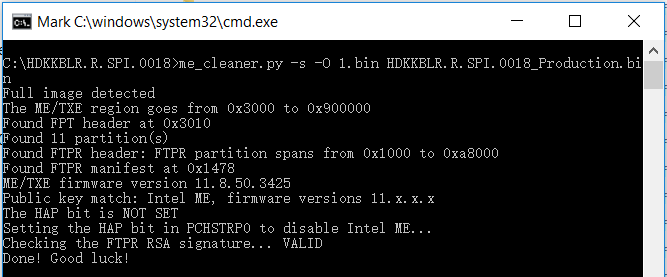
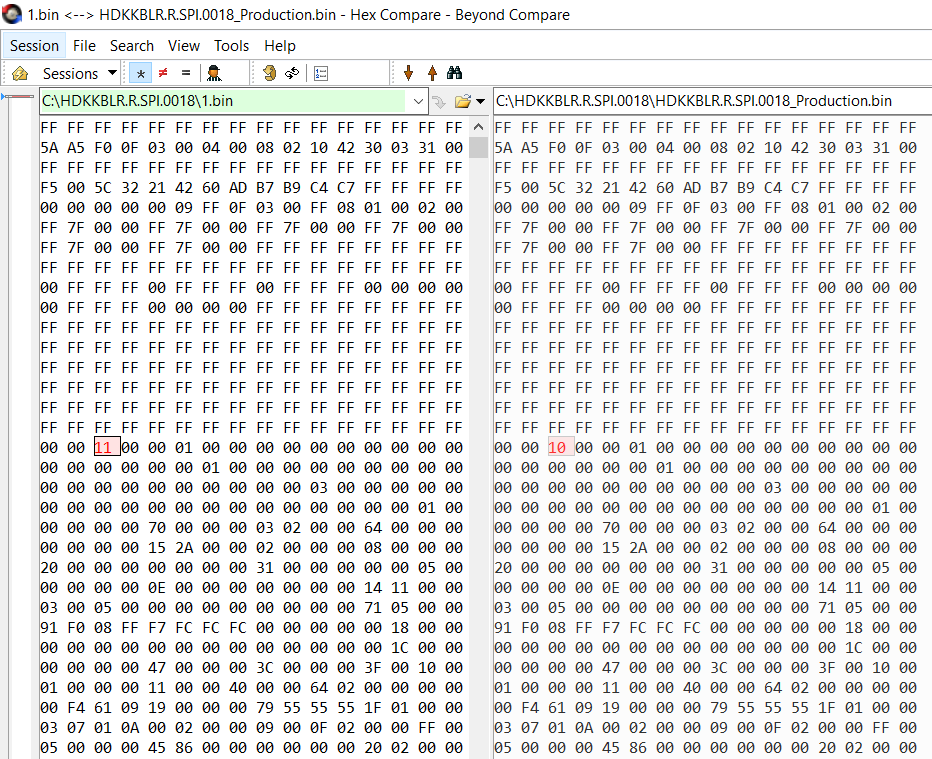
最近在使用 Pets ,研究了一下 Power States, 找到一篇微软的文章【参考1】,有兴趣的朋友可以看一下:
To the user, the system appears to be either on or off. There are no other detectable states. However, the system supports multiple power states that correspond to the power states defined in the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) specification. There are also variations of these states, such as hybrid sleep and fast startup. This topic introduces these states and describes how they relate to each other.
Note System integrators and developers creating drivers or applications with a system service should be particularly careful of driver quality issues, such as memory leaks. While driver quality has always been important, the up time between kernel reboots may be significantly longer than on previous versions of the OS because on user initiated sleeps and shutdowns, the kernel, drivers, and services will be preserved and restored, not re-started.
The following table lists the ACPI power states from highest to lowest power consumption.
| Power state |
ACPI state |
Description |
| Working |
S0 |
The system is fully usable. Hardware components that are not in use can save power by entering a lower power state. |
| Sleep
(Modern Standby) |
S0 low-power idle |
Some SoC systems support a low-power idle state known as Modern Standby. In this state, the system can very quickly switch from a low-power state to high-power state, so that it can respond quickly to hardware and network events. Systems that support Modern Standby do not use S1-S3. |
| Sleep |
S1
S2
S3 |
The system appears to be off. Power consumed in these states (S1-S3) is less than S0 and more than S4; S3 consumes less power than S2, and S2 consumes less power than S1. Systems typically support one of these three states, not all three.
In these states (S1-S3), volatile memory is kept refreshed to maintain the system state. Some components remain powered so the computer can wake from input from the keyboard, LAN, or a USB device.
Hybrid sleep, used on desktops, is where a system uses a hibernation file with S1-S3. The hibernation file saves the system state in case the system loses power while in sleep.
Note SoC systems that support modern standby (the low-power idle state) do not use S1-S3.
|
| Hibernate |
S4 |
The system appears to be off. Power consumption is reduced to the lowest level. The system saves the contents of volatile memory to a hibernation file to preserve system state. Some components remain powered so the computer can wake from input from the keyboard, LAN, or a USB device. The working context can be restored if it is stored on nonvolatile media.
Fast startup is where the user is logged off before the hibernation file is created. This allows for a smaller hibernation file, more appropriate for systems with less storage capabilities. |
| Soft Off |
S5 |
The system appears to be off. This state is comprised of a full shutdown and boot cycle. |
| Mechanical Off |
G3 |
The system is completely off and consumes no power. The system returns to the working state only after a full reboot. |
The SYSTEM_POWER_STATE enumeration defines values that are used to specify system power states.
Working state (S0)
During the working state, the system is awake and running. In simple terms, the device is “on.” Whether the screen is on or off, the device is in a full running state. To conserve energy, especially on battery powered devices, we highly recommend powering-down hardware components when they’re not being used.
Important Power-down hardware components whenever they’re not being used – regardless of the state. Low power consumption is an important consideration for mobile device consumers.
Sleep state (Modern Standby)
In the S0 low-power idle mode of the working state, also referred to as Modern Standby, the system remains partially running. During Modern Standby, the system can stay up-to-date whenever a suitable network is available and also wake when real-time action is required, such as OS maintenance. Modern Standby wakes significantly faster than S1-S3. For more info, see Modern Standby.
Note Modern Standby is only available on some SoC systems. When it’s supported, the system does not support S1-S3.
Sleep state (S1-S3)
The system enters sleep based on a number of criteria, including user or application activity and preferences that the user sets on the Power & sleep page of the Settings app. By default, the system uses the lowest-powered sleep state supported by all enabled wake-up devices. For more information about how the system determines when to enter sleep, see System Sleep Criteria.
Before the system enters sleep, it determines the appropriate sleep state, notifies applications and drivers of the pending transition, and then transitions the system to the sleep state. In the case of a critical transition, such as when the critical battery threshold is reached, the system does not notify applications and drivers. Applications need to be prepared for this and take the appropriate action when the system returns to the working state.
In these states (S1-S3), volatile memory is kept refreshed to maintain the system state. Some components remain powered so the computer can wake from input from the keyboard, LAN, or a USB device.
The system also wakes from sleep in response to user activity or a wake-up event defined by an application. For more information, see System Wake-up Events. The amount of time it takes the system to wake depends on the sleep state it is waking from. The system takes more time to wake from a lower-powered state (S3) than from a higher-powered state (S1) because of the extra work the hardware may have to do (stabilize the power supply, reinitialize the processor, and so forth).
Caution When calling
SetThreadExecutionState, the
ES_AWAYMODE_REQUIRED value should be used only when absolutely necessary by media applications that require the system to perform background tasks such as recording television content or streaming media to other devices while the system appears to be sleeping. Applications that do not require critical background processing or that run on portable computers should not enable away mode because it prevents the system from conserving power by entering true sleep.
Hybrid sleep (S1-S3 + hibernation file)
Hybrid sleep is a special state that’s a combination of the sleep and hibernation states, it’s when a system uses a hibernation file with S1-S3. It’s only available on some systems. When enabled, the system writes a hibernation file but enters a higher-powered sleep state. If power is lost while the system is sleeping, the system wakes from hibernation, which takes longer but restores the user’s system state.
Hibernate state (S4)
Windows uses hibernation to provide a fast startup experience. When available, it’s also used on mobile devices to extend the usable battery life of a system by giving a mechanism to save all of the user’s state prior to shutting down the system. In a Hibernate transition, all the contents of memory are written to a file on the primary system drive, the hibernation file. This preserves the state of the operating system, applications, and devices. In the case where the combined memory footprint consumes all of physical memory, the hibernation file must be large enough to ensure there will be space to save all the contents of physical memory. Since data is written to non-volatile storage, DRAM does not need to maintain self-refresh and can be powered off, which means power consumption of hibernation is very low, almost the same as power off.
During a full shutdown and boot (S5), the entire user session is torn down and restarted on the next boot. In contrast, during a hibernation (S4), the user session is closed and the user state is saved.
Fast startup (reduced hibernation file)
Fast startup is a type of shutdown that uses a hibernation file to speed up the subsequent boot. During this type of shutdown, the user is logged off before the hibernation file is created. Fast startup allows for a smaller hibernation file, more appropriate for systems with less storage capabilities. For more info, see Hibernation file types.
When using fast startup, the system appears to the user as though a full shutdown (S5) has occurred, even though the system has actually gone through S4. This includes how the system responds to device wake alarms.
Fast startup logs off user sessions, but the contents of kernel (session 0) are written to hard disk. This enables faster boot.
To programmatically initiate a fast startup-style shutdown, call the InitiateShutdown function with the SHUTDOWN_HYBRID flag or the ExitWindowsEx function with the EWX_HYBRID_SHUTDOWN flag.
Note Starting in Windows 8, fast startup is the default transition when a system shutdown is requested. A full shutdown (S5) occurs when a system restart is requested (or an application calls a shutdown API).
Entering hibernation
When a hibernate request is made, the following steps occur as the system enters hibernation:
- Apps and services are notified
- Drivers are notified
- User and system state is saved to disk in a compressed format
- Firmware is notified
Note Starting in Windows 8, all cores on the system are used to compress the data in memory and write it to disk.
To programmatically initiate a hibernate transition, call the SetSuspendState function.
Resuming from hibernation
When a system resumes from hibernation.
When a system is powered on, the following steps occur as the system resumes from hibernation.
- System POST
- System memory is decompressed and restored from the hibernation file
- Device initialization
- Drivers are restored to the state they were in prior to hibernation
- Services are restored to the state they were in prior to hibernation
- System becomes available for login
A resume from hibernation starts with a system POST that is similar to an S5 shutdown. The OS boot manager determines that a resume from hibernation is required by detecting a valid hibernation file. Then it directs the system to resume, restoring the contents of memory and all architectural registers. In the case of a resume from hibernation, the contents of the system memory are read back in from the disk, decompressed, and restored, putting the system in the exact state it was in when it was hibernated. After memory is restored, the devices are re-started, the machine returns to a running state, ready for login.
Note During a resume from hibernation, drivers and services are notified, but are not restarted. They are only restored to the state they were in prior to hibernation.
Hibernation file types
Hibernation files are used for hybrid sleep, fast startup, and standard hibernation (described earlier). There are two types, differentiated by size, a full and reduced size hibernation file. Only fast startup can use a reduced hibernation file.
| Hibernation file type |
Default size |
Supports… |
| Full |
40% of physical memory |
hibernate, hybrid sleep, fast startup |
| Reduced |
20% of physical memory |
fast startup |
To verify or change the type of hibernation file used, run the powercfg.exe utility. The following examples demonstrate how. For more information, run powercfg /? hibernate.
| Example |
Description |
powercfg /a |
Verify the hibernation file type. When a full hibernation file is used, the results state that hibernation is an available option. When a reduced hibernation file is used, the results will say hibernation is not supported. If the system has no hibernation file at all, the results will say hibernation has not been enabled. |
powercfg /h /type full |
Change the hibernation file type to full. This is not recommended on systems with less than 32GB of storage. |
powercfg /h /type reduced |
Change the hibernation file type to reduced. If the command returns “the parameter is incorrect”, see the following example. |
powercfg /h /size 0
powercfg /h /type reduced
|
Retry changing the hibernation file type to reduced. If the hibernation file is set to a custom size greater than 40%, you must first set the size of the file to zero. Then retry the reduced configuration. |
Soft Off state (S5)
The soft off state is when the system fully shuts down without a hibernation file. Soft off is also known as a “full shutdown.” During a full shutdown and boot, the entire user session is torn down and restarted on the next boot. Consequently, a boot/startup from this state takes significantly longer than S1-S4. A full shutdown (S5) occurs when a system restart is requested (or an application calls a shutdown API).
Mechanical Off state (G3)
In this state, the system is completely off and consumes no power. The system returns to the working state only after a full reboot.
Wake-on-LAN behavior
The wake-on-LAN (WOL) feature wakes the computer from a low power state when a network adapter detects a WOL event (typically, a specially constructed Ethernet packet).
WOL is supported from sleep (S3) or hibernate (S4). It is not supported from fast startup or soft off (S5) shutdown states. NICs are not armed for wake in these states because users do not expect their systems to wake up on their own.
Note WOL is not officially supported from soft off (S5). However, the BIOS on some systems may support arming NICs for wake, even though Windows is not involved in the process.
参考:
1.https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa373229(v=vs.85).aspx