我对手表有着深厚的感情,每当人生遇到坎坷时,或者愤怒不已的时候,我都会想象和安慰自己“我去年买了块表”。刚有taobao的时候,我买了一块卡西欧的太阳能手表,时至今日我还记得价格是 258元。十多年过去了,这块表的卖家已经消失,我从来没有给他更换过电池,这块手表依然行走完好。

古人云“穷玩车,富玩表”。为了体验一下富人的感觉,最近入手了一块麦步智能手表。对于这块手表,最重要的是可以写程序。于是我就尝试给他编写程序,听上去又在重复“屌丝玩电脑”。

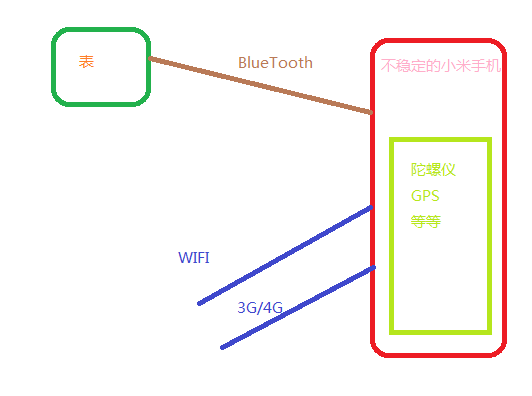
首先通读API,了解这个手表的原理。简单的说,这块手表通过蓝牙连接,从而实现WIFI通讯。
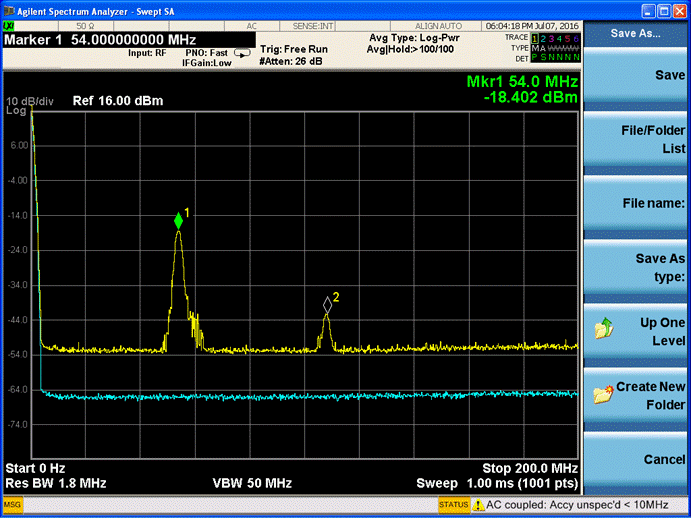
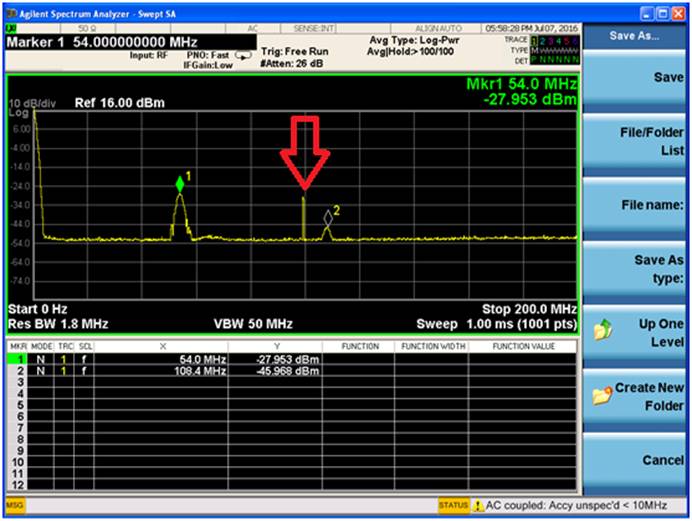
目标是编写一个获取当前比特币行情。huobi 网提供了行情API, http://api.huobi.com/staticmarket/ticker_btc_json.js 可以显示实时行情。例如:一次返回数据如下
{“time”:”1467817886″,”ticker”:{“open”:4479,”vol”:604962.2546,”symbol”:”btccny”,”last”:4522.79,”buy”:4522.79,”sell”:4523.03,”high”:4612,”low”:4467.64} }。 其中的 last 就是当前的价格。
配合麦步手表提供的显示股票行情的代码,编写自己的程序如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "maibu_sdk.h"
#include "maibu_res.h"
/*Web通讯ID*/
static uint32_t g_comm_id_web = 0;
/*Web request地址*/
#define DATA_WEB "http://api.huobi.com/staticmarket/ticker_btc_json.js"
/* 时间项 */
#define DATE_TEXT_POS_X 2
#define DATE_TEXT_POS_Y 6
#define DATE_TEXT_SIZE_W 70
#define DATE_TEXT_SIZE_H 14
#define TIME_TEXT_POS_X 90
#define TIME_TEXT_POS_Y 6
#define TIME_TEXT_SIZE_W 36
#define TIME_TEXT_SIZE_H 14
static const char weekday[7][11] =
{
{"周日"},
{"周一"},
{"周二"},
{"周三"},
{"周四"},
{"周五"},
{"周六"}
};
/*窗口ID*/
static int32_t g_window_id = -1;
//数据提示
static int32_t g_layer_id_text = -1;
//数据内容
static int32_t g_layer_id_data = -1;
//时间的句柄
static int32_t g_layer_id_time = -1;
//日期的句柄
static int32_t g_layer_id_date = -1;
//整个窗体句柄
static P_Window h_window;
void data_request_web()
{
/*拼接url请求地址, 注意url的缓存大小*/
char url[200] = "";
sprintf(url, "%s", DATA_WEB);
/*
拼接过滤参数,即只接受和过滤参数匹配的返回值
个人感觉这里的过滤可能是让手机做的,就是这里通知手机:json中的数据除了我制定的其他都过滤掉
*/
/*发送一次*/
g_comm_id_web = maibu_comm_request_web(url, "last", 0);
}
void add_text_layer(P_Window p_window, int32_t *p_layer_id, char *p_str, GRect *p_frame, enum GAlign align, int8_t font, enum GColor color)
{
LayerText text_cfg = {p_str, *p_frame, align, font, 0};
P_Layer layer = app_layer_create_text(&text_cfg);
app_layer_set_bg_color(layer, color);
P_Layer old_layer = app_window_get_layer_by_id(p_window, *p_layer_id);
if(old_layer)
{
*p_layer_id = app_window_replace_layer(p_window, old_layer, layer);
}
else
{
*p_layer_id = app_window_add_layer(p_window, layer);
}
}
static void add_time_bar(P_Window p_window)
{
/* 添加时间图层 */
uint8_t text_buf[40];
struct date_time t;
app_service_get_datetime(&t);
memset(text_buf, 0, sizeof(text_buf));
sprintf((char *)text_buf, "%s", (char *)&weekday[t.wday][0]);
sprintf(&text_buf[6], "%02d-%02d", t.mon, t.mday);
GRect frame;
frame.origin.x = DATE_TEXT_POS_X;
frame.origin.y = DATE_TEXT_POS_Y;
frame.size.h = DATE_TEXT_SIZE_H;
frame.size.w = DATE_TEXT_SIZE_W;
add_text_layer(p_window, &g_layer_id_date, (char*)text_buf, &frame, GAlignLeft, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
frame.origin.x = TIME_TEXT_POS_X;
frame.origin.y = TIME_TEXT_POS_Y;
frame.size.h = TIME_TEXT_SIZE_H;
frame.size.w = TIME_TEXT_SIZE_W;
memset(text_buf, 0, sizeof(text_buf));
sprintf(text_buf, "%02d:%02d", t.hour, t.min);
add_text_layer(p_window, &g_layer_id_time, (char*)text_buf, &frame, GAlignLeft, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
}
P_Window init_btc_window()
{
static P_Window p_window;
p_window = app_window_create();
if (NULL == p_window)
{
return NULL;
}
/* 添加表盘背景 */
GRect frame = {{0, 0}, {128, 128}};
GBitmap bitmap;
res_get_user_bitmap(BMP_STOCK_BG, &bitmap);
LayerBitmap layer_bitmap = {bitmap, frame, GAlignCenter};
P_Layer layer = app_layer_create_bitmap(&layer_bitmap);
app_window_add_layer(p_window, layer);
/* 添加时间栏 */
add_time_bar(p_window);
/*加入你的代码 begin*/
/*添加数据提示信息*/
GRect frame_main = {{0, 30}, {16, 128}};
add_text_layer(p_window, &g_layer_id_text, "BTC", &frame_main, GAlignCenter, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
/*添加数据*/
GRect frame_data = {{0, 60}, {16, 128}};
add_text_layer(p_window, &g_layer_id_data, "waiting", &frame_data, GAlignCenter, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
return p_window;
}
void data_comm_result_callback(enum ECommResult result, uint32_t comm_id, void *context)
{
/*如果上一次请求WEB通讯失败,并且通讯ID相同,则重新发送*/
if ((result == ECommResultFail) && (comm_id == g_comm_id_web))
{
data_request_web();
}
}
static void web_recv_callback(const uint8_t *buff, uint16_t size)
{
char stock_gid[10];
char i;
maibu_get_json_str(buff, "last", stock_gid, 10);
for (i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if (stock_gid[i]=='}')
{
stock_gid[i]=0;
}
}
/*添加数据*/
GRect frame_data = {{0, 60}, {16, 128}};
add_text_layer(h_window, &g_layer_id_data, stock_gid, &frame_data, GAlignCenter, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
app_window_update(h_window);
}
static void watch_time_change_callback(enum SysEventType type, void *context)
{
/*时间更改,分变化*/
if (type == SysEventTypeTimeChange)
{
uint8_t text_buf[40];
struct date_time t;
app_service_get_datetime(&t);
memset(text_buf, 0, sizeof(text_buf));
sprintf((char *)text_buf, "%s", (char *)&weekday[t.wday][0]);
sprintf(&text_buf[6], "%02d-%02d", t.mon, t.mday);
GRect frame;
frame.origin.x = DATE_TEXT_POS_X;
frame.origin.y = DATE_TEXT_POS_Y;
frame.size.h = DATE_TEXT_SIZE_H;
frame.size.w = DATE_TEXT_SIZE_W;
add_text_layer(h_window, &g_layer_id_date, (char*)text_buf, &frame, GAlignLeft, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
frame.origin.x = TIME_TEXT_POS_X;
frame.origin.y = TIME_TEXT_POS_Y;
frame.size.h = TIME_TEXT_SIZE_H;
frame.size.w = TIME_TEXT_SIZE_W;
memset(text_buf, 0, sizeof(text_buf));
sprintf(text_buf, "%02d:%02d", t.hour, t.min);
add_text_layer(h_window, &g_layer_id_time, (char*)text_buf, &frame, GAlignLeft, U_ASCII_ARIAL_14, GColorWhite);
app_window_update(h_window);
}
}
static void data_timer_callback(date_time_t tick_time, uint32_t millis, void *context)
{
data_request_web();
}
int main()
{
/*创建消息列表窗口*/
h_window = init_btc_window();
//订阅时间改变事件
maibu_service_sys_event_subscribe(watch_time_change_callback);
/*放入窗口栈显示*/
g_window_id = app_window_stack_push(h_window);
data_request_web();
/*注册通讯结果回调*/
maibu_comm_register_result_callback(data_comm_result_callback);
//注册网络请求回调函数
maibu_comm_register_web_callback(web_recv_callback);
//聚合数据源每隔10s更新数据
app_window_timer_subscribe(h_window, 10000, data_timer_callback, (void *)h_window);
return 0;
}
编译之后上传到手表上就OK了。
看起来工作正常,美中不足就是屏幕有点小,如果能像美国队长那块一样大就完美了。

这块手表的一大重要特性就是采用电纸屏幕,就是那种 Kindle 的屏幕材质,不改变内容无需耗电,这样待机可以很长时间(标称21天)。说道这里,我想起来一个很老的苏联笑话:
有一个人在机场等六点的飞机,可是他忘记了带手表,于是他想找
个人问问。这时,他看见一个人提着两个巨大的手提箱吃力的走过来,手腕上戴
着一块异常漂亮的一看就知道是高科技产品的手表。
“请问,几点了?”他问道。
“哪个国家的时间?”那人反问。
“哦?”他的好奇心来了,“你都知道哪些国家的时间呢?”
“所有的国家,”那人回答道。
“哇!那可真是一块好手表呀!”
“还不止这些呢,这块表还有GPS卫星系统,可以随时收发电子邮件、
传真,这个彩色的屏幕可以收看NTSC制式的电视节目!”那人给他
演示,果真如此!
“哦!太棒了,我真想拥有一块这样的手表,您……您可以把它卖给我吗?”
“说实话,我已经烦透了这块表了,这样吧,900美元,如何?”
他马上掏出支票簿,写了900美元给那人,“成交!”
“好的,现在,它是你的了。”那人如释重负,把手表交给他,“这个是你
的手表”,然后指着地上的两个大箱子说,“这两个是电池!”
无数的科学家和工程师在不断的努力改造着我们的生活。