对于BIOS来说,用户能够看到的是非常重要的事情。开机Logo就是这样。自从 Win8.1开始,Windows在进入桌面的时候可以显示用户自定义的Logo,而不是Microsoft自定义的图片,这是很有意思的事情。
最近看了一篇介绍的文章,恍然大悟,原来是BIOS解压自己的Logo在内存中,然后通过ACPI Table将这个Logo传递给Windows,于是开机Logo比以前显示的时间更长更持久。
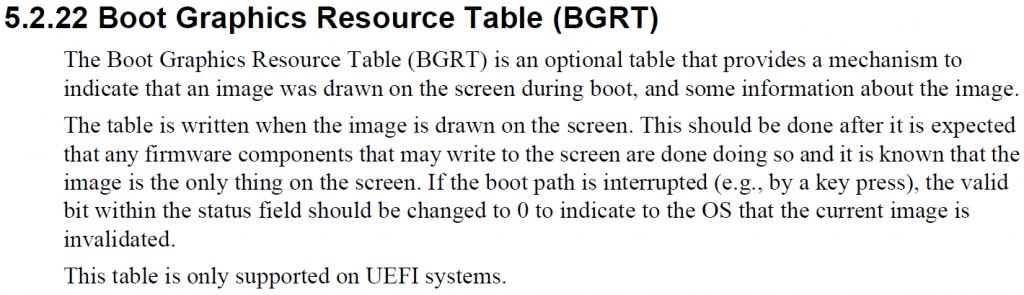
具体的Table就是 Boot Graphics Resource Table。在 ACPI 6.1的5.2.22有专门的介绍。
根据上面的原理,我们可以编写一个UEFI Application,将内存存放的 Logo Dump出来。具体操作:
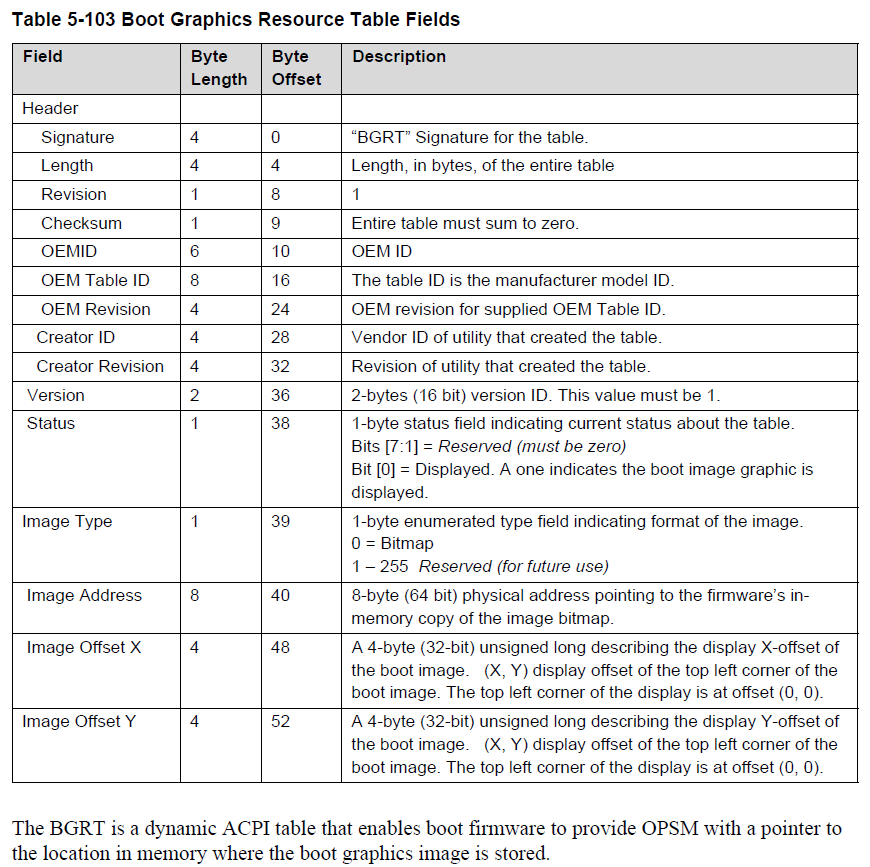
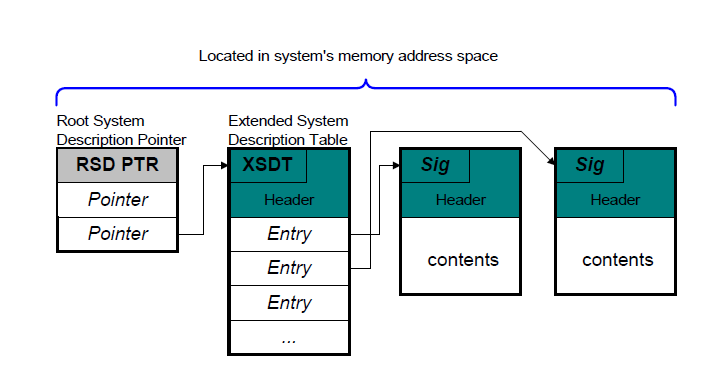
1. 找到RSDP,找到 XSDT
2. 在XSDT中检查每一个Entry,根据 Signature 找到BGRT
3. 解析 BGRT ,得到Logo 图像的地址,这个 Logo一定是 BMP格式的
4. 根据BMP格式能够解析出文件大小,直接Memory Dump即可得到结果
完整的代码:
/** @file
A simple, basic, application showing how the Hello application could be
built using the "Standard C Libraries" from StdLib.
Copyright (c) 2010 - 2011, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.<BR>
This program and the accompanying materials
are licensed and made available under the terms and conditions of the BSD License
which accompanies this distribution. The full text of the license may be found at
http://opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.
THE PROGRAM IS DISTRIBUTED UNDER THE BSD LICENSE ON AN "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
**/
#include <Library/BaseLib.h>
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/PrintLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include "acpi.h"
#include "acpi61.h"
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
#pragma pack(push, 1)
/** BGRT structure */
typedef struct {
EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER header;
UINT16 version;
UINT8 status;
UINT8 image_type;
UINT64 image_address;
UINT32 image_offset_x;
UINT32 image_offset_y;
} ACPI_BGRT;
/** Bitmap file header */
typedef struct {
UINT8 magic_BM[2];
UINT32 file_size;
UINT8 unused_0x06[4];
UINT32 pixel_data_offset;
UINT32 dib_header_size;
UINT32 width;
UINT32 height;
UINT16 planes;
UINT16 bpp;
} BMP;
#pragma pack(pop)
EFI_GUID gEfiAcpi20TableGuid = { 0x8868E871, 0xE4F1, 0x11D3,
{ 0xBC, 0x22, 0x00, 0x80, 0xC7, 0x3C, 0x88, 0x81 }};
EFI_GUID gEfiSimpleFileSystemProtocolGuid ={ 0x964E5B22, 0x6459, 0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x39, 0x00, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69, 0x72, 0x3B }};
EFI_STATUS
SaveToFile(
IN UINT8 *FileData,
IN UINTN FileDataLength)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *FileHandle;
UINTN BufferSize;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *Root;
EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL *SimpleFileSystem;
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(
&gEfiSimpleFileSystemProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID **)&SimpleFileSystem);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Cannot find EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = SimpleFileSystem->OpenVolume(SimpleFileSystem, &Root);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"OpenVolume error \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = Root->Open(
Root,
&FileHandle,
L"BIOSLogo.bmp",
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ |
EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE |
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE,
0);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)){
Print(L"Error Open NULL [%r]\n",Status);
return Status;
}
BufferSize = FileDataLength;
Status = FileHandle->Write(FileHandle, &BufferSize, FileData);
FileHandle->Close(FileHandle);
return Status;
}
/***
Demonstrates basic workings of the main() function by displaying a
welcoming message.
Note that the UEFI command line is composed of 16-bit UCS2 wide characters.
The easiest way to access the command line parameters is to cast Argv as:
wchar_t **wArgv = (wchar_t **)Argv;
@param[in] Argc Number of argument tokens pointed to by Argv.
@param[in] Argv Array of Argc pointers to command line tokens.
@retval 0 The application exited normally.
@retval Other An error occurred.
***/
INTN
EFIAPI
ShellAppMain (
IN UINTN Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER *XSDT;
EFI_ACPI_6_1_ROOT_SYSTEM_DESCRIPTION_POINTER *RSDP;
UINT8 *p;
UINTN Index;
UINT64 *Entry;
ACPI_BGRT *pBGRT;
BMP *pBMP;
//1. Find RSDP
Status=EfiGetSystemConfigurationTable(&gEfiAcpi20TableGuid,(VOID**)&RSDP);
if(EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Can't find Acpi Table\n");
return 0;
}
//2. Find XSDT
Print(L"RSDP address [%X]\n",RSDP);
Print(L"XSDT address [%X]\n",RSDP->XsdtAddress);
XSDT=(EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER*)RSDP->XsdtAddress;
Print(L"XSDT information\n");
p=(UINT8*)XSDT;
//Show some DSDT information
Print(L" Signature [%c%c%c%c]\n",*p,*(p+1),*(p+2),*(p+3));
//3.Find entries
Entry=(UINT64*)&XSDT[1];
Print(L" Entry 0 @[0x%x]\n",Entry);
for (Index=0;Index<(XSDT->Length-sizeof(EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER))/8;Index++) {
//Print(L" Entry [0x%x]",Index);
p=(UINT8*)(*Entry);
//You can show every signature here
//Print(L" [%x][%c%c%c%c]\n",*Entry,*p,*(p+1),*(p+2),*(p+3));
if ((*p=='B')&&(*(p+1)=='G')&&(*(p+2)=='R')&&(*(p+3)=='T')) {
pBGRT=(ACPI_BGRT*)p;
Print(L" Found BGRT @[0x%X]\n",*Entry);
Print(L" Image address @[0x%X]\n",pBGRT->image_address);
//Get BMP address
pBMP=(BMP*)(pBGRT->image_address);
Print(L" [0x%X]\n",pBMP);
Print(L" Image size [0x%X]\n",pBMP->file_size);
Print(L" Data offset [0x%X]\n",pBMP->pixel_data_offset);
Print(L" Header size [0x%X]\n",pBMP->dib_header_size);
Print(L" Width [0x%X]\n",pBMP->width);
Print(L" Height[0x%X]\n",pBMP->height);
Print(L" Planes[0x%X]\n",pBMP->planes);
Print(L" BPP [0x%X]\n",pBMP->bpp);
SaveToFile((UINT8*)pBMP,pBMP->file_size);
Print(L"BIOS logo has been saved to 'BIOSLogo.bmp'\n");
}
Entry++;
}
return 0;
}
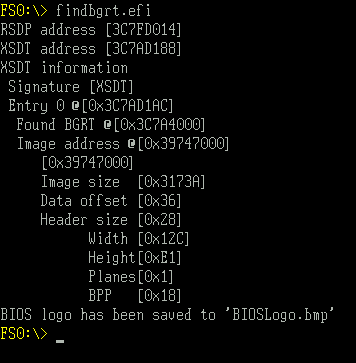
运行结果,测试平台为 Intel Kabylake-R HDK,使用的是 Byo BIOS
(不知道为啥,他家的 Shell分辨率很高, 字体极小,看起来简直要瞎)
取得的 BIOSLogo.bmp 结果如下

完整的代码下载:
X64 Application下载:
特别鸣谢sssky307在之前的文章中给出了EfiGetSystemConfigurationTable函数使得代码能够能够大幅度化简。