 04
Report Count (1) 95 01
Logical Maximum (7) 25 07
Physical Maximum (315) 46 3B 01
Unit (Eng Rot: Degree) 65 14
Usage (Hat Switch) 09 39
Input (Data,Var,Abs,NWrp,Lin,Pref,Null,Bit) 81 42
Unit (None) 65 00
Report Size (1) 75 01
Report Count (12) 95 0C
Logical Maximum (1) 25 01
Physical Maximum (1) 45 01
Usage Page (Button) 05 09
Usage Minimum (Button 1) 19 01
上面红色标记出来的是这次使用的USB手柄的有效部分。除了红色还有黑色的字体,从实验来看,在手柄时没有使用。我们将有效部分取出,合成一个蓝牙使用的Report Map如下:
// 1st Gamepad
0x05, 0x01, // Usage Page (Generic Desktop Ctrls)
0x09, 0x04, // Usage (Joystick)
0xA1, 0x01, // Collection (Application)
0x85, 0x01, // Report ID (1)
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x15, 0x00, // Logical Minimum (0)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x35, 0x00, // Physical Minimum (0)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x35, // Usage (Rz)
0x09, 0x32, // Usage (Z)
0x09, 0x30, // Usage (X)
0x09, 0x31, // Usage (Y)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x75, 0x04, // Report Size (4)
0x95, 0x01, // Report Count (1)
0x25, 0x07, // Logical Maximum (7)
0x46, 0x3B, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (315)
0x65, 0x14, // Unit (System: English Rotation, Length: Centimeter)
0x09, 0x39, // Usage (Hat switch)
0x81, 0x42, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,Null State)
0x65, 0x00, // Unit (None)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x0C, // Report Count (12)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x05, 0x09, // Usage Page (Button)
0x19, 0x01, // Usage Minimum (0x01)
0x29, 0x0C, // Usage Maximum (0x0C)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x06, 0x00, 0xFF, // Usage Page (Vendor Defined 0xFF00)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x08, // Report Count (8)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x09, 0x01, // Usage (0x01)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x02, // Usage (0x02)
0x91, 0x02, // Output (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xC0, // End Collection
// 2nd Gamepad
0x05, 0x01, // Usage Page (Generic Desktop Ctrls)
0x09, 0x04, // Usage (Joystick)
0xA1, 0x01, // Collection (Application)
0x85, 0x02, // Report ID (2)
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x15, 0x00, // Logical Minimum (0)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x35, 0x00, // Physical Minimum (0)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x35, // Usage (Rz)
0x09, 0x32, // Usage (Z)
0x09, 0x30, // Usage (X)
0x09, 0x31, // Usage (Y)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x75, 0x04, // Report Size (4)
0x95, 0x01, // Report Count (1)
0x25, 0x07, // Logical Maximum (7)
0x46, 0x3B, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (315)
0x65, 0x14, // Unit (System: English Rotation, Length: Centimeter)
0x09, 0x39, // Usage (Hat switch)
0x81, 0x42, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,Null State)
0x65, 0x00, // Unit (None)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x0C, // Report Count (12)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x05, 0x09, // Usage Page (Button)
0x19, 0x01, // Usage Minimum (0x01)
0x29, 0x0C, // Usage Maximum (0x0C)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x06, 0x00, 0xFF, // Usage Page (Vendor Defined 0xFF00)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x08, // Report Count (8)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x09, 0x01, // Usage (0x01)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x02, // Usage (0x02)
0x91, 0x02, // Output (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xC0, // End Collection
可以看到,上面的 Descriptor 红色部分和其余部分的区别只是 Report ID 不同。 Report ID 是USB HID 设备用来区分功能的一个设计。例如,我们经常遇到同时带有键盘和鼠标的混合设备。通常它的Descriptor 写法就是:
Report ID 1
鼠标数据[0], 鼠标数据[1], ……鼠标数据[M-1],
Report ID 2
键盘数据[0], 键盘数据[1],……键盘数据[N-1],
当设备上有鼠标动作发生时,鼠标动作描述为 :M 长度的鼠标数据;设备对主机的报告是:
1, 鼠标数据[0], 鼠标数据[1],…… 鼠标数据[M-1]
当设备上有键盘动作发生时,键盘动作描述为 :N 长度的键盘数据;设备对主机的报告是:
2,键盘数据[0], 键盘数据[1],…… 键盘数据[N-1]
当然,你还可以继续给这个设备加入功能。比如:Report ID 3 , 键盘数据[0], 键盘数据[1],……键盘数据[P-1] 这样就又加入了一个键盘的功能(实际上这样做是有意义的,比如,通常的USB键盘数据包只有8个按键信息,如果我们同时按下9个按键就会超出它的运载能力。这就是一种“键位冲突”。如果你的设备同时声明了2个键盘,那么可以用将第九个按键的信息放置在第二个键盘的数据中发出去。如果你肯声明三个键盘设备,每个带有8个按键,理论上对于人类是完全够用的)。显而易见,通过 Report ID 主机能够分清楚当收到的数据属于哪个设备。
这次的设计,USB 手柄产生数据如下:
1, 手柄数据[0], 手柄数据[1],…… 手柄数据[M-1]
(第一个1是来自USB 手柄 Descriptor 的 Report ID 1)
我们无需解析了解每一位的含义,去掉最前面的 Report ID 然后将剩余数据转发出去即可。具体代码如下:
if (DataBuffer[0] == 0) {
input->setValue(&DataBuffer[2], RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN - 2);
input->notify();
}
if (DataBuffer[0] == 1) {
input2->setValue(&DataBuffer[2], RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN - 2);
input2->notify();
}
主机收到数据之后,能够分清楚来源,然后将数据通过蓝牙转发出去即可。完整代码如下:
#include <BLEDevice.h>
#include <BLEUtils.h>
#include <BLEServer.h>
#include "BLE2902.h"
#include "BLEHIDDevice.h"
#include "HIDTypes.h"
#include <usbhid.h>
#include <hiduniversal.h>
#include <usbhub.h>
#define DEBUGMODE 0
// Satisfy IDE, which only needs to see the include statment in the ino.
#ifdef dobogusinclude
#include <spi4teensy3.h>
#endif
#include <SPI.h>
#include "hidjoystickrptparser.h"
USB Usb;
USBHub Hub(&Usb);
HIDUniversal Hid1(&Usb);
HIDUniversal Hid2(&Usb);
JoystickEvents JoyEvents;
JoystickReportParser Joy(&JoyEvents);
BLEHIDDevice* hid;
BLECharacteristic* input;
BLECharacteristic* input2;
BLECharacteristic* output2;
bool connected = false;
const uint8_t report[] = {
// 1st Gamepad
0x05, 0x01, // Usage Page (Generic Desktop Ctrls)
0x09, 0x04, // Usage (Joystick)
0xA1, 0x01, // Collection (Application)
0x85, 0x01, // Report ID (1)
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x15, 0x00, // Logical Minimum (0)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x35, 0x00, // Physical Minimum (0)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x35, // Usage (Rz)
0x09, 0x32, // Usage (Z)
0x09, 0x30, // Usage (X)
0x09, 0x31, // Usage (Y)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x75, 0x04, // Report Size (4)
0x95, 0x01, // Report Count (1)
0x25, 0x07, // Logical Maximum (7)
0x46, 0x3B, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (315)
0x65, 0x14, // Unit (System: English Rotation, Length: Centimeter)
0x09, 0x39, // Usage (Hat switch)
0x81, 0x42, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,Null State)
0x65, 0x00, // Unit (None)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x0C, // Report Count (12)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x05, 0x09, // Usage Page (Button)
0x19, 0x01, // Usage Minimum (0x01)
0x29, 0x0C, // Usage Maximum (0x0C)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x06, 0x00, 0xFF, // Usage Page (Vendor Defined 0xFF00)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x08, // Report Count (8)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x09, 0x01, // Usage (0x01)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x02, // Usage (0x02)
0x91, 0x02, // Output (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xC0, // End Collection
// 2nd Gamepad
0x05, 0x01, // Usage Page (Generic Desktop Ctrls)
0x09, 0x04, // Usage (Joystick)
0xA1, 0x01, // Collection (Application)
0x85, 0x02, // Report ID (2)
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x15, 0x00, // Logical Minimum (0)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x35, 0x00, // Physical Minimum (0)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x35, // Usage (Rz)
0x09, 0x32, // Usage (Z)
0x09, 0x30, // Usage (X)
0x09, 0x31, // Usage (Y)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x75, 0x04, // Report Size (4)
0x95, 0x01, // Report Count (1)
0x25, 0x07, // Logical Maximum (7)
0x46, 0x3B, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (315)
0x65, 0x14, // Unit (System: English Rotation, Length: Centimeter)
0x09, 0x39, // Usage (Hat switch)
0x81, 0x42, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,Null State)
0x65, 0x00, // Unit (None)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x0C, // Report Count (12)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x05, 0x09, // Usage Page (Button)
0x19, 0x01, // Usage Minimum (0x01)
0x29, 0x0C, // Usage Maximum (0x0C)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0x06, 0x00, 0xFF, // Usage Page (Vendor Defined 0xFF00)
0x75, 0x01, // Report Size (1)
0x95, 0x08, // Report Count (8)
0x25, 0x01, // Logical Maximum (1)
0x45, 0x01, // Physical Maximum (1)
0x09, 0x01, // Usage (0x01)
0x81, 0x02, // Input (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xA1, 0x02, // Collection (Logical)
0x75, 0x08, // Report Size (8)
0x95, 0x04, // Report Count (4)
0x46, 0xFF, 0x00, // Physical Maximum (255)
0x26, 0xFF, 0x00, // Logical Maximum (255)
0x09, 0x02, // Usage (0x02)
0x91, 0x02, // Output (Data,Var,Abs,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile)
0xC0, // End Collection
0xC0, // End Collection
};
class ServerCallbacks: public BLEServerCallbacks
{
void onConnect(BLEServer* pServer)
{
connected = true;
//digitalWrite(CONNECT_LED_PIN, HIGH);
BLE2902* desc = (BLE2902*)input->getDescriptorByUUID(BLEUUID((uint16_t)0x2902));
desc->setNotifications(true);
}
void onDisconnect(BLEServer* pServer)
{
connected = false;
// digitalWrite(CONNECT_LED_PIN, LOW);
BLE2902* desc = (BLE2902*)input->getDescriptorByUUID(BLEUUID((uint16_t)0x2902));
desc->setNotifications(false);
}
};
void JoystickEvents::OnGamePadChanged(int Index) {
if (DEBUGMODE) {
/* for (uint8_t i = 0; i < RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN; i++) {
Serial.print(Joy.oldPad[Index][i]); Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println(" ");
*/
}
uint8_t DataBuffer[RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN];
memcpy(DataBuffer, &Joy.oldPad[Index][0], RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN);
DataBuffer[0] = Index;
// Send message via ESP-NOW
//esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(broadcastAddress, (uint8_t *) DataBuffer, RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN);
if (DEBUGMODE) {
Serial.print("BT send");
for (int i = 0; i < RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN; i++) {
if (DataBuffer[i] < 0x10) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(DataBuffer[i], HEX); Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println(" ");
}
if (DataBuffer[0] == 0) {
input->setValue(&DataBuffer[2], RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN - 2);
input->notify();
}
if (DataBuffer[0] == 1) {
input2->setValue(&DataBuffer[2], RPT_GEMEPAD_LEN - 2);
input2->notify();
}
}
void setup() {
if (DEBUGMODE) {
Serial.begin(1000000);
printf("Starting BLE Gamepad device\n!");
}
BLEDevice::init("ESP32-Gamepad");
BLEServer *pServer = BLEDevice::createServer();
pServer->setCallbacks(new ServerCallbacks());
hid = new BLEHIDDevice(pServer);
input = hid->inputReport(1); // <-- input REPORTID 1 from report map
input2 = hid->inputReport(2); // <-- input REPORTID 2 from report map
output2 = hid->outputReport(2); // <-- output REPORTID 2 from report map
//output2->setCallbacks(new OutputCallbacks());
BLESecurity *pSecurity = new BLESecurity();
pSecurity->setAuthenticationMode(ESP_LE_AUTH_BOND);
std::string name = "DeonVanDerWesthuysen";
hid->manufacturer()->setValue(name);
hid->pnp(0x02, 0xADDE, 0xEFBE, 0x0100); // High and low bytes of words get swapped
hid->hidInfo(0x00, 0x02);
hid->reportMap((uint8_t*)report, sizeof(report));
hid->startServices();
BLEAdvertising *pAdvertising = BLEDevice::getAdvertising();
pAdvertising->setAppearance(HID_GAMEPAD);
pAdvertising->addServiceUUID(hid->hidService()->getUUID());
pAdvertising->start();
hid->setBatteryLevel(100);
if (DEBUGMODE) {
Serial.println("Init complete!\n");
}
if (!Hid1.SetReportParser(0, &Joy))
ErrorMessage<uint8_t > (PSTR("SetReportParser"), 1);
if (!Hid2.SetReportParser(0, &Joy))
ErrorMessage<uint8_t > (PSTR("SetReportParser"), 1);
if (Usb.Init() == -1)
Serial.println("OSC did not start.");
delay(200);
}
void loop() {
Usb.Task();
}
上面就是双USB 转蓝牙的代码,实际上它这个框架可以根据需求改造成各种蓝牙HID 设备,比如:蓝牙鼠标加蓝牙键盘,蓝牙键盘加蓝家键盘,蓝牙手柄加蓝牙键盘。有兴趣的朋友不妨动手尝试。
上述代码完整版:
本文提到的电路图和 PCB:
工作的测试视频: