阅读《UEFI原理与编程》,第八章,开发UEFI服务。其中提到了 Protocol的私有数据。
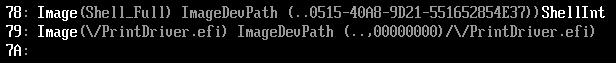
之前我们介绍过 EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL,在【参考1】的程序中,就有涉及到LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA,简单的说,定义的 PROTOCOL是这个结构体的一部分,就能够找到整个LOADED_IMAGE_PRIVATE_DATA的结构体,从而获得一些额外的信息。
总结一下,这样的私有数据是这样定义的:
#define PROTOCOLNAME_PRIVATE_DATA_SIGNATURE SIGNATURE_32('p','r','t','9')
typedef struct {
UINTN Signature;
UINTN Var1;
PROTOCOLNAME _PROTOCOL PROTOCOLNAME;
} PROTOCOLNAME_PRIVATE_DATA;
#define PROTOCOLNAME _PRIVATE_DATA_FROM_THIS(a) \
CR(a, PROTOCOLNAME_PRIVATE_DATA, PROTOCOLNAME, PROTOCOLNAME _PRIVATE_DATA_SIGNATURE)
在初始化的时候,要创建一个实际的PROTOCOLNAME_PRIVATE_DATA,然后初始化需要的变量,最后像其他的Protocol安装一样,将PROTOCOLNAME_PRIVATE_DATA. PROTOCOLNAME 安装到合适的Handle上即可。
编写代码测试一下,基于之前我们写的 PrintDriver 代码,先修改 Print9.h。加入了下面的定义:
#define PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA_SIGNATURE SIGNATURE_32('p','r','t','9')
typedef struct {
UINTN Signature;
UINTN Var1;
/// loaded PROTOCOLNAME
EFI_PRINT9_PROTOCOL PRINT9;
} EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA;
#define EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA_FROM_THIS(a) \
CR(a, EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA, PRINT9, PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA_SIGNATURE)
之后修改print.c。 这个 driver实现的功能很简单,每次调用UnicodeSPrint 函数的时候,会自动显示 EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA 中的 Var1,并且增加1.
#include <PiDxe.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include "Print9.h"
#include <Library/PrintLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiBootServicesTableLib.h>
#include <Library/DebugLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiDriverEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA *Image;
EFI_HANDLE mPrintThunkHandle = NULL;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
//Copied from \MdeModulePkg\Library\DxePrintLibPrint2Protocol\PrintLib.c
UINTN
EFIAPI
MyUnicodeSPrint (
OUT CHAR16 *StartOfBuffer,
IN UINTN BufferSize,
IN CONST CHAR16 *FormatString,
...
)
{
VA_LIST Marker;
UINTN NumberOfPrinted=1;
CHAR16 *Buffer=L"12345678";
VA_START (Marker, FormatString);
//NumberOfPrinted = UnicodeVSPrint (StartOfBuffer, BufferSize, FormatString, Marker);
VA_END (Marker);
UnicodeSPrint(Buffer,8,L"%d",Image->Var1);
gST->ConOut->OutputString(gST->ConOut,Buffer);
Image->Var1++;
return NumberOfPrinted;
}
/**
The user Entry Point for Print module.
This is the entry point for Print DXE Driver. It installs the Print2 Protocol.
@param[in] ImageHandle The firmware allocated handle for the EFI image.
@param[in] SystemTable A pointer to the EFI System Table.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The entry point is executed successfully.
@retval Others Some error occurs when executing this entry point.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
PrintEntryPoint (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status=EFI_SUCCESS;
//
// Allocate a new image structure
//
Image = AllocateZeroPool (sizeof(EFI_PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA));
if (Image == NULL) {
Status = EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES;
goto Done;
}
Image->Signature = PRINT9_PRIVATE_DATA_SIGNATURE;
Image->PRINT9.UnicodeBSPrint=UnicodeBSPrint;
Image->PRINT9.UnicodeSPrint=MyUnicodeSPrint;
Image->PRINT9.UnicodeBSPrintAsciiFormat=UnicodeBSPrintAsciiFormat;
Image->PRINT9.UnicodeSPrintAsciiFormat=UnicodeSPrintAsciiFormat;
Image->PRINT9.UnicodeValueToString=UnicodeValueToString;
Image->PRINT9.AsciiBSPrint=AsciiBSPrint;
Image->PRINT9.AsciiSPrint=AsciiSPrint;
Image->PRINT9.AsciiBSPrintUnicodeFormat=AsciiBSPrintUnicodeFormat;
Image->PRINT9.AsciiSPrintUnicodeFormat=AsciiSPrintUnicodeFormat;
Image->PRINT9.AsciiValueToString=AsciiValueToString;
Status = gBS->InstallMultipleProtocolInterfaces (
&mPrintThunkHandle,
&gEfiPrint9ProtocolGuid,
&Image->PRINT9,
NULL
);
ASSERT_EFI_ERROR (Status);
Done:
return Status;
}
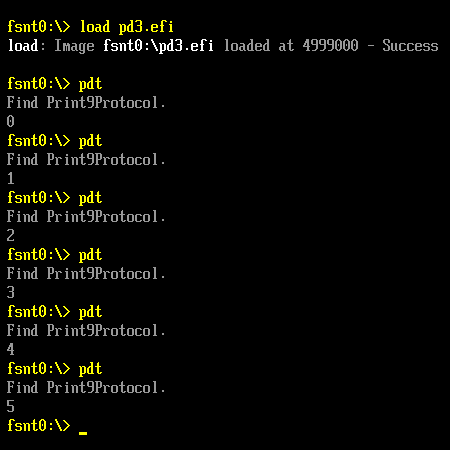
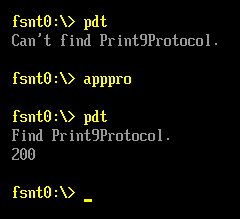
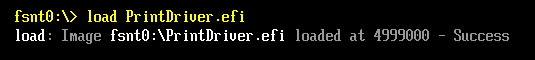
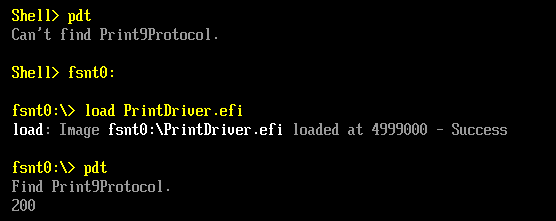
测试这个 Protocol 使用的还是之前的 pdt.efi,运行结果如下:
完整的代码下载
参考:
1. Step to UEFI (48) —– 被加载程序的ENTRYPOINT