前面做过了 GDT 的解析,这次研究一下 IDT。
X86 上有2种中断模式:中断(interrupts)和异常(exceptions )
Interrupt 是异步,通常由 I/O 设备来生成,比如:设置一个定时器在某个时间之后发生;
Exception 是同步的,当处理器执行某个指令之后产生的。对于 Exception 还分为 faults, traps 和 abort. X86处理器对于上面两种处理方式相同,当某一个中断发生之后,CPU会通过 IDT来找到对应的处理函数。处理完成之后将控制权返回产生的位置。
X86处理器有32个预定义中断异常,余下224个可以由用户自己定义。每个IDT有一个定义的数值: vector。当然,我们更常见的是IRQXX 的说法,在X86中还有一套让 IRQ 和 Vector对应起来的机制,未来会继续研究。
和 GDT 非常类似,可以通过 IDTR寄存器获得IDT 长度和它在内存中的位置。
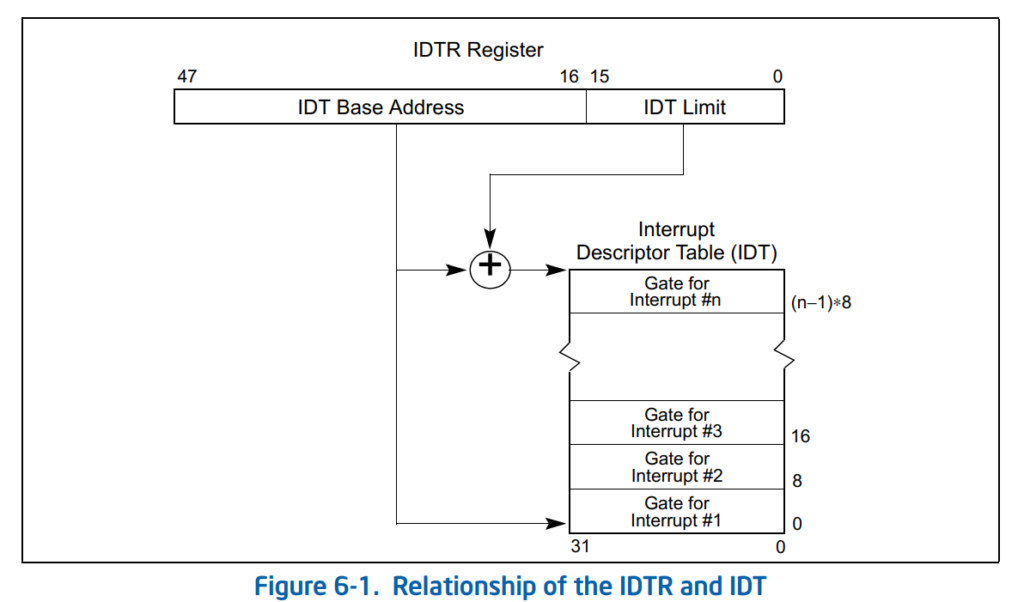
其中的描述符定义在\MdePkg\Include\Library\BaseLib.h 文件中如下:
///
/// Byte packed structure for an x64 Interrupt Gate Descriptor.
///
typedef union {
struct {
UINT32 OffsetLow:16; ///< Offset bits 15..0.
UINT32 Selector:16; ///< Selector.
UINT32 Reserved_0:8; ///< Reserved.
UINT32 GateType:8; ///< Gate Type. See #defines above.
UINT32 OffsetHigh:16; ///< Offset bits 31..16.
UINT32 OffsetUpper:32; ///< Offset bits 63..32.
UINT32 Reserved_1:32; ///< Reserved.
} Bits;
struct {
UINT64 Uint64;
UINT64 Uint64_1;
} Uint128;
} IA32_IDT_GATE_DESCRIPTOR;
GateType可能是下面三种类型之一:
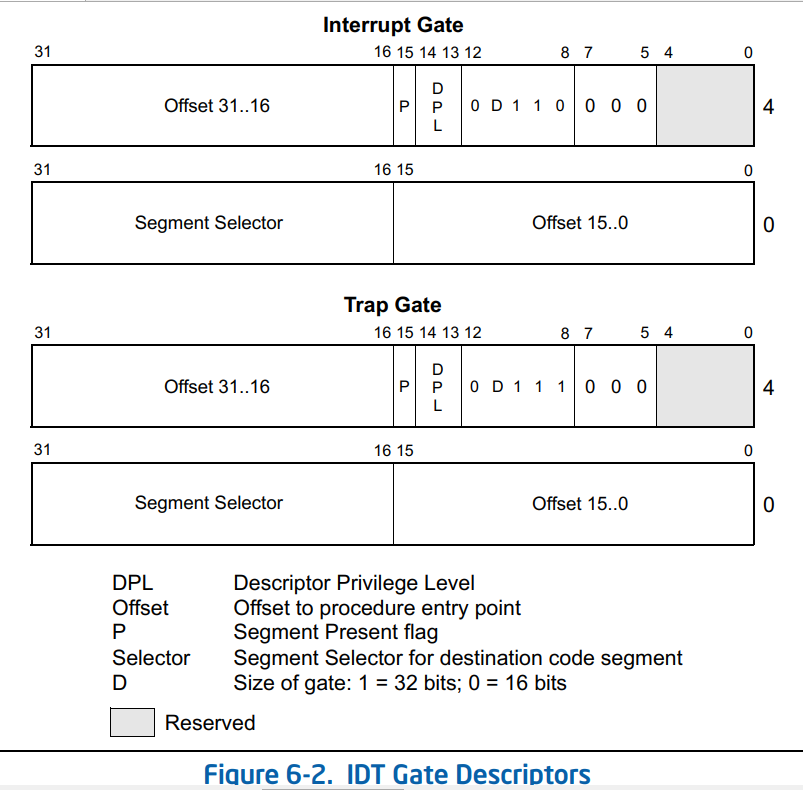
具体类型定义如下:
#define IA32_IDT_GATE_TYPE_TASK 0x85
#define IA32_IDT_GATE_TYPE_INTERRUPT_16 0x86
#define IA32_IDT_GATE_TYPE_TRAP_16 0x87
#define IA32_IDT_GATE_TYPE_INTERRUPT_32 0x8E
#define IA32_IDT_GATE_TYPE_TRAP_32 0x8F
接下来编程解析 Shell 下 IDT完整代码如下:
/** @file
Application for Cryptographic Primitives Validation.
Copyright (c) 2009 - 2016, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.<BR>
This program and the accompanying materials
are licensed and made available under the terms and conditions of the BSD License
which accompanies this distribution. The full text of the license may be found at
http://opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php
THE PROGRAM IS DISTRIBUTED UNDER THE BSD LICENSE ON AN "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
**/
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/BaseLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/DebugLib.h>
#include <Protocol/PciIo.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
GDTMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
IA32_DESCRIPTOR Idtr;
IA32_IDT_GATE_DESCRIPTOR *IdtTable;
UINT16 Index;
UINT16 IdtEntryCount;
ShellSetPageBreakMode(TRUE);
AsmReadIdtr (&Idtr);
IdtEntryCount = (UINT16) ((Idtr.Limit + 1) / sizeof (IA32_IDT_GATE_DESCRIPTOR));
IdtTable = (IA32_IDT_GATE_DESCRIPTOR *) Idtr.Base;
Print(L"IDTR=0x%lX\n",IdtTable);
for (Index = 0; Index < IdtEntryCount; Index++) {
Print(L"No.[%d] ",Index);
Print(L"Selector[%d] ",IdtTable->Bits.Selector);
Print(L"Type [0x%X] ",IdtTable->Bits.GateType);
Print(L"Offset [0x%lX]\n",
(IdtTable->Bits.OffsetUpper<<32)|
(IdtTable->Bits.OffsetHigh <<16)|
(IdtTable->Bits.OffsetLow)
);
IdtTable++;
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
在实体机上运行结果如下:
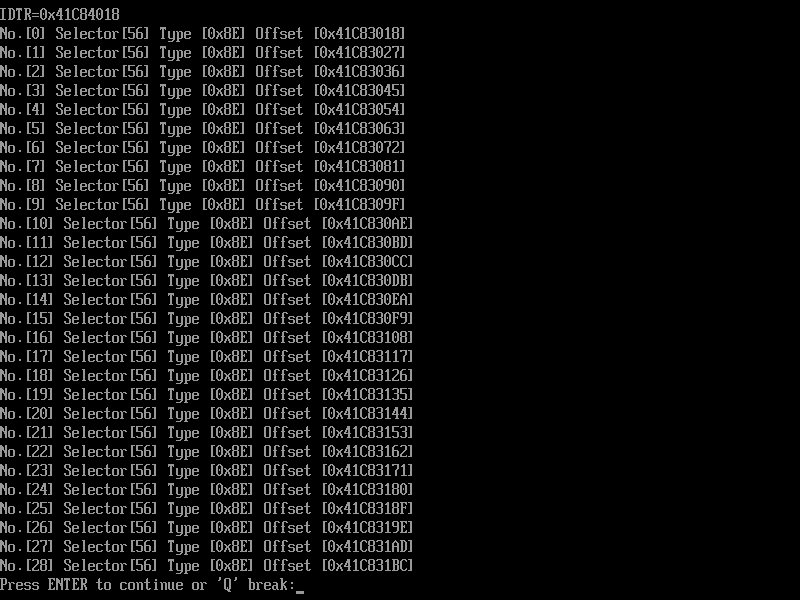
感觉最早实模式下的中断向量表非常类似,只是中断向量表一定是在内存从0开始的位置,而这个可以放置在内存的任何位置。
前面提到处理器有18个预定义的异常:
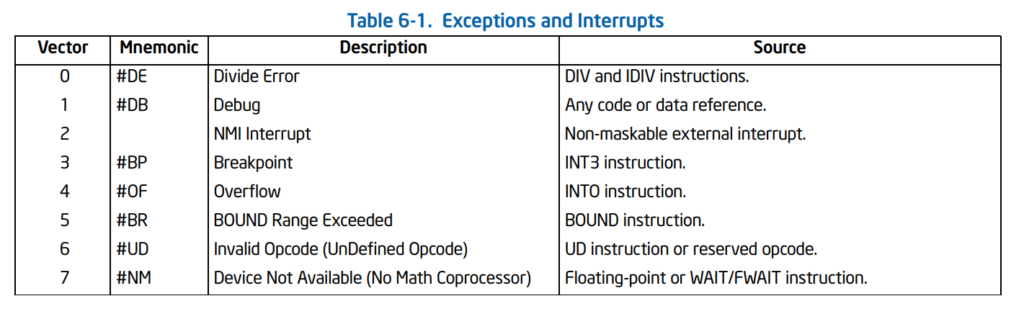
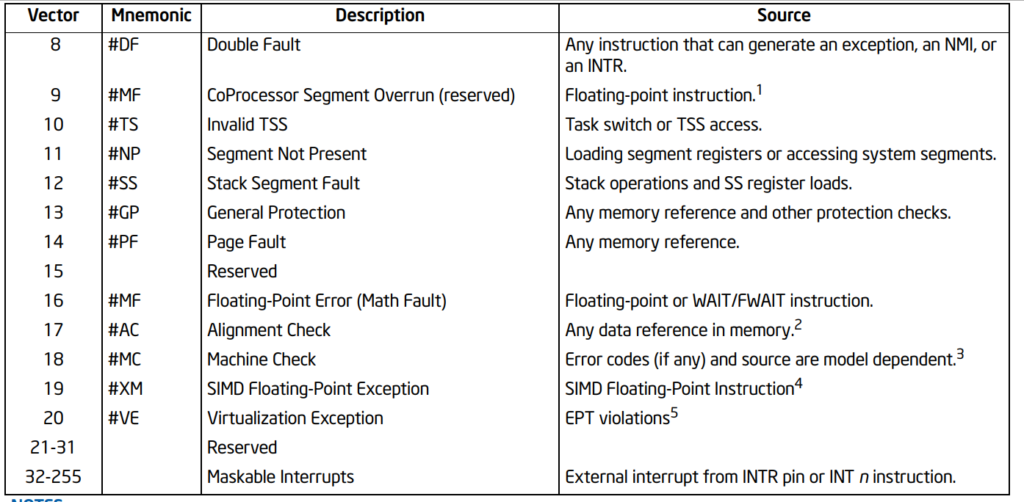
可以看到上面预定义了21个异常,此外还有11个被 Reserved 起来。
接下来我们用DCI来trace #DE(Divide Error)的处理。
首先编写一个产生 #DE 的代码。这个是除数为0错误。主要代码如下:
INTN
EFIAPI
ShellAppMain (
IN UINTN Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
volatile x=0;
//CpuDeadLoop();
for (x = 0; x == 0;);
x=x/x;
return(0);
}
对应的汇编语言如下:
ShellAppMain PROC ; COMDAT
; 21 : {
$LN6:
00000 48 89 54 24 10 mov QWORD PTR [rsp+16], rdx
00005 48 89 4c 24 08 mov QWORD PTR [rsp+8], rcx
0000a 48 83 ec 18 sub rsp, 24
; 22 : volatile x=0;
0000e c7 04 24 00 00
00 00 mov DWORD PTR x$[rsp], 0
; 23 :
; 24 : //CpuDeadLoop();
; 25 : for (x = 0; x == 0;);
00015 c7 04 24 00 00
00 00 mov DWORD PTR x$[rsp], 0
$LN2@ShellAppMa:
0001c 8b 04 24 mov eax, DWORD PTR x$[rsp]
0001f 85 c0 test eax, eax
00021 75 02 jne SHORT $LN3@ShellAppMa
00023 eb f7 jmp SHORT $LN2@ShellAppMa
$LN3@ShellAppMa:
; 26 :
; 27 : x=x/x;
00025 8b 04 24 mov eax, DWORD PTR x$[rsp]
00028 8b 0c 24 mov ecx, DWORD PTR x$[rsp]
0002b 99 cdq
0002c f7 f9 idiv ecx
0002e 89 04 24 mov DWORD PTR x$[rsp], eax
; 28 :
; 29 : return(0);
00031 33 c0 xor eax, eax
; 30 : }
00033 48 83 c4 18 add rsp, 24
00037 c3 ret 0
ShellAppMain ENDP
为了便于观察这里面我们使用 for (x = 0; x == 0;); 等效于 CpuDeadLoop(); 可以让我们在运行的时候停下来。具体的调试操作如下:
1.先用 IDT 确定 Vector 0 的入口是 0x42254018 (这里和上一次查看的位置不同,这是一个安全特性,同样的BIOS每次运行各种 Table 的位置有所不同);
2.运行DETest.efi。运行之后会 Hang 在 Shell下。在调试机上运行 itp.halt() 停止;
3.使用 itp.threads[0].asm(“$”,20)查看停的位置
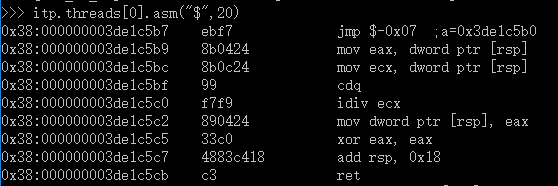
可以看到这里就是前面的 “eb f7 jmp SHORT $LN2@ShellAppMa”,是我们让CPU Dead loop 的代码。
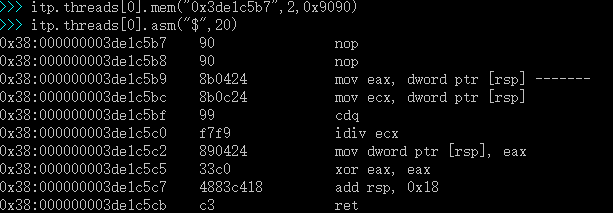
4.使用 itp.threads[0].mem 修改内存代码跳过去。再次查看,可以看到 jmp 已经被修改为 nop
5.使用 itp.threads[0].brnew(“0x42254018”,”exe global”) 加入一个断点,当运行到 vector 0 给出的内存位置时自动停止。这时,使用 itp.go() 即触发了了停在了入口。
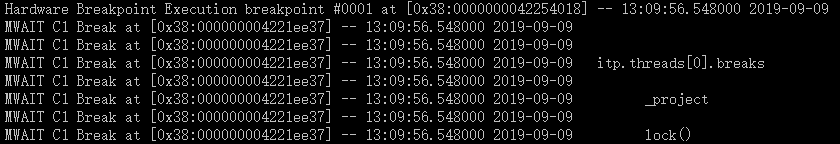
6.使用命令查看当前位置的汇编代码
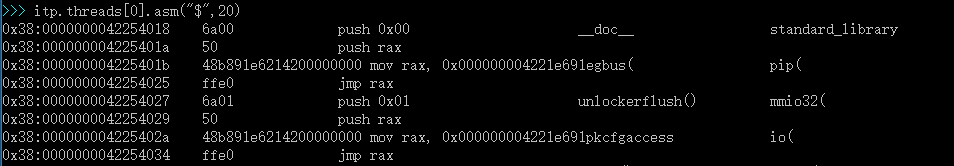
具体代码在 \UefiCpuPkg\Library\CpuExceptionHandlerLib\X64\ExceptionHandlerAsm.nasm 中:
AsmIdtVectorBegin:
%rep 32
db 0x6a ; push #VectorNum
db ($ - AsmIdtVectorBegin) / ((AsmIdtVectorEnd - AsmIdtVectorBegin) / 32) ; VectorNum
push rax
mov rax, strict qword 0 ; mov rax, CommonInterruptEntry 【参考2】
jmp rax
%endrep
AsmIdtVectorEnd:
7.下面可以使用 itp.trheads[0].step 单步执行,最终代码跳入下面的代码段中
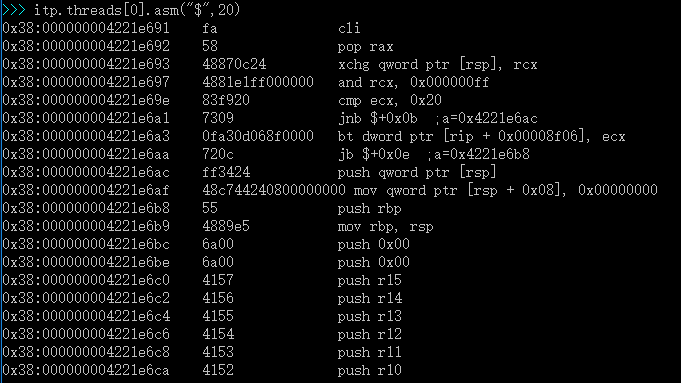
对应的代码还是上面还在提到的 ExceptionHandlerAsm.nasm 文件中:
global ASM_PFX(CommonInterruptEntry)
ASM_PFX(CommonInterruptEntry):
cli
pop rax
;
; All interrupt handlers are invoked through interrupt gates, so
; IF flag automatically cleared at the entry point
;
xchg rcx, [rsp] ; Save rcx into stack and save vector number into rcx
and rcx, 0xFF
cmp ecx, 32 ; Intel reserved vector for exceptions?
jae NoErrorCode
bt [ASM_PFX(mErrorCodeFlag)], ecx
jc HasErrorCode
这里使用的是在vector 0 入口地址下断点拦截的方式,除此之外,我还尝试了使用 step指令一直跟踪 到 idiv 指令的方法,会导致死机,具体原因不清楚。我记得有看过介绍性的文章,说 step 是通过不断在下一条指令之后插入 int 1来实现的,而这里我们同时在调试int0,有可能是因为这样的原因会导致冲突所以无法用 step 跟踪查看到。
参考:
- Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Combined Volumes: 1, 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D, 3A, 3B, 3C, 3D and 4 P2903
- STRICT约束优化 :当汇编时将优化器打开到2或更高级别时,nasm会使用尺寸约束,会给(byte word dword qword tword)尽可能小的尺寸,可以使用关键字STRICT来制约这种优化。
强制一个特定的操作数为原来尺寸:
push strict dword 33
但当优化器关闭时,无论是否有strict,都会产生相同代码。 来自 https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/24926