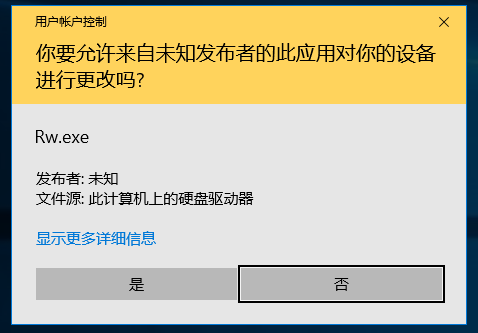
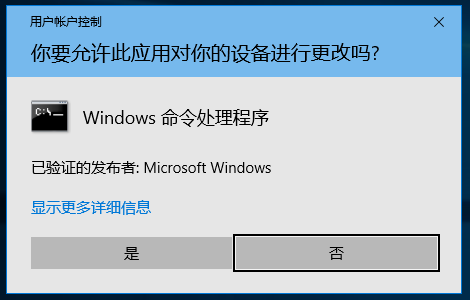
前面介绍过 RSA 算法,因为它能够实现非对称的加密所以还可以用来进行数字签名。比如:我在网站上公布了自己的公钥,然后每次发送消息的时候会附上使用私钥对这个消息签名结果。这样,别人就无法冒充我发布消息。这次展示使用 OpenSSL 实现UEFI下面的签名和验证。
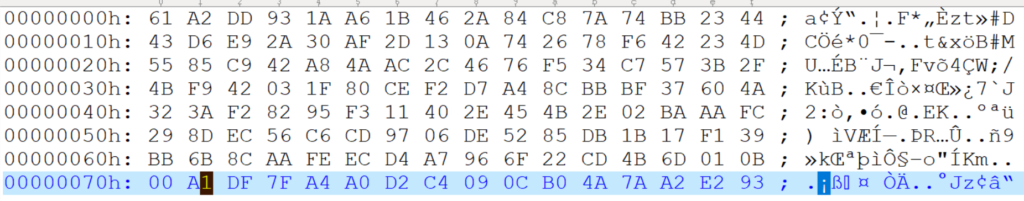
第三步,有了上面的密钥包(其实是其中的私钥)即可对消息进行签名。例如,我们使用“This message from
lab-z.com”作为被签名的字符串,将这一段存放在 string.txt 文件中。然后对其签名:
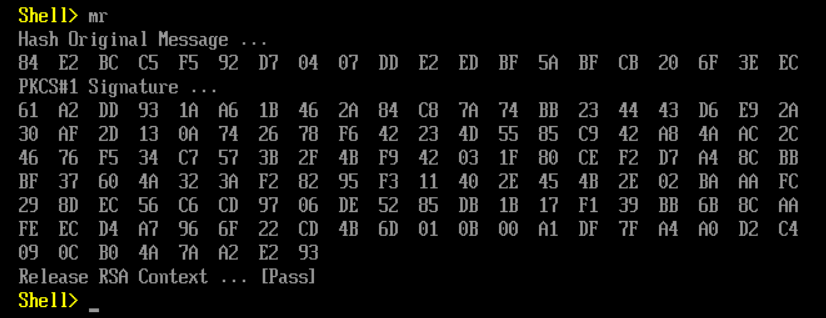
上面就是使用 OpenSSL.exe 来完成 RSA 签名校验的过程。接下来介绍使用 UEFI 完成这些操作。代码改编自 UDK2017 中的 CryptoPkg 下面 Application 的例子(但是从 UDK2018开始这部分代码被移除了)
/** @file
Application for Cryptographic Primitives Validation.
Copyright (c) 2009 - 2016, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.<BR>
This program and the accompanying materials
are licensed and made available under the terms and conditions of the BSD License
which accompanies this distribution. The full text of the license may be found at
http://opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php
THE PROGRAM IS DISTRIBUTED UNDER THE BSD LICENSE ON AN "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
**/
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/BaseLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/UefiApplicationEntryPoint.h>
#include <Library/DebugLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseCryptLib.h>
#define RSA_MODULUS_LENGTH 1024
//
// Public Modulus of RSA Key
//
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST UINT8 RsaN[] = {
0xd3,0x88,0x4c,0x6e,0xf0,0x5e,0x97,0xfd,0x55,0x8f,0xa8,0xf9,0xb3,0x05,
0xcd,0xe6,0xa9,0x47,0xcc,0xbc,0xe0,0x74,0xc6,0xd6,0x93,0x64,0x04,0x1b,0x49,
0xfc,0xad,0xfa,0xea,0xb1,0xbb,0xb1,0x8d,0x69,0x2b,0x46,0xa5,0xd2,0x6f,0x0a,
0xe3,0x85,0x2f,0xbf,0x85,0x15,0x74,0x85,0x2c,0x97,0xe6,0x66,0xc8,0x98,0x45,
0xa8,0x8e,0x4a,0x93,0xc3,0x0e,0xe4,0x0b,0x06,0x41,0xb4,0x9b,0xf0,0x01,0x93,
0xca,0x4b,0xb6,0x86,0xc4,0xcb,0xa5,0x20,0x24,0xfa,0x52,0xe8,0xe8,0xa4,0xbb,
0x5e,0xb5,0xf3,0xeb,0xb0,0x60,0xa7,0x19,0xa4,0xf8,0xf6,0x16,0xdb,0xb9,0x77,
0xe1,0x45,0x32,0x24,0xb6,0xdd,0x20,0x88,0xf3,0x38,0x4b,0x70,0x5d,0xdf,0x33,
0x62,0x7b,0xfc,0x85,0xee,0x74,0x23,0x84,0xad
};
//
// Public Exponent of RSA Key
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST UINT8 RsaE[] = { 0x01, 0x00,0x01 };
//
// Private Exponent of RSA Key
//
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST UINT8 RsaD[] = {
0x05,0xb8,0x2d,0xb8,0xe2,0x2e,0xec,0x95,0x20,0xf7,0x1d,0x6e,0x82,0xf4,0xa9,
0x38,0x8f,0x63,0x2d,0x99,0xfd,0xc7,0xaa,0x88,0xaa,0xbb,0x8d,0x90,0xdf,0x53,
0x41,0xb1,0x03,0x1f,0x83,0x1f,0xad,0xdf,0x26,0x18,0x66,0xeb,0x65,0xad,0x39,
0xb1,0xa4,0x34,0xdd,0x78,0x53,0x0a,0x36,0xc6,0x74,0xa8,0x5a,0xcc,0x23,0x36,
0x07,0x82,0xe4,0xb3,0xd8,0xdb,0xd2,0x8b,0xc0,0xd8,0x25,0x2f,0xb9,0x7f,0xac,
0xc5,0x41,0xd7,0x76,0x01,0x05,0x7a,0x41,0x2f,0xfd,0x55,0x48,0xcd,0xe9,0xb7,
0xaa,0xdd,0x05,0x90,0xc5,0x7e,0x95,0x25,0xfb,0xe8,0x5f,0xc2,0x91,0x5e,0x17,
0x5c,0xe3,0xb8,0x1f,0x5a,0xd8,0x8d,0xae,0xc1,0x39,0xb9,0x7f,0x8c,0x53,0x23,
0x4e,0x94,0x60,0x3e,0x1d,0x20,0xe0,0x01
};
//
// Known Answer Test (KAT) Data for RSA PKCS#1 Signing
//
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST CHAR8 RsaSignData[] = "This message from lab-z.com";
//
// Known Signature for the above message, under SHA-1 Digest
//
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST UINT8 RsaPkcs1Signature[] = {
0x61,0xA2,0xDD,0x93,0x1A,0xA6,0x1B,0x46,0x2A,0x84,0xC8,0x7A,0x74,0xBB,0x23,0x44,
0x43,0xD6,0xE9,0x2A,0x30,0xAF,0x2D,0x13,0x0A,0x74,0x26,0x78,0xF6,0x42,0x23,0x4D,
0x55,0x85,0xC9,0x42,0xA8,0x4A,0xAC,0x2C,0x46,0x76,0xF5,0x34,0xC7,0x57,0x3B,0x2F,
0x4B,0xF9,0x42,0x03,0x1F,0x80,0xCE,0xF2,0xD7,0xA4,0x8C,0xBB,0xBF,0x37,0x60,0x4A,
0x32,0x3A,0xF2,0x82,0x95,0xF3,0x11,0x40,0x2E,0x45,0x4B,0x2E,0x02,0xBA,0xAA,0xFC,
0x29,0x8D,0xEC,0x56,0xC6,0xCD,0x97,0x06,0xDE,0x52,0x85,0xDB,0x1B,0x17,0xF1,0x39,
0xBB,0x6B,0x8C,0xAA,0xFE,0xEC,0xD4,0xA7,0x96,0x6F,0x22,0xCD,0x4B,0x6D,0x01,0x0B,
0x00,0xA1,0xDF,0x7F,0xA4,0xA0,0xD2,0xC4,0x09,0x0C,0xB0,0x4A,0x7A,0xA2,0xE2,0x93
};
/**
Entry Point of Cryptographic Validation Utility.
@param ImageHandle The image handle of the UEFI Application.
@param SystemTable A pointer to the EFI System Table.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The entry point is executed successfully.
@retval other Some error occurs when executing this entry point.
**/
EFI_STATUS
EFIAPI
CryptestMain (
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *SystemTable
)
{
VOID *Rsa;
UINT8 HashValue[SHA1_DIGEST_SIZE];
UINTN HashSize;
UINTN CtxSize;
VOID *Sha1Ctx;
UINT8 *Signature;
UINTN SigSize;
BOOLEAN Status;
UINTN i;
UINT8 sign[SHA1_DIGEST_SIZE];
RandomSeed (NULL, 0);
//
// SHA-1 Digest Message for PKCS#1 Signature
//
Print (L"Hash Original Message ...\n");
HashSize = SHA1_DIGEST_SIZE;
ZeroMem (HashValue, HashSize);
CtxSize = Sha1GetContextSize ();
Sha1Ctx = AllocatePool (CtxSize);
Status = Sha1Init (Sha1Ctx);
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
Status = Sha1Update (Sha1Ctx, RsaSignData, AsciiStrLen (RsaSignData));
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
Status = Sha1Final (Sha1Ctx, HashValue);
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
for (i=0;i<HashSize;i++) {Print (L"%02X ",HashValue[i]);}
FreePool (Sha1Ctx);
//
// Sign RSA PKCS#1-encoded Signature
//
Print (L"PKCS#1 Signature ...\n");
Rsa = RsaNew ();
if (Rsa == NULL) {
Print (L"[Fail]t\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
Status = RsaSetKey (Rsa, RsaKeyN, RsaN, sizeof (RsaN));
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]p\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
Status = RsaSetKey (Rsa, RsaKeyE, RsaE, sizeof (RsaE));
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]h\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
//Private Key
Status = RsaSetKey (Rsa, RsaKeyD, RsaD, sizeof (RsaD));
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]q\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
SigSize = 0;
Status = RsaPkcs1Sign (Rsa, HashValue, HashSize, sign, &SigSize);
if (Status || SigSize == 0) {
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
Signature = AllocatePool (SigSize);
Status = RsaPkcs1Sign (Rsa, HashValue, HashSize, Signature, &SigSize);
if (!Status) {
Print (L"[Fail]y\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
for (i=0;i<SigSize;i++) { Print(L"%02X ",Signature[i]);} Print(L" \n");
if (SigSize != sizeof (RsaPkcs1Signature)) {
Print (L"[Fail]\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
if (CompareMem (Signature, RsaPkcs1Signature, SigSize) != 0) {
Print (L"[Fail]a2\n");
return EFI_ABORTED;
}
//
// Release Resources
//
RsaFree (Rsa);
Print (L"Release RSA Context ... [Pass]");
Print (L"\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}