有朋友留言我才想起来很早之前介绍过 zLib 的编译,但是没有编写一个完整的例子。这次补上这一块。
首先需要安装好zLib(现在都是在 UDK2015下面进行编译),我在 AppPkg.dsc 中加入下面的语句:
CacheMaintenanceLib|MdePkg/Library/BaseCacheMaintenanceLib/BaseCacheMaintenanceLib.inf UefiHandleParsingLib|ShellPkg/Library/UefiHandleParsingLib/UefiHandleParsingLib.inf zLib|AppPkg/Applications/zsource/zlib.inf ################################################################################################### # # Components Section - list of the modules and components that will be processed by compilation # tools and the EDK II tools to generate PE32/PE32+/Coff image files.
之后就可以直接使用了。
压缩很简单,用下面这个函数即可
int compress (Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen, const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen);
特别需要注意的是,压缩是在内存中进行的,所以需要开辟一段用来存放压缩结果的空间,这个空间的大小也就是上面的destLen。因此,在运行这个函数之前最好线运行一下预测压缩之后大小的函数:
uLong compressBound (uLong sourceLen);
压缩之后的结果不会超过这个函数返回值(一般情况下要小得多)
压缩很简单,下面介绍解压缩:
int uncompress (Bytef *dest, uLongf *destLen,const Bytef *source, uLong sourceLen);
和压缩函数非常类似,但是有一点特别注意的:这个函数用到的 destLen 是解压之后的大小,但是zLib没有提供预测解压之后大小的函数。据说原因是因为解压缩是压缩的“反函数”,因此,在压缩的时候应该已经知道解压后的大小。具体在使用的时候需要想办法自己定义结构体之类的将原始大小传递给解压函数以便开辟内存空间。譬如,在存放压缩的buffer前面加上4字节的大小之类的。
基本概念了解完就上代码,例子实现的功能是将 zlibtest.efi 压缩为test.lbz。然后再解压保存为 test.efi。
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include "zlib.h"
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
RETURN_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_INFO *FileInfo = NULL;
UINT32 SourceSize;
UINT32 preSize;
CHAR8 *source=NULL;
CHAR8 *dest=NULL;
//Read a source file
//Open the file given by the parameter
Status =
ShellOpenFileByName(
L"zlibtest.efi",
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ ,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
//Get file size
FileInfo =
ShellGetFileInfo((SHELL_FILE_HANDLE)FileHandle);
//Allocate a memory buffer
source =
AllocateZeroPool((UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize);
if (source == NULL) {
Print(L"Allocate source memory error!\n");
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
SourceSize = (UINT32) (FileInfo-> FileSize & 0xFFFFFFFF);
//Load the whole file to the buffer
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&SourceSize,source);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Read file error [%r]\n",Status);
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
return (EFI_SUCCESS);
}
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
//Compress
preSize = compressBound((UINT32)SourceSize);
Print(L"Source file size : %d\n",SourceSize);
Print(L"Compress Bound Size: %d\n",preSize);
dest = AllocateZeroPool(preSize);
if (dest == NULL) {
Print(L"Allocate dest memory error!\n");
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
//Output
Print(L"Compressing.........\n");
Status=compress(dest,&preSize,source,SourceSize);
if (Status != Z_OK) {
Print(L"Compress error!\n");
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
Print(L"Compressing complete!\n");
Print(L"Compressed size: %d\n",preSize);
//Save compressed result to a file
//Create a new file
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(L"test.lbz",
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ |
EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"CreatFile failed [%r]!\n",Status);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Status = ShellWriteFile(FileHandle,
&preSize,
dest
);
//Close the source file
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
//This program is just a demo for showing how to use zlib.
//Uncompress test
Status=uncompress(source,&SourceSize,dest,preSize);
if (Status != Z_OK) {
Print(L"Decompress error!\n");
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
//Output
Print(L"decompress Size: %d\n",SourceSize);
//Create a new file
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(L"test.efi",
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ |
EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"CreatFile failed [%r]!\n",Status);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Status = ShellWriteFile(FileHandle,
&SourceSize,
source
);
//Close the source file
ShellCloseFile(&FileHandle);
FreePool(dest);
FreePool(source);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
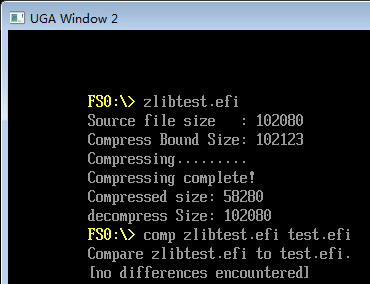
运行结果:
我们直接比较压缩前和解压后的结果,是相同的。
完整的代码下载:
参考:
1. http://www.cppblog.com/woaidongmao/archive/2009/09/07/95495.html zlib用法简单说明
已编译生成了一个liba.lib,我在AppPkg下建立一个自己的应用module:B,B的inf中[LibraryClasses]添加liba,AppPkg.dsc中[LibraryClasses]添加liba|libpath/liba.inf,AppPkg.dec中[LibraryClasses]添加liba|Include/Library/a.h。
发现每次编译B时还是要对liba进行一次编译,而非直接使用已有的liba.lib。如果我删掉了liba的源码,就会导致编译B失败。
请问该怎样避免库liba的二次编译?
我找人问了一下,直接使用 LIB 加入编译是完全没有问题的,需要特别注意的是你的 LIB 和当前编译使用的编译参数必须完全一致,否则会导致错误。