继续介绍 EFI 下面的常用字符串函数
\MdePkg\Include\Library\BaseLib.h
1.StrStr 函数作用:在字符串中查找另外的字符串
/**
Returns the first occurrence of a Null-terminated Unicode sub-string
in a Null-terminated Unicode string.
This function scans the contents of the Null-terminated Unicode string
specified by String and returns the first occurrence of SearchString.
If SearchString is not found in String, then NULL is returned. If
the length of SearchString is zero, then String is returned.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If SearchString is NULL, then ASSERT().
If SearchString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and SearchString
or String contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode
characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@param SearchString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string to search for.
@retval NULL If the SearchString does not appear in String.
@return others If there is a match.
**/
CHAR16 *
EFIAPI
StrStr (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String,
IN CONST CHAR16 *SearchString
);
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 *s2=L"COM";
CHAR16 *s3=L"com";
CHAR16 s4[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
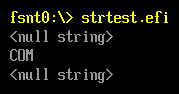
Result=StrStr(s4,s1);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
Result=StrStr(s4,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
Result=StrStr(s4,s3);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
2.StrDecimalToUintn 作用:把字符串转换为数字
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode decimal string to a value of
type UINTN.
This function returns a value of type UINTN by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a decimal number. The format
of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces] [decimal digits].
The valid decimal digit character is in the range [0-9]. The
function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or
tab characters, before [decimal digits]. The running zero in the
beginning of [decimal digits] will be ignored. Then, the function
stops at the first character that is a not a valid decimal character
or a Null-terminator, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then 0 is returned.
If String has no pad spaces or valid decimal digits,
then 0 is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according
to the range defined by UINTN, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains
more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including
the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
StrDecimalToUintn (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
实例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100";
CHAR16 *s2=L"77F";
CHAR16 *s3=L"77f";
CHAR16 *s4=L"77z";
UINTN Result;
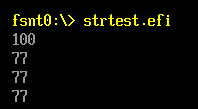
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s3);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s4);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
具体实现的代码可以在下面找到:
\MdePkg\Library\BaseLib\String.c
while (InternalIsDecimalDigitCharacter (*String)) {
//
// If the number represented by String overflows according
// to the range defined by UINTN, then ASSERT().
//
ASSERT (Result <= ((((UINTN) ~0) - (*String - L'0')) / 10));
Result = Result * 10 + (*String - L'0');
String++;
}
/**
Check if a Unicode character is a decimal character.
This internal function checks if a Unicode character is a
decimal character. The valid decimal character is from
L'0' to L'9'.
@param Char The character to check against.
@retval TRUE If the Char is a decmial character.
@retval FALSE If the Char is not a decmial character.
**/
BOOLEAN
EFIAPI
InternalIsDecimalDigitCharacter (
IN CHAR16 Char
)
{
return (BOOLEAN) (Char >= L'0' && Char <= L'9');
}
从上面可以看到:最后一个字符会被忽略,所以你写 77f 或者 77z都能得到同样的结果
再测试一下具体取值的大小
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100000000";
CHAR16 *s2=L"987654321Z";
CHAR16 *s3=L"2147483647"; // == 7FFFFFFF
CHAR16 *s4=L"2147483648"; // == 80000000
CHAR16 *s5=L"-1";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s3);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s4);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s5);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
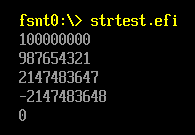
3.StrDecimalToUint64 函数用途:将字符串转换为数值,和前面的函数相比,可用范围更大
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode decimal string to a value of
type UINT64.
This function returns a value of type UINT64 by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a decimal number. The format
of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces] [decimal digits].
The valid decimal digit character is in the range [0-9]. The
function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or
tab characters, before [decimal digits]. The running zero in the
beginning of [decimal digits] will be ignored. Then, the function
stops at the first character that is a not a valid decimal character
or a Null-terminator, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then 0 is returned.
If String has no pad spaces or valid decimal digits,
then 0 is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according
to the range defined by UINT64, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains
more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including
the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINT64
EFIAPI
StrDecimalToUint64 (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
实例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100000000";
CHAR16 *s2=L"9876543210000Z";
CHAR16 *s3=L"2147483647"; // == 7FFFFFFF
CHAR16 *s4=L"2147483648"; // == 80000000
CHAR16 *s5=L"-1";
UINT64 Result;
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s1);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s2);
Print(L"\n%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s2);
Print(L"%LX\n\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s3);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s4);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s5);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
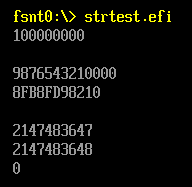
4.StrHexToUintn 函数作用:将字符串按照十六进制处理转换为数值
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode hexadecimal string to a value of type UINTN.
This function returns a value of type UINTN by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a hexadecimal number.
The format of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces][zeros][x][hexadecimal digits].
The valid hexadecimal digit character is in the range [0-9], [a-f] and [A-F].
The prefix "0x" is optional. Both "x" and "X" is allowed in "0x" prefix.
If "x" appears in the input string, it must be prefixed with at least one 0.
The function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or tab characters,
before [zeros], [x] or [hexadecimal digit]. The running zero before [x] or
[hexadecimal digit] will be ignored. Then, the decoding starts after [x] or the
first valid hexadecimal digit. Then, the function stops at the first character
that is a not a valid hexadecimal character or NULL, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then zero is returned.
If String has no leading pad spaces, leading zeros or valid hexadecimal digits,
then zero is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according to the range defined by
UINTN, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator,
then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
StrHexToUintn (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"0x234";
CHAR16 *s2=L"1024";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrHexToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrHexToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
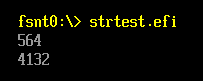
5.StrHexToUint64 函数作用:把字符串按照十六进制处理转化为数值
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode hexadecimal string to a value of type UINT64.
This function returns a value of type UINT64 by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a hexadecimal number.
The format of the input Unicode string String is
[spaces][zeros][x][hexadecimal digits].
The valid hexadecimal digit character is in the range [0-9], [a-f] and [A-F].
The prefix "0x" is optional. Both "x" and "X" is allowed in "0x" prefix.
If "x" appears in the input string, it must be prefixed with at least one 0.
The function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or tab characters,
before [zeros], [x] or [hexadecimal digit]. The running zero before [x] or
[hexadecimal digit] will be ignored. Then, the decoding starts after [x] or the
first valid hexadecimal digit. Then, the function stops at the first character that is
a not a valid hexadecimal character or NULL, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then zero is returned.
If String has no leading pad spaces, leading zeros or valid hexadecimal digits,
then zero is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according to the range defined by
UINT64, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator,
then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINT64
EFIAPI
StrHexToUint64 (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"0x234";
CHAR16 *s2=L"0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF";
UINT64 Result;
Result=StrHexToUint64(s1);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
Result=StrHexToUint64(s2);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
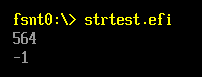
6.UnicodeStrToAsciiStr 函数作用:将Unicode的字符串转换为 ASCII的字符串
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode string to a Null-terminated
ASCII string and returns the ASCII string.
This function converts the content of the Unicode string Source
to the ASCII string Destination by copying the lower 8 bits of
each Unicode character. It returns Destination.
The caller is responsible to make sure Destination points to a buffer with size
equal or greater than ((StrLen (Source) + 1) * sizeof (CHAR8)) in bytes.
If any Unicode characters in Source contain non-zero value in
the upper 8 bits, then ASSERT().
If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Source is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains
more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including
the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more
than PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength Unicode characters not including the
Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated ASCII string.
@return Destination.
**/
CHAR8 *
EFIAPI
UnicodeStrToAsciiStr (
IN CONST CHAR16 *Source,
OUT CHAR8 *Destination
);
示例代码
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
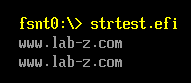
CHAR16 *s1=L"www.lab-z.com";
CHAR8 *s2=" ";
CHAR8 *Result;
Result=UnicodeStrToAsciiStr(s1,s2);
Print(L"%a\n",s2);
Print(L"%a\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
7.AsciiStrToUnicodeStr 函数作用:将 ASCII的字符串转换为 Unicode的字符串
/**
Convert one Null-terminated ASCII string to a Null-terminated
Unicode string and returns the Unicode string.
This function converts the contents of the ASCII string Source to the Unicode
string Destination, and returns Destination. The function terminates the
Unicode string Destination by appending a Null-terminator character at the end.
The caller is responsible to make sure Destination points to a buffer with size
equal or greater than ((AsciiStrLen (Source) + 1) * sizeof (CHAR16)) in bytes.
If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If Source is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than
PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength ASCII characters not including the Null-terminator,
then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength ASCII characters not including the
Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated ASCII string.
@param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@return Destination.
**/
CHAR16 *
EFIAPI
AsciiStrToUnicodeStr (
IN CONST CHAR8 *Source,
OUT CHAR16 *Destination
);
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR8 *s1="www.lab-z.com";
CHAR16 *s2=L" ";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=AsciiStrToUnicodeStr (s1,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",s2);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果和前面的相同。