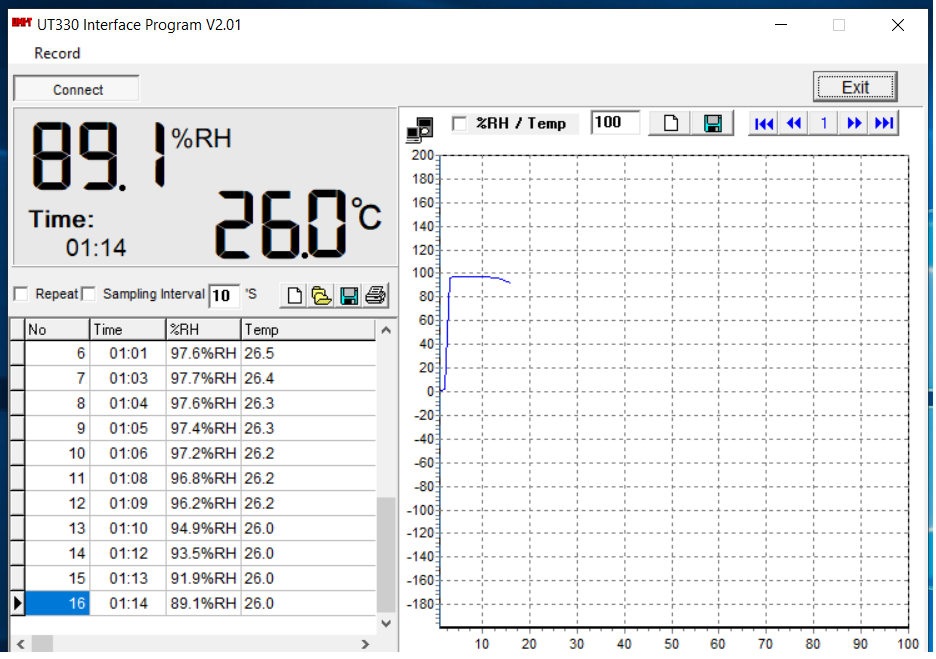
UT331/332 是优利德出品的温湿度表,它带有USB 接口可供电脑读取实时温湿度。
需要注意的是官网提供下载的是 UT331+ UT332+ 的上位机程序,无法连接UT331/332。
后来我联系官方售后,要到的匹配的 UT331 上位机,有需要的朋友可以下载:
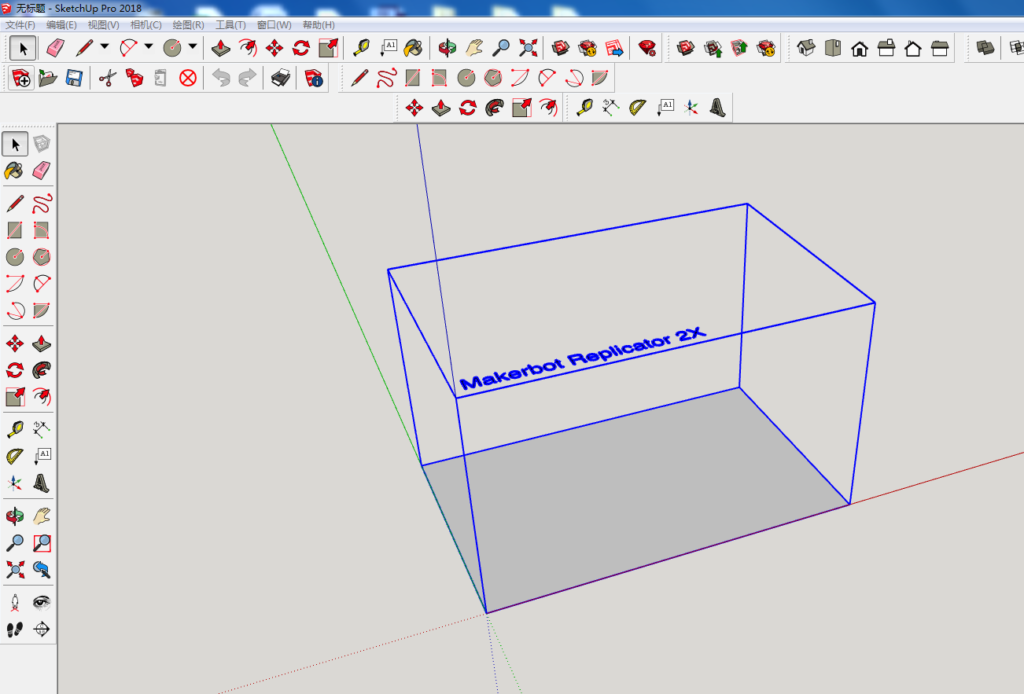
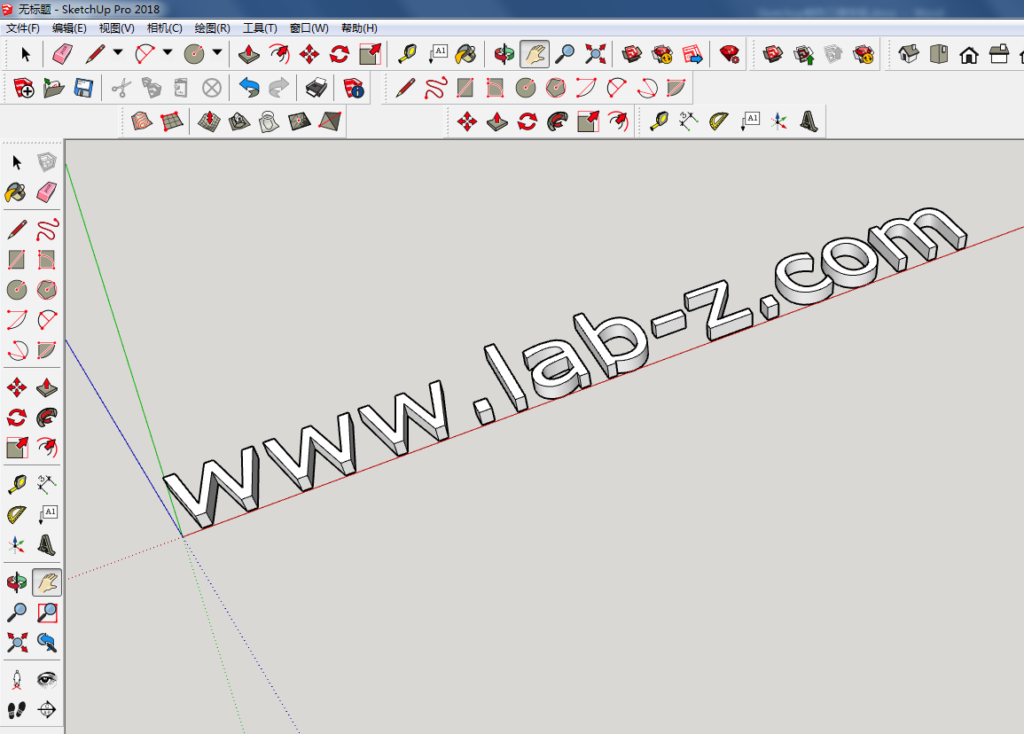
1.打开Sketchup
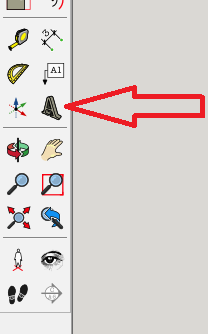
2.选择左侧的“三维文字”功能
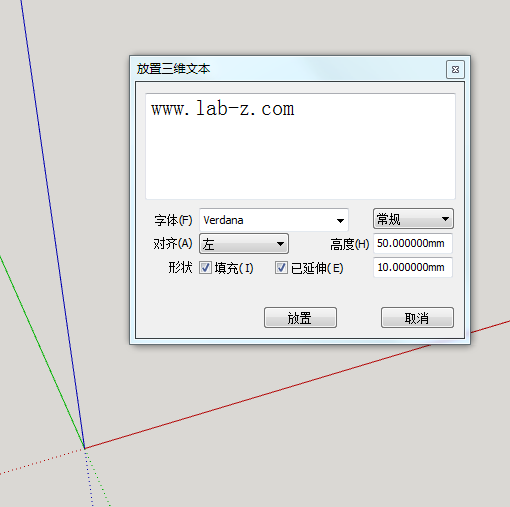
3.输入你想制作的文字内容
4.制作完成,可以保存成三维的模型文件
这次介绍的是在 Arduino 1.8.16 + ESP32 2.0.1 下实现假U盘的例子。特别强调:ESP32 Arduino 环境必须是 2.0.1, 更高的版本反倒有兼容问题。
实现的方法和之前的相同【参考1】:
完整代码如下:
#include "USB.h"
#include "USBMSC.h"
#include "256MBDisk.h"
#if ARDUINO_USB_CDC_ON_BOOT
#define HWSerial Serial0
#define USBSerial Serial
#else
#define HWSerial Serial
//USBCDC USBSerial;
#endif
USBMSC MSC;
uint32_t findLBA(uint32_t LBA) {
for (uint32_t i=0; i<415;i++) {
if (Index[i]==LBA) {
if (i>=205) {i=i-205+4;}
return i;
}
}
return 0xFFFFFF;
}
static const uint32_t DISK_SECTOR_COUNT = 520192;
static int32_t onRead(uint32_t lba, uint32_t offset, void* buffer, uint32_t bufsize){
//HWSerial.printf("MSC READ: lba: %u, offset: %u, bufsize: %u\n", lba, offset, bufsize);
uint32_t getLBA=0;
uint8_t *p;
p=(uint8_t *)buffer;
//HWSerial.printf("Buffer1 %X\n", buffer);
for (uint32_t i=0;i<bufsize/DISK_SECTOR_SIZE;i++) {
//HWSerial.printf("Check %u\n", lba+i);
getLBA=findLBA(lba+i);
//HWSerial.printf("getLBA %u %u\n", getLBA,lba+i);
if (getLBA!=0xFFFFFF) { //如果找到了
memcpy((void *)&p[i*DISK_SECTOR_SIZE], &msc_disk[getLBA][0], DISK_SECTOR_SIZE);
//HWSerial.printf("%u %u %u %u\n", msc_disk[getLBA][0],msc_disk[getLBA][1],msc_disk[getLBA][2],msc_disk[getLBA][3]);
//HWSerial.printf("Send %u\n", getLBA);
//HWSerial.printf("Buffer2 %X\n", (void *)&p[i*DISK_SECTOR_SIZE]);
} else {
//HWSerial.printf("Send all zero to %u\n", getLBA);
for (uint16_t j=0;j<DISK_SECTOR_SIZE;j++) {
p[i*DISK_SECTOR_SIZE+j]=0;
}
}
}
return bufsize;
}
static bool onStartStop(uint8_t power_condition, bool start, bool load_eject){
HWSerial.printf("MSC START/STOP: power: %u, start: %u, eject: %u\n", power_condition, start, load_eject);
return true;
}
static void usbEventCallback(void* arg, esp_event_base_t event_base, int32_t event_id, void* event_data){
if(event_base == ARDUINO_USB_EVENTS){
arduino_usb_event_data_t * data = (arduino_usb_event_data_t*)event_data;
switch (event_id){
case ARDUINO_USB_STARTED_EVENT:
HWSerial.println("USB PLUGGED");
break;
case ARDUINO_USB_STOPPED_EVENT:
HWSerial.println("USB UNPLUGGED");
break;
case ARDUINO_USB_SUSPEND_EVENT:
HWSerial.printf("USB SUSPENDED: remote_wakeup_en: %u\n", data->suspend.remote_wakeup_en);
break;
case ARDUINO_USB_RESUME_EVENT:
HWSerial.println("USB RESUMED");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
static int32_t onWrite(uint32_t lba, uint32_t offset, uint8_t* buffer, uint32_t bufsize){
HWSerial.printf("MSC WRITE: lba: %u, offset: %u, bufsize: %u\n", lba, offset, bufsize);
return bufsize;
}
void setup() {
HWSerial.begin(115200);
HWSerial.setDebugOutput(true);
USB.onEvent(usbEventCallback);
MSC.vendorID("ESP32");//max 8 chars
MSC.productID("USB_MSC");//max 16 chars
MSC.productRevision("1.02");//max 4 chars
MSC.onStartStop(onStartStop);
MSC.onRead(onRead);
MSC.onWrite(onWrite);
MSC.mediaPresent(true);
MSC.begin(DISK_SECTOR_COUNT, DISK_SECTOR_SIZE);
//USBSerial.begin();
USB.begin();
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}
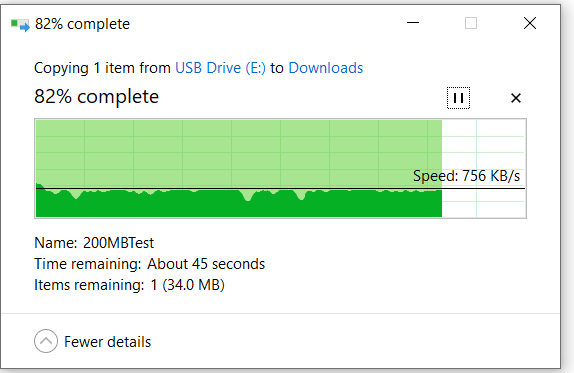
速度测试:
本文提到的用于测试的 U盘镜像:
代码1,这个是完整的分区:
代码2,这个是压缩后的分区(分区的FAT 表有部分是相同的,所以可以对这部分进行压缩)
参考:
GOP是 Grapshics Output Protocol 的缩写,这是 UEFI 定义的 Pre-OS 显示接口,目标就是提供显示的基本功能。 无论你使用何种显卡,如果想让屏幕在开机过程有所显示,必须遵从这个协议。这次简单介绍一下 Intel 的 GOP。
Intel 的GOP 会放在BIOS 中,可以看作 BIOS 的一部分。Intel Release 的 GOP有三部分:
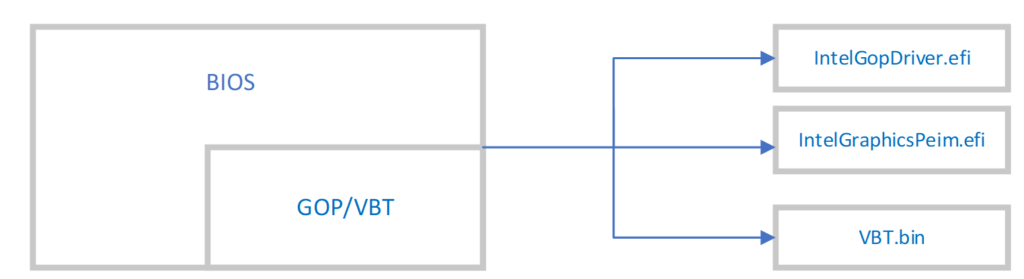
1.IntelGopDriver: 这是DXE 的GOP Driver
2.IntelGraphicsPeim: 这是 PEI 阶段的 GOP。用户按下开机键后会希望尽快点亮屏幕看到提示信息,因此在 PEI 阶段点亮屏幕是非常必要的。如果希望上电就能显示,还可以去找屏幕厂商进行定制。
3.VBT:GOP 的配置文件,比如:要求某个端口输出eDP 还是HDMI信号。
BIOS 会在 PEI 阶段 调用IntelGraphicsPeim,然后 DXE 阶段调用IntelGopDriver.efi。和其他的 UEFI 下的Driver一样,这两个文件是C语言编写的,如果由需要可以联系Intel FAE 索要 DEBUG 版本的 GOP。
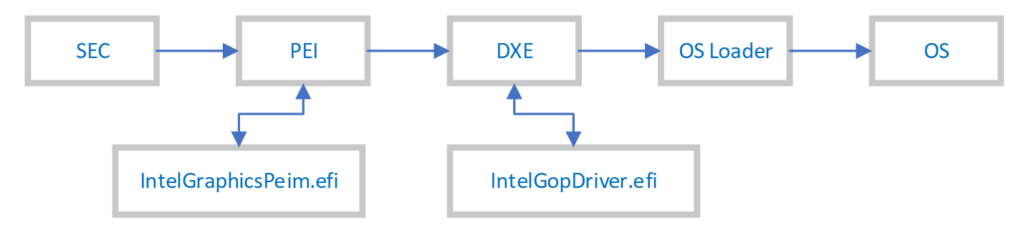
在OS启动过程中,OS Loader会通过 ExitBootervices()通知 Driver 退出,这时 GOP 会在从系统中卸载。但是 Intel GFX Driver会继续使用 VBT 提供的配置信息(之前的文章提到过如何在 Windows 下查找VBT)。
在 S4 和 S5 的阶段,会调用 GOP。但是 S3 和 ModernStandby 不会调用 GOP。特别是后者,如果遇到问题通常都是 Graphics Driver的问题。
目前用于修改 VBT 进行 GOP 配置的软件是: DisCon (Display Conigureation Tool),上一代的工具是 BMP (至少用了十年以上)。个人感觉这两种没有什么差别。使用的方法都是一个 Binary File 配合一个解释文件(BMP 用的是 BSF , DisCon 用的是 XML文件)来使用。特别注意,我感觉目前 DisCon 似乎还不稳定,有时候在解析 XML 配置文件的时候会遇到问题。出现这种问题请检查 DisCon 的版本和 VBT/Json 文件是否匹配。
特别提一下 VBT 一个新功能:LFP PnP ID。使用场景是:当你打算使用一个 VBT 支持多个LFP(Local Front Panel,内置屏幕),比如一个型号的笔记本有多个 SKU,使用了几种不同的屏幕。之前的解决方法是在 BIOS 中放置多个 VBT,然后通过 GPIO 之类的作为 BoardID,在POST过程中Load不同的 VBT。显而易见的是这样会比较麻烦,BIOS 改动较大(作为BIOS工程师,最好的设计就是不要BIOS修改)。另外,还有直接在C 代码中,通过结构体来更改 VBT 数值的方法,这种方法会让接手的人一头雾水:放在BIOS 中的 VBT 和最终 OS 下 Dump 出来的结果不同。因此,在新版的 VBT 中增加了使用 LFP PnP ID 来区分不同Panel 的方法。
1.在Select Panel Type 中选择Panel #FF

2.在 Panel #0X 的 PnP ID 中填写你屏幕的 PnP ID
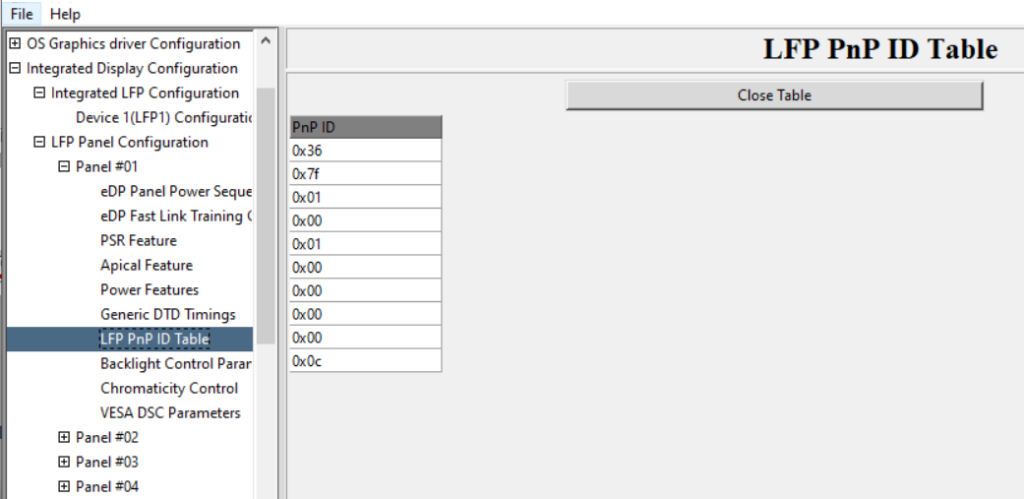
3.在开机过程中 GOP ,会从 Panel #01 开始扫描,如果发现有匹配的 PnP ID ,那就会使用对应的 Panel 参数
4.对于这个功能,如果 GOP 扫描中没有发现,那么会使用 Panel #01 的设定值;如果Select Panel Type 中没有使用Panel #FF,那么这个功能不会开启。
最近在看《圈圈教你玩USB(第一版)》,我手上的这本是作者签名版,十多年前买的。


书中提到了一个USB设备同时实现键盘鼠标功能的方案,其中的一种是:在 HID 描述符中分别报告鼠标和键盘,然后通过Report ID 对数据进行区分。于是手工编写一个代码,实现了一个USB设备下有3个键盘的功能。
代码是基于CustomHIDDevice编写的,对于 HID 设备来说,彼此之间主要差别就是 HID 描述符。这里定义了三个键盘的HID描述符:
//报告ID,(这里定义键盘报告的ID为1报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x01, //Report ID (1)
….
//报告ID,这里定义键盘报告的ID为2(报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x02, //Report ID (2)
….
//报告ID,这里定义键盘报告的ID为3(报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x03, //Report ID (3)
之后,主循环中有三个发送数据的部分,其中axis[0] 给出每隔Report 的ID,之后的8Bytes就是键盘的数据。
//键盘1 输出一个 a
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 1
axis[0]=0x01;axis[3]=0x04;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x01;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
发送数据部分:
delay(20);
//键盘2 输出一个 b
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 2
axis[0]=0x02;axis[3]=0x05;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x02;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
//键盘3 输出一个 c
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 3
axis[0]=0x03;axis[3]=0x06;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x03;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
此外,代码中还修改了每一次发送的数据从8个改为9个(就是ReportID+8Byte 键盘数据):
bool send(uint8_t * value){
return HID.SendReport(0, value, 9);
}
设备管理器中可以看到:

每隔10秒,电脑会收到输入的 abc 三个字符.
#include "USB.h"
#include "USBHID.h"
USBHID HID;
static const uint8_t report_descriptor[] = { // 8 axis
//每行开始的第一字节为该条目的前缀,前缀的格式为:
//D7~D4:bTag。D3~D2:bType;D1~D0:bSize。以下分别对每个条目注释。
/************************USB键盘部分报告描述符**********************/
/*******************************************************************/
//这是一个全局(bType为1)条目,将用途页选择为普通桌面Generic Desktop Page(0x01)
//后面跟一字节数据(bSize为1),后面的字节数就不注释了,
//自己根据bSize来判断。
0x05, 0x01, // USAGE_PAGE (Generic Desktop)
//这是一个局部(bType为2)条目,说明接下来的集合用途用于键盘
0x09, 0x06, // USAGE (Keyboard)
//这是一个主条目(bType为0)条目,开集合,后面跟的数据0x01表示
//该集合是一个应用集合。它的性质在前面由用途页和用途定义为
//普通桌面用的键盘。
0xa1, 0x01, // COLLECTION (Application)
//报告ID,(这里定义键盘报告的ID为1报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x01, //Report ID (1)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘(Keyboard/Keypad(0x07))
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最小值为0xe0。实际上是键盘左Ctrl键。
//具体的用途值可在HID用途表中查看。
0x19, 0xe0, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Keyboard LeftControl)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最大值为0xe7。实际上是键盘右GUI键。
0x29, 0xe7, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Right GUI)
//这是一个全局条目,说明返回的数据的逻辑值(就是我们返回的数据域的值)
//最小为0。因为我们这里用Bit来表示一个数据域,因此最小为0,最大为1。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的数量为八个。
0x95, 0x08, // REPORT_COUNT (8)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为1个bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个主条目,说明有8个长度为1bit的数据域(数量和长度
//由前面的两个全局条目所定义)用来做为输入,
//属性为:Data,Var,Abs。Data表示这些数据可以变动,Var表示
//这些数据域是独立的,每个域表示一个意思。Abs表示绝对值。
//这样定义的结果就是,当某个域的值为1时,就表示对应的键按下。
//bit0就对应着用途最小值0xe0,bit7对应着用途最大值0xe7。
0x81, 0x02, // INPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为1个
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为8bit。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个主条目,输入用,由前面两个全局条目可知,长度为8bit,
//数量为1个。它的属性为常量(即返回的数据一直是0)。
//该字节是保留字节(保留给OEM使用)。
0x81, 0x03, // INPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为6个。
0x95, 0x06, // REPORT_COUNT (6)
//这是一个全局条目。定义每个位域长度为8bit。
//其实这里这个条目不要也是可以的,因为在前面已经有一个定义
//长度为8bit的全局条目了。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最小值为0。
//同上,这里这个全局条目也是可以不要的,因为前面已经有一个
//定义逻辑最小值为0的全局条目了。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最大值为255。
0x25, 0xFF, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (255)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘。
//前面已经选择过用途页为键盘了,所以该条目不要也可以。
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最小值为0(0表示没有键按下)
0x19, 0x00, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Reserved (no event indicated))
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最大值为0x65
0x29, 0x65, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Application)
//这是一个主条目。它说明这六个8bit的数据域是输入用的,
//属性为:Data,Ary,Abs。Data说明数据是可以变的,Ary说明
//这些数据域是一个数组,即每个8bit都可以表示某个键值,
//如果按下的键太多(例如超过这里定义的长度或者键盘本身无法
//扫描出按键情况时),则这些数据返回全1(二进制),表示按键无效。
//Abs表示这些值是绝对值。
0x81, 0x00, // INPUT (Data,Ary,Abs)
//以下为输出报告的描述
//逻辑最小值前面已经有定义为0了,这里可以省略。
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为5个。
0x95, 0x05, // REPORT_COUNT (5)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的长度为1bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明使用的用途页为指示灯(LED)
0x05, 0x08, // USAGE_PAGE (LEDs)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最小值为数字键盘灯。
0x19, 0x01, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Num Lock)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最大值为Kana灯。
0x29, 0x05, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Kana)
//这是一个主条目。定义输出数据,即前面定义的5个LED。
0x91, 0x02, // OUTPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为1个。
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域长度为3bit。
0x75, 0x03, // REPORT_SIZE (3)
//这是一个主条目,定义输出常量,前面用了5bit,所以这里需要
//3个bit来凑成一字节。
0x91, 0x03, // OUTPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//下面这个主条目用来关闭前面的集合。bSize为0,所以后面没数据。
0xc0, // END_COLLECTION
/************************USB键盘部分报告描述符**********************/
/*******************************************************************/
//这是一个全局(bType为1)条目,将用途页选择为普通桌面Generic Desktop Page(0x01)
//后面跟一字节数据(bSize为1),后面的字节数就不注释了,
//自己根据bSize来判断。
0x05, 0x01, // USAGE_PAGE (Generic Desktop)
//这是一个局部(bType为2)条目,说明接下来的集合用途用于键盘
0x09, 0x06, // USAGE (Keyboard)
//这是一个主条目(bType为0)条目,开集合,后面跟的数据0x01表示
//该集合是一个应用集合。它的性质在前面由用途页和用途定义为
//普通桌面用的键盘。
0xa1, 0x01, // COLLECTION (Application)
//报告ID,这里定义键盘报告的ID为2(报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x02, //Report ID (2)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘(Keyboard/Keypad(0x07))
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最小值为0xe0。实际上是键盘左Ctrl键。
//具体的用途值可在HID用途表中查看。
0x19, 0xe0, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Keyboard LeftControl)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最大值为0xe7。实际上是键盘右GUI键。
0x29, 0xe7, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Right GUI)
//这是一个全局条目,说明返回的数据的逻辑值(就是我们返回的数据域的值)
//最小为0。因为我们这里用Bit来表示一个数据域,因此最小为0,最大为1。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的数量为八个。
0x95, 0x08, // REPORT_COUNT (8)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为1个bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个主条目,说明有8个长度为1bit的数据域(数量和长度
//由前面的两个全局条目所定义)用来做为输入,
//属性为:Data,Var,Abs。Data表示这些数据可以变动,Var表示
//这些数据域是独立的,每个域表示一个意思。Abs表示绝对值。
//这样定义的结果就是,当某个域的值为1时,就表示对应的键按下。
//bit0就对应着用途最小值0xe0,bit7对应着用途最大值0xe7。
0x81, 0x02, // INPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为1个
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为8bit。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个主条目,输入用,由前面两个全局条目可知,长度为8bit,
//数量为1个。它的属性为常量(即返回的数据一直是0)。
//该字节是保留字节(保留给OEM使用)。
0x81, 0x03, // INPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为6个。
0x95, 0x06, // REPORT_COUNT (6)
//这是一个全局条目。定义每个位域长度为8bit。
//其实这里这个条目不要也是可以的,因为在前面已经有一个定义
//长度为8bit的全局条目了。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最小值为0。
//同上,这里这个全局条目也是可以不要的,因为前面已经有一个
//定义逻辑最小值为0的全局条目了。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最大值为255。
0x25, 0xFF, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (255)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘。
//前面已经选择过用途页为键盘了,所以该条目不要也可以。
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最小值为0(0表示没有键按下)
0x19, 0x00, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Reserved (no event indicated))
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最大值为0x65
0x29, 0x65, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Application)
//这是一个主条目。它说明这六个8bit的数据域是输入用的,
//属性为:Data,Ary,Abs。Data说明数据是可以变的,Ary说明
//这些数据域是一个数组,即每个8bit都可以表示某个键值,
//如果按下的键太多(例如超过这里定义的长度或者键盘本身无法
//扫描出按键情况时),则这些数据返回全1(二进制),表示按键无效。
//Abs表示这些值是绝对值。
0x81, 0x00, // INPUT (Data,Ary,Abs)
//以下为输出报告的描述
//逻辑最小值前面已经有定义为0了,这里可以省略。
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为5个。
0x95, 0x05, // REPORT_COUNT (5)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的长度为1bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明使用的用途页为指示灯(LED)
0x05, 0x08, // USAGE_PAGE (LEDs)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最小值为数字键盘灯。
0x19, 0x01, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Num Lock)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最大值为Kana灯。
0x29, 0x05, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Kana)
//这是一个主条目。定义输出数据,即前面定义的5个LED。
0x91, 0x02, // OUTPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为1个。
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域长度为3bit。
0x75, 0x03, // REPORT_SIZE (3)
//这是一个主条目,定义输出常量,前面用了5bit,所以这里需要
//3个bit来凑成一字节。
0x91, 0x03, // OUTPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//下面这个主条目用来关闭前面的集合。bSize为0,所以后面没数据。
0xc0, // END_COLLECTION
/************************USB键盘部分报告描述符**********************/
/*******************************************************************/
//这是一个全局(bType为1)条目,将用途页选择为普通桌面Generic Desktop Page(0x01)
//后面跟一字节数据(bSize为1),后面的字节数就不注释了,
//自己根据bSize来判断。
0x05, 0x01, // USAGE_PAGE (Generic Desktop)
//这是一个局部(bType为2)条目,说明接下来的集合用途用于键盘
0x09, 0x06, // USAGE (Keyboard)
//这是一个主条目(bType为0)条目,开集合,后面跟的数据0x01表示
//该集合是一个应用集合。它的性质在前面由用途页和用途定义为
//普通桌面用的键盘。
0xa1, 0x01, // COLLECTION (Application)
//报告ID,这里定义键盘报告的ID为3(报告ID 0是保留的)
0x85, 0x03, //Report ID (3)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘(Keyboard/Keypad(0x07))
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最小值为0xe0。实际上是键盘左Ctrl键。
//具体的用途值可在HID用途表中查看。
0x19, 0xe0, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Keyboard LeftControl)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途的最大值为0xe7。实际上是键盘右GUI键。
0x29, 0xe7, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Right GUI)
//这是一个全局条目,说明返回的数据的逻辑值(就是我们返回的数据域的值)
//最小为0。因为我们这里用Bit来表示一个数据域,因此最小为0,最大为1。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的数量为八个。
0x95, 0x08, // REPORT_COUNT (8)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为1个bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个主条目,说明有8个长度为1bit的数据域(数量和长度
//由前面的两个全局条目所定义)用来做为输入,
//属性为:Data,Var,Abs。Data表示这些数据可以变动,Var表示
//这些数据域是独立的,每个域表示一个意思。Abs表示绝对值。
//这样定义的结果就是,当某个域的值为1时,就表示对应的键按下。
//bit0就对应着用途最小值0xe0,bit7对应着用途最大值0xe7。
0x81, 0x02, // INPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为1个
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明每个数据域的长度为8bit。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个主条目,输入用,由前面两个全局条目可知,长度为8bit,
//数量为1个。它的属性为常量(即返回的数据一直是0)。
//该字节是保留字节(保留给OEM使用)。
0x81, 0x03, // INPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为6个。
0x95, 0x06, // REPORT_COUNT (6)
//这是一个全局条目。定义每个位域长度为8bit。
//其实这里这个条目不要也是可以的,因为在前面已经有一个定义
//长度为8bit的全局条目了。
0x75, 0x08, // REPORT_SIZE (8)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最小值为0。
//同上,这里这个全局条目也是可以不要的,因为前面已经有一个
//定义逻辑最小值为0的全局条目了。
0x15, 0x00, // LOGICAL_MINIMUM (0)
//这是一个全局条目,定义逻辑最大值为255。
0x25, 0xFF, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (255)
//这是一个全局条目,选择用途页为键盘。
//前面已经选择过用途页为键盘了,所以该条目不要也可以。
0x05, 0x07, // USAGE_PAGE (Keyboard/Keypad)
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最小值为0(0表示没有键按下)
0x19, 0x00, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Reserved (no event indicated))
//这是一个局部条目,定义用途最大值为0x65
0x29, 0x65, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Keyboard Application)
//这是一个主条目。它说明这六个8bit的数据域是输入用的,
//属性为:Data,Ary,Abs。Data说明数据是可以变的,Ary说明
//这些数据域是一个数组,即每个8bit都可以表示某个键值,
//如果按下的键太多(例如超过这里定义的长度或者键盘本身无法
//扫描出按键情况时),则这些数据返回全1(二进制),表示按键无效。
//Abs表示这些值是绝对值。
0x81, 0x00, // INPUT (Data,Ary,Abs)
//以下为输出报告的描述
//逻辑最小值前面已经有定义为0了,这里可以省略。
//这是一个全局条目,说明逻辑值最大为1。
0x25, 0x01, // LOGICAL_MAXIMUM (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域数量为5个。
0x95, 0x05, // REPORT_COUNT (5)
//这是一个全局条目,说明数据域的长度为1bit。
0x75, 0x01, // REPORT_SIZE (1)
//这是一个全局条目,说明使用的用途页为指示灯(LED)
0x05, 0x08, // USAGE_PAGE (LEDs)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最小值为数字键盘灯。
0x19, 0x01, // USAGE_MINIMUM (Num Lock)
//这是一个局部条目,说明用途最大值为Kana灯。
0x29, 0x05, // USAGE_MAXIMUM (Kana)
//这是一个主条目。定义输出数据,即前面定义的5个LED。
0x91, 0x02, // OUTPUT (Data,Var,Abs)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域数量为1个。
0x95, 0x01, // REPORT_COUNT (1)
//这是一个全局条目。定义位域长度为3bit。
0x75, 0x03, // REPORT_SIZE (3)
//这是一个主条目,定义输出常量,前面用了5bit,所以这里需要
//3个bit来凑成一字节。
0x91, 0x03, // OUTPUT (Cnst,Var,Abs)
//下面这个主条目用来关闭前面的集合。bSize为0,所以后面没数据。
0xc0, // END_COLLECTION
};
class CustomHIDDevice: public USBHIDDevice {
public:
CustomHIDDevice(void){
static bool initialized = false;
if(!initialized){
initialized = true;
HID.addDevice(this, sizeof(report_descriptor));
}
}
void begin(void){
HID.begin();
}
uint16_t _onGetDescriptor(uint8_t* buffer){
memcpy(buffer, report_descriptor, sizeof(report_descriptor));
return sizeof(report_descriptor);
}
bool send(uint8_t * value){
return HID.SendReport(0, value, 9);
}
};
CustomHIDDevice Device;
const int buttonPin = 0;
int previousButtonState = HIGH;
uint8_t axis[9];
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.setDebugOutput(true);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
Device.begin();
USB.begin();
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
if (HID.ready() && buttonState != previousButtonState) {
previousButtonState = buttonState;
if (buttonState == LOW) {
Serial.println("Button Pressed");
axis[0] = random() & 0xFF;
Device.send(axis);
} else {
Serial.println("Button Released");
}
delay(100);
}
//每隔10秒
delay(10000);
//键盘1 输出一个 a
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 1
axis[0]=0x01;axis[3]=0x04;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x01;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
//键盘2 输出一个 b
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 2
axis[0]=0x02;axis[3]=0x05;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x02;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
//键盘3 输出一个 c
//其中 axis[0] 是 report ID 这里为 3
axis[0]=0x03;axis[3]=0x06;
Device.send(axis);
delay(20);
axis[0]=0x03;axis[3]=0x00;
Device.send(axis);
}
对于 PS2 键盘来说是“全键无冲突的”,意思是可以按下任意多的按键;对于标准的USB 键盘来说,最多只能同时按下6个按键。这是因为 PS2 是分开发送按下和抬起消息的;而标准USB键盘,有8Bytes的数据,其中第一个byte 用来指示 alt ctrl 等等,第二个Byte 始终为0,接下来剩下6Byte,需要放置按下键的信息,如果抬起还需要用0来指示。这样只能支持同时按下6个键。上面提到的这个方法可以用来扩展USB键盘,比如,声明3个键盘就可以支持 6*3=18键无冲突。
1.最原始的 ESP32 支持 SDIO
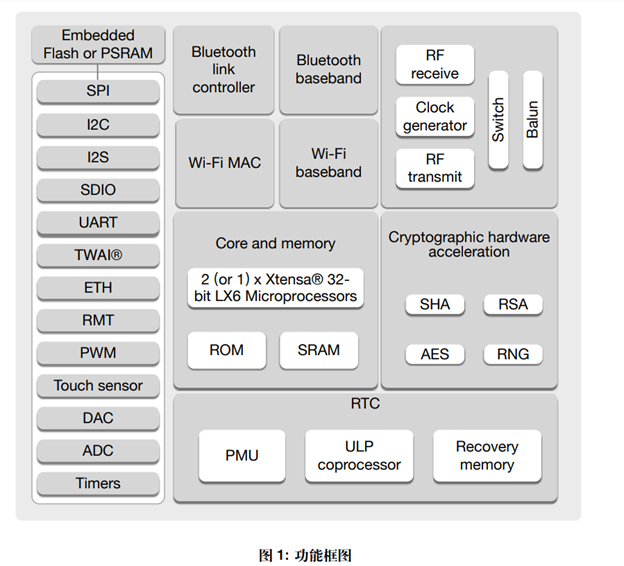
SDIO/SPI 从机控制器 ESP32 集成了符合工业标准 SDIO 2.0 规格的 SD 设备接口,并允许主机控制器使用 SDIO 总线协议访问 SoC 设备。ESP32 用作 SDIO 总线上的从机。主机可以直接访问 SDIO 接口的寄存器并通过使用 DMA 引擎访问设备 中的共享内存,从而不需要处理器内核即可使性能最优化。 SDIO/SPI 从机控制器具有以下特性:
• 时钟范围为 0 至 50 MHz,支持 SPI、1-bit SDIO 和 4-bit SDIO 的传输模式
• 采样和驱动的时钟边沿可配置
• 主机可直接访问的专用寄存器
• 可中断主机,启动数据传输
• 支持自动填充 SDIO 总线上的发送数据,同样支持自动丢弃 SDIO 总线上的填充数据
• 字节块大小可达 512 字节
• 主机与从机间有中断向量可以相互中断对方
• 用于数据传输的 DMA 详细信息请参考 《ESP32 技术参考手册》中的 SDIO 从机控制器章节。
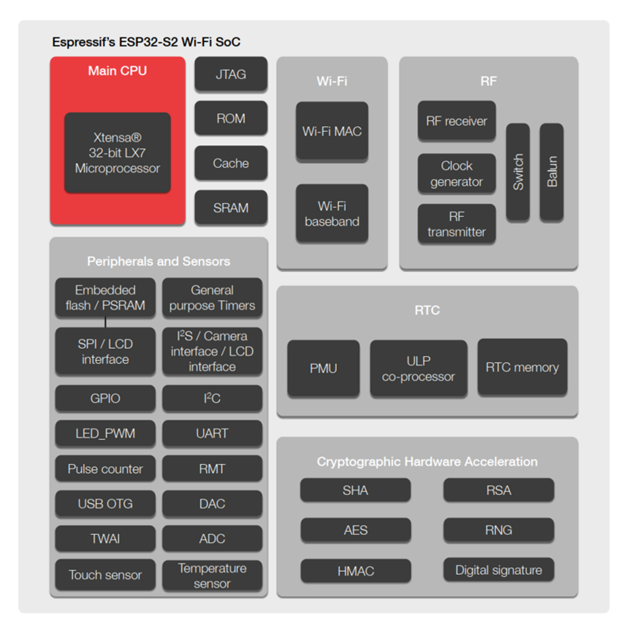
2.ESP32 S2 不支持 SDIO, 如果想用 SD 卡只能走 SPI
3.ESP32 S3 支持 SDIO
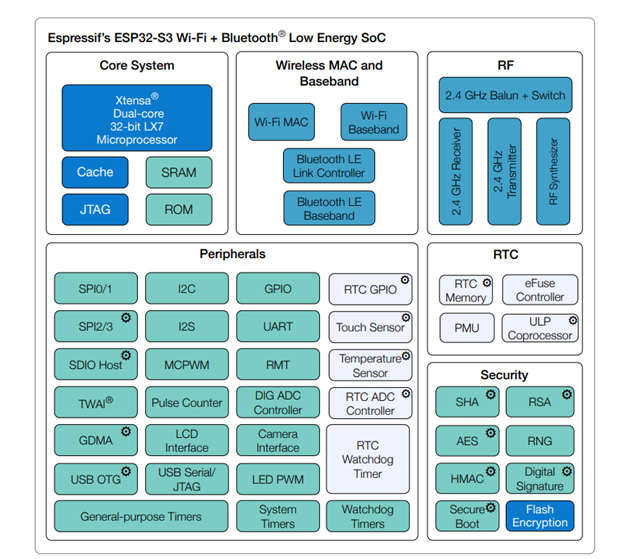
支持 SDIO 3.0 版本
上述来自各自的技术规格书。
继续我们的研究。从Log中可以看到,加载了ReportStatusCodeRouterPei.efi:
Loading PEIM A3610442-E69F-4DF3-82CA-2360C4031A23
Loading PEIM at 0x000008470A0 EntryPoint=0x000008475A0 ReportStatusCodeRouterPei.efi
对应代码位于\MdeModulePkg\Universal\ReportStatusCodeRouter\Pei目录下:
/**
Entry point of Status Code PEIM.
This function is the entry point of this Status Code Router PEIM.
It produces Report Stataus Code Handler PPI and Status Code PPI.
@param FileHandle Handle of the file being invoked.
@param PeiServices Describes the list of possible PEI Services.
@retval EFI_SUCESS The entry point of DXE IPL PEIM executes successfully.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
GenericStatusCodePeiEntry (
IN EFI_PEI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle,
IN CONST EFI_PEI_SERVICES **PeiServices
)
接下来Log 如下:
Install PPI: 0065D394-9951-4144-82A3-0AFC8579C251
Install PPI: 229832D3-7A30-4B36-B827-F40CB7D45436
这两个 GUID 在 \MdePkg\MdePkg.dec 有定义:
## Include/Ppi/ReportStatusCodeHandler.h
gEfiPeiRscHandlerPpiGuid = { 0x65d394, 0x9951, 0x4144, {0x82, 0xa3, 0xa, 0xfc, 0x85, 0x79, 0xc2, 0x51 }}
## Include/Ppi/StatusCode.h
gEfiPeiStatusCodePpiGuid = { 0x229832d3, 0x7a30, 0x4b36, {0xb8, 0x27, 0xf4, 0xc, 0xb7, 0xd4, 0x54, 0x36 } }
这个里面比较有意思的是这里面注册了2个Ppi,其中一个是 ReportStatusCode的Ppi,另外一个是用来给ReportStatusCode 注册实际工作的函数,接下来的模块会调用这个Ppi能够让我们理解实际动作。
继续查看 Log 有如下:
Loading PEIM 9D225237-FA01-464C-A949-BAABC02D31D0
Loading PEIM at 0x0000084BFA0 EntryPoint=0x0000084C4A0 StatusCodeHandlerPei.efi
StatusCodeHandlerPei对应的代码位于 \MdeModulePkg\Universal\StatusCodeHandler\Pei目录
/**
Entry point of Status Code PEIM.
This function is the entry point of this Status Code PEIM.
It initializes supported status code devices according to PCD settings,
and installs Status Code PPI.
@param FileHandle Handle of the file being invoked.
@param PeiServices Describes the list of possible PEI Services.
@retval EFI_SUCESS The entry point of DXE IPL PEIM executes successfully.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
StatusCodeHandlerPeiEntry (
IN EFI_PEI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle,
IN CONST EFI_PEI_SERVICES **PeiServices
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_PEI_RSC_HANDLER_PPI *RscHandlerPpi;
Status = PeiServicesLocatePpi (
&gEfiPeiRscHandlerPpiGuid,
0,
NULL,
(VOID **) &RscHandlerPpi
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
//
// Dispatch initialization request to sub-statuscode-devices.
// If enable UseSerial, then initialize serial port.
// if enable UseMemory, then initialize memory status code worker.
//
if (PcdGetBool (PcdStatusCodeUseSerial)) {
Status = SerialPortInitialize();
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
Status = RscHandlerPpi->Register (SerialStatusCodeReportWorker);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
if (PcdGetBool (PcdStatusCodeUseMemory)) {
Status = MemoryStatusCodeInitializeWorker ();
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
Status = RscHandlerPpi->Register (MemoryStatusCodeReportWorker);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
就是说通过 RscHandlerPpi 注册了2个Callback函数SerialStatusCodeReportWorker 和MemoryStatusCodeReportWorker。当有人使用 ReportStatusCode时,会先后进入 SerialStatusCodeReportWorker() 和MemoryStatusCodeReportWorker()。
再进一步检查,在\OvmfPkg\OvmfPkgX64.dsc 有如下定义:
gEfiMdeModulePkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdStatusCodeUseSerial|FALSE
gEfiMdeModulePkgTokenSpaceGuid.PcdStatusCodeUseMemory|TRUE
从 PCD可以看到在 OVMF 中,没有使用 SerialStatusCodeReportWorker。当代码使用了ReportStatusCode时,会执行MemoryStatusCodeReportWorker()。
这是一种非常巧妙的实现,有兴趣的朋友可以研究 \MdeModulePkg\Universal\ReportStatusCodeRouter\Pei\ReportStatusCodeRouterPei.c 这个文件。
数学,在日常生活中出了买菜之外,还能发挥很大的作用。笔者的一个朋友在朋友圈发布了一条保险的广告:
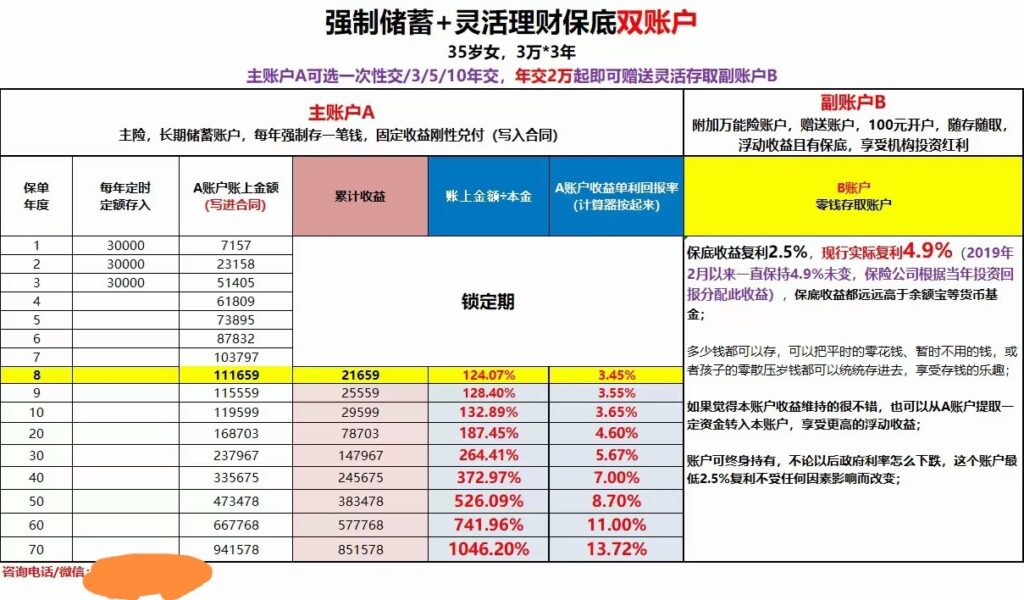
简单的说:连续三年每年存3万,然后第八年就能够取出来 111,659元。根据他们的说法,第八年的收益是 21,659元,因此利息是:(21659/90000)=24.1%,这算得每年利息 24.1%/7=3.45% (我也不知道为什么他们要除以7 )。从直觉上看我感觉这个非常可疑,按照复利计算得年利率应该不高。于是动笔进行计算。
假设年利率为x,那么一年之后本金加利率为 p=1+x。
第一年末尾一共有: 3*p
第二年末尾一共有: (3*p+3)*p
第三年末尾一共有: ((3*p+3)*p+3)*p
第四年末尾一共有: ((3*p+3)*p+3)*(p^2)
……………………………………….
第八年末尾一共有: ((3*p+3)*p+3)*(p^6)
第N年末尾一共有: ((3*p+3)*p+3)*(p^(N-2))
针对第八年进行研究,展开算式一共有 3*(P^8) +3*(P^7) +3*(P^6), 对照上面表格有方程
3*(P^8) +3*(P^7) +3*(P^6)= 111659
这是一元八次方程,我没有办法直接从数学角度解开。于是编写代码来解。因为我们知道这是一个单调递增函数,所以我们可以给定一个初始值Start,然后给出一个步长 Step,不断尝试计算f(Start+Step)的值,如果它小于目标,那么 Start=Start+Step,否则 Step=Step/2 继续尝试。最终得到一个值: 1.03123863220215
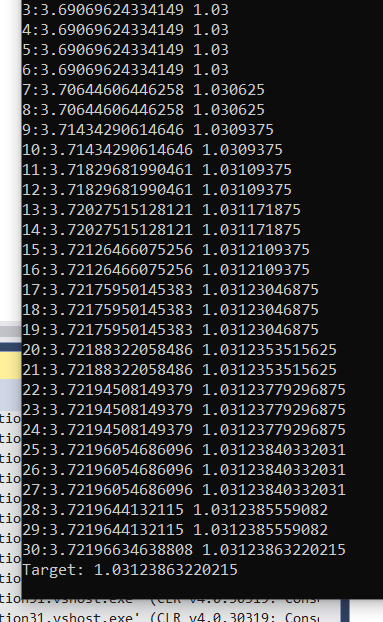
换句话说,以复利计算年利率 3.123%。
之后,我们再使用20年的收益168703进行计算,结果是:1.03360308647156。以复利计算年利率 3.36%。
C#编写的完整代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace ConsoleApplication31
{
class Program
{
static double f(double value,int year)
{
return Math.Pow(value, year) + Math.Pow(value, year-1) + Math.Pow(value, year-2);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
const double ESP = 1e-6;
const int YEAR = 8;
double start = 1.00;
double step = 0.01;
double target = 111659.00 / 30000;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
if (Math.Abs(f(start, YEAR) - target) <ESP)
{
Console.WriteLine("Target: {0}", start);
break;
}
// 增加之后 f(x) 大于 target
if (f(start + step, YEAR) > target)
{
step = step / 2;
}
else {
start += step;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}:{1} {2}", i, f(start, YEAR), start);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
从上面可以看出:在查看这种收益表格时,因为计算复杂,消费者很容易被误导。另外,这种产品周期太长,风险很大,是另外的成本。
St这个系列是根据 QEMU 执行输出的 Log 来研究代码的。这里继续跟踪研究代码,这次研究的对象是下面这条串口输出:
Register PPI Notify: DCD0BE23-9586-40F4-B643-06522CED4EDE
这句话来自 \MdeModulePkg\Core\Pei\Security\Security.c 文件中的InitializeSecurityServices() 函数:
/**
Initialize the security services.
@param PeiServices An indirect pointer to the EFI_PEI_SERVICES table published by the PEI Foundation.
@param OldCoreData Pointer to the old core data.
NULL if being run in non-permanent memory mode.
**/
VOID
InitializeSecurityServices (
IN EFI_PEI_SERVICES **PeiServices,
IN PEI_CORE_INSTANCE *OldCoreData
)
{
if (OldCoreData == NULL) {
PeiServicesNotifyPpi (&mNotifyList);
}
return;
}
其中 mNotifyList 注册了一个 Ppi Notify 的 Callback 函数:SecurityPpiNotifyCallback()
EFI_PEI_NOTIFY_DESCRIPTOR mNotifyList = {
EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_NOTIFY_DISPATCH | EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_TERMINATE_LIST,
&gEfiPeiSecurity2PpiGuid,
SecurityPpiNotifyCallback
};
PeiServicesNotifyPpi() 的定义在 \MdePkg\Library\PeiServicesLib\PeiServicesLib.c:
/**
This service enables PEIMs to register a given service to be invoked when another service is
installed or reinstalled.
@param NotifyList A pointer to the list of notification interfaces
that the caller shall install.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The interface was successfully installed.
@retval EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER The NotifyList pointer is NULL.
@retval EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER Any of the PEI notify descriptors in the list do
not have the EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_NOTIFY_TYPES
bit set in the Flags field.
@retval EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES There is no additional space in the PPI database.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
PeiServicesNotifyPpi (
IN CONST EFI_PEI_NOTIFY_DESCRIPTOR *NotifyList
)
这个函数的功能是:注册一个 Callback函数,当给定的 Service 安装(install)或者重安装(re-install)时触发这个 callback函数。
经过检查,代码中没有人安装gEfiPeiSecurity2PpiGuid,所以 CallBack 不会发生。接下来找一个有触发 CallBack 函数的作为例子看一下这个如何动作的。
串口输出” Register PPI Notify: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB397” 和上面的函数类似,这个 GUID定义在 \MdePkg\MdePkg.dec 中:
## Include/Ppi/FirmwareVolumeInfo.h
gEfiPeiFirmwareVolumeInfoPpiGuid = { 0x49edb1c1, 0xbf21, 0x4761, { 0xbb, 0x12, 0xeb, 0x0, 0x31, 0xaa, 0xbb, 0x39 } }
1. 首先注册Notify,在\MdeModulePkg\Core\Pei\FwVol\FwVol.c 中:
EFI_PEI_NOTIFY_DESCRIPTOR mNotifyOnFvInfoList[] = {
{
EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_NOTIFY_CALLBACK,
&gEfiPeiFirmwareVolumeInfoPpiGuid,
FirmwareVolumeInfoPpiNotifyCallback
},
{
(EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_NOTIFY_CALLBACK | EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_TERMINATE_LIST),
&gEfiPeiFirmwareVolumeInfo2PpiGuid,
FirmwareVolumeInfoPpiNotifyCallback
}
};
接下来可以在在串口 Log 中找到如下字样:
Install PPI: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB39
Notify: PPI Guid: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB39, Peim notify entry point: 82153C
2. “Install PPI: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB39”来自:
\MdePkg\Library\PeiServicesLib\PeiServicesLib.c 中的InternalPeiServicesInstallFvInfoPpi () 函数,首先给PpiGuid赋值
//
// To install FvInfo Ppi.
//
FvInfoPpi = AllocateZeroPool (sizeof (EFI_PEI_FIRMWARE_VOLUME_INFO_PPI));
ASSERT (FvInfoPpi != NULL);
PpiGuid = &gEfiPeiFirmwareVolumeInfoPpiGuid;
接下来PeiServicesInstallPpi (FvInfoPpiDescriptor) 会安装这个 Ppi:
FvInfoPpiDescriptor->Guid = PpiGuid;
FvInfoPpiDescriptor->Flags = EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_PPI | EFI_PEI_PPI_DESCRIPTOR_TERMINATE_LIST;
FvInfoPpiDescriptor->Ppi = (VOID *) FvInfoPpi;
Status = PeiServicesInstallPpi (FvInfoPpiDescriptor);
安装过程会出现“Install PPI: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB39” 的提示。
3. “Notify: PPI Guid: 49EDB1C1-BF21-4761-BB12-EB0031AABB39, Peim notify entry point: 82153C”
因为这里安装了gEfiPeiFirmwareVolumeInfoPpiGuid 所以会执行FirmwareVolumeInfoPpiNotifyCallback() 这个 Callback 函数。在函数中有定义
DEBUG ((
EFI_D_INFO,
"The %dth FV start address is 0x%11p, size is 0x%08x, handle is 0x%p\n",
(UINT32) CurFvCount,
(VOID *) FvInfo2Ppi.FvInfo,
FvInfo2Ppi.FvInfoSize,
FvHandle
));
于是我们在串口上能看到如下 Log :
“The 1th FV start address is 0x00000900000, size is 0x00C00000, handle is 0x900000”
就是说按照我们的预期一样,PeiServicesNotifyPpi 函数是用来注册一个 Callback 函数,当安装给定 GUID 的Service 后,触发这个 Callback 函数。
前文提到PEI阶段加载了7个模块,从Log 中的如下字样,我们知道当前跳入了 PcdPeim.efi 运行
Loading PEIM at 0x0000083D120 EntryPoint=0x0000083D620 PcdPeim.efi
执行输出的 Log 如下:
Install PPI: 06E81C58-4AD7-44BC-8390-F10265F72480
Install PPI: 01F34D25-4DE2-23AD-3FF3-36353FF323F1
Install PPI: 4D8B155B-C059-4C8F-8926-06FD4331DB8A
Install PPI: A60C6B59-E459-425D-9C69-0BCC9CB27D81
Register PPI Notify: 605EA650-C65C-42E1-BA80-91A52AB618C6
其中的 GUID 可以在 \MdePkg\MdePkg.dec 中查到:
## Include/Ppi/Pcd.h
gPcdPpiGuid = { 0x6e81c58, 0x4ad7, 0x44bc, { 0x83, 0x90, 0xf1, 0x2, 0x65, 0xf7, 0x24, 0x80 } }
## Include/Ppi/PiPcd.h
gEfiPeiPcdPpiGuid = { 0x1f34d25, 0x4de2, 0x23ad, { 0x3f, 0xf3, 0x36, 0x35, 0x3f, 0xf3, 0x23, 0xf1 } }
## Include/Ppi/PcdInfo.h
gGetPcdInfoPpiGuid = { 0x4d8b155b, 0xc059, 0x4c8f, { 0x89, 0x26, 0x6, 0xfd, 0x43, 0x31, 0xdb, 0x8a } }
## Include/Ppi/PiPcdInfo.h
gEfiGetPcdInfoPpiGuid = { 0xa60c6b59, 0xe459, 0x425d, { 0x9c, 0x69, 0xb, 0xcc, 0x9c, 0xb2, 0x7d, 0x81 } }
最后的一个 PPI Notify 定义为:
## Include/Ppi/EndOfPeiPhase.h
gEfiEndOfPeiSignalPpiGuid = {0x605EA650, 0xC65C, 0x42e1, {0xBA, 0x80, 0x91, 0xA5, 0x2A, 0xB6, 0x18, 0xC6 } }
继代码位于 MdeModulePkg\Universal\PCD\Pei\Pcd.c 中。
/**
Main entry for PCD PEIM driver.
This routine initialize the PCD database for PEI phase and install PCD_PPI/EFI_PEI_PCD_PPI.
@param FileHandle Handle of the file being invoked.
@param PeiServices Describes the list of possible PEI Services.
@return Status of install PCD_PPI
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
PcdPeimInit (
IN EFI_PEI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle,
IN CONST EFI_PEI_SERVICES **PeiServices
)
从代码上看,QEMU 模拟了 SPI ROM,使可以看到,这个 PEI Module 主要作用是注册了多个和PCD 相关的 Ppi Service 以便后续使用。