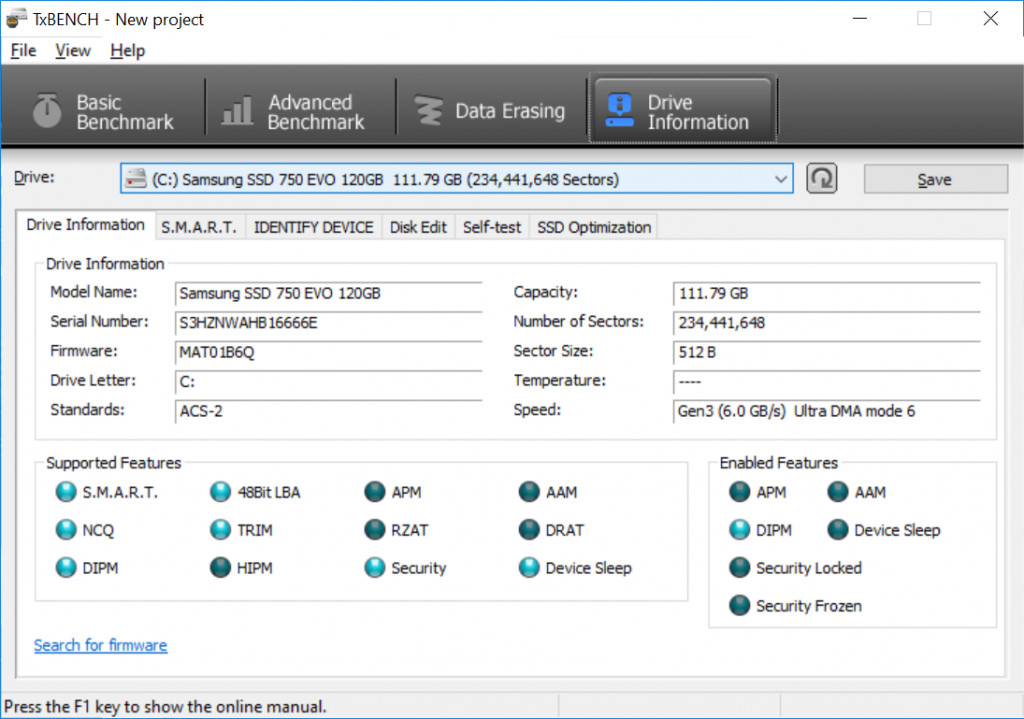
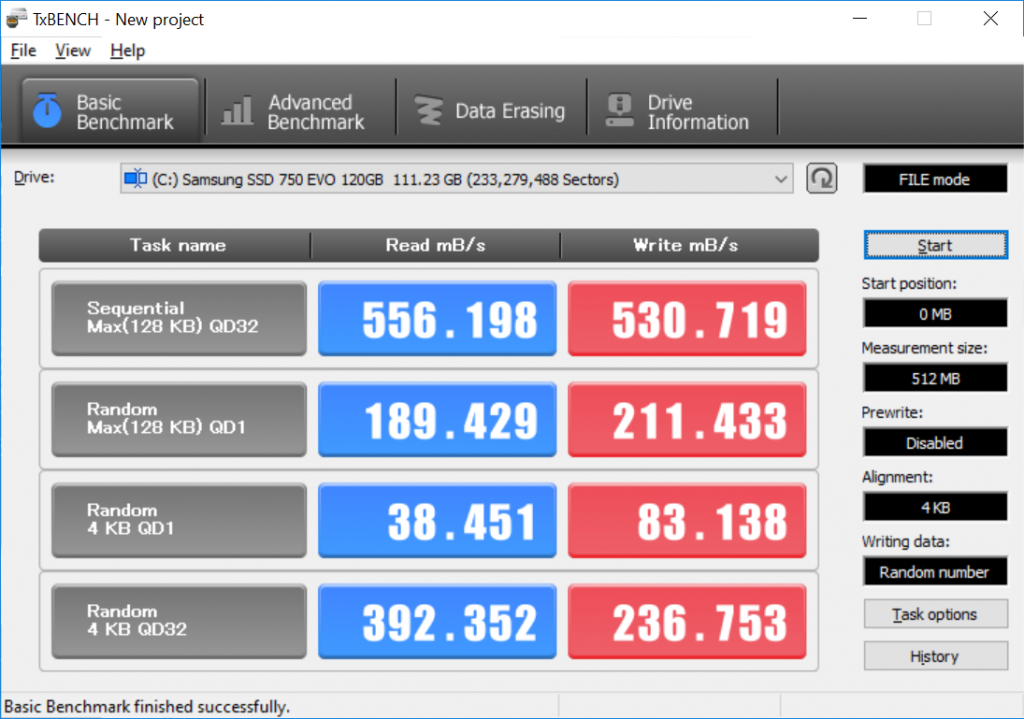
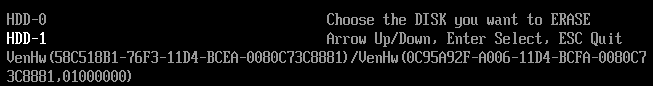
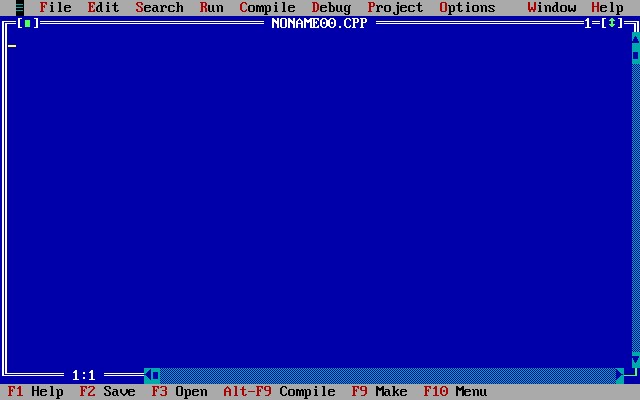
每一个 Protocol 都有一个GUID,这是Protocol 正式的名称。编写一个Application,标准的做法是:
1. 在Application 的inf 文件, [Packages] 节中引用 MdePkg.dec , 实际上你用到的UEFI 标准的 Protocol GUID 在这个文件中都有定义;[Protocols] 节中定义你用到的 ProtocolGuid;
2.在Application的 c 文件中 extern 一下代码中用到的 GUID;
当然,这样的做法看起来不如直接在代码中使用 EFI_GUID 定义直接易懂,之前我写的很多代码为了省事采用的就是在 Application中重新定义的方法。
下面列出常用的 Protocol 的定义:
EFI_GUID gEfiLoadedImageProtocolGuid = {0x5B1B31A1, 0x9562,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x3F,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiLoadedImageDevicePathProtocolGuid = {0xBC62157E, 0x3E33,0x4FEC,
{ 0x99, 0x20,0x2D, 0x3B, 0x36, 0xD7,0x50, 0xDF } };
EFI_GUID gEfiSimpleTextOutProtocolGuid = {0x387477C2, 0x69C7,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x39,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDevicePathProtocolGuid = {0x9576E91, 0x6D3F,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x39,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiSimplePointerProtocolGuid = {0x31878C87, 0xB75,0x11D5,
{ 0x9A, 0x4F,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiAbsolutePointerProtocolGuid = {0x8D59D32B, 0xC655,0x4AE9,
{ 0x9B, 0x15,0xF2, 0x59, 0x4, 0x99,0x2A, 0x43 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiSerialIoProtocolGuid = {0xBB25CF6F, 0xF1D4,0x11D2,
{ 0x9A, 0xC,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0xFD } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEdidDiscoveredProtocolGuid = {0x1C0C34F6, 0xD380,0x41FA,
{ 0xA0, 0x49,0x8A, 0xD0, 0x6C, 0x1A,0x66, 0xAA } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEdidActiveProtocolGuid = {0xBD8C1056, 0x9F36,0x44EC,
{ 0x92, 0xA8,0xA6, 0x33, 0x7F, 0x81,0x79, 0x86 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEdidOverrideProtocolGuid = {0x48ECB431, 0xFB72,0x45C0,
{ 0xA9, 0x22,0xF4, 0x58, 0xFE, 0x4,0xB, 0xD5 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiLoadFileProtocolGuid = {0x56EC3091, 0x954C,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x3F,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiLoadFile2ProtocolGuid = {0x4006C0C1, 0xFCB3,0x403E,
{ 0x99, 0x6D,0x4A, 0x6C, 0x87, 0x24,0xE0, 0x6D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTapeIoProtocolGuid = {0x1E93E633, 0xD65A,0x459E,
{ 0xAB, 0x84,0x93, 0xD9, 0xEC, 0x26,0x6D, 0x18 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDiskIoProtocolGuid = {0xCE345171, 0xBA0B,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x4F,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiBlockIoProtocolGuid = {0x964E5B21, 0x6459,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x39,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUnicodeCollationProtocolGuid = {0x1D85CD7F, 0xF43D,0x11D2,
{ 0x9A, 0xC,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiPciRootBridgeIoProtocolGuid = {0x2F707EBB, 0x4A1A,0x11D4,
{ 0x9A, 0x38,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiPciIoProtocolGuid = {0x4CF5B200, 0x68B8,0x4CA5,
{ 0x9E, 0xEC,0xB2, 0x3E, 0x3F, 0x50,0x2, 0x9A } };
EFI_GUID gEfiScsiPassThruProtocolGuid = {0xA59E8FCF, 0xBDA0,0x43BB,
{ 0x90, 0xB1,0xD3, 0x73, 0x2E, 0xCA,0xA8, 0x77 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiScsiIoProtocolGuid = {0x932F47E6, 0x2362,0x4002,
{ 0x80, 0x3E,0x3C, 0xD5, 0x4B, 0x13,0x8F, 0x85 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiExtScsiPassThruProtocolGuid = {0x143B7632, 0xB81B,0x4CB7,
{ 0xAB, 0xD3,0xB6, 0x25, 0xA5, 0xB9,0xBF, 0xFE } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIScsiInitiatorNameProtocolGuid = {0x59324945, 0xEC44,0x4C0D,
{ 0xB1, 0xCD,0x9D, 0xB1, 0x39, 0xDF,0x7, 0xC } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUsbIoProtocolGuid = {0x2B2F68D6, 0xCD2,0x44CF,
{ 0x8E, 0x8B,0xBB, 0xA2, 0xB, 0x1B,0x5B, 0x75 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUsbHcProtocolGuid = {0xF5089266, 0x1AA0,0x4953,
{ 0x97, 0xD8,0x56, 0x2F, 0x8A, 0x73,0xB5, 0x19 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUsb2HcProtocolGuid = {0x3E745226, 0x9818,0x45B6,
{ 0xA2, 0xAC,0xD7, 0xCD, 0xE, 0x8B,0xA2, 0xBC } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDebugSupportProtocolGuid = {0x2755590C, 0x6F3C,0x42FA,
{ 0x9E, 0xA4,0xA3, 0xBA, 0x54, 0x3C,0xDA, 0x25 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDebugPortProtocolGuid = {0xEBA4E8D2, 0x3858,0x41EC,
{ 0xA2, 0x81,0x26, 0x47, 0xBA, 0x96,0x60, 0xD0 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDecompressProtocolGuid = {0xD8117CFE, 0x94A6,0x11D4,
{ 0x9A, 0x3A,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiAcpiTableProtocolGuid = {0xFFE06BDD, 0x6107,0x46A6,
{ 0x7B, 0xB2,0x5A, 0x9C, 0x7E, 0xC5,0x27, 0x5C } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEbcProtocolGuid = {0x13AC6DD1, 0x73D0,0x11D4,
{ 0xB0, 0x6B,0x0, 0xAA, 0x0, 0xBD,0x6D, 0xE7 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiSimpleNetworkProtocolGuid = {0xA19832B9, 0xAC25,0x11D3,
{ 0x9A, 0x2D,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiNetworkInterfaceIdentifierProtocolGuid = {0xE18541CD, 0xF755,0x4F73,
{ 0x92, 0x8D,0x64, 0x3C, 0x8A, 0x79,0xB2, 0x29 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiNetworkInterfaceIdentifierProtocolGuid_31 = {0x1ACED566, 0x76ED,0x4218,
{ 0xBC, 0x81,0x76, 0x7F, 0x1F, 0x97,0x7A, 0x89 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiPxeBaseCodeProtocolGuid = {0x3C4E603, 0xAC28,0x11D3,
{ 0x9A, 0x2D,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiPxeBaseCodeCallbackProtocolGuid = {0x245DCA21, 0xFB7B,0x11D3,
{ 0x8F, 0x1,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiBisProtocolGuid = {0xB64AAB0, 0x5429,0x11D4,
{ 0x98, 0x16,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x1F,0xAD, 0xCF } };
EFI_GUID gEfiManagedNetworkServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xF36FF770, 0xA7E1,0x42CF,
{ 0x9E, 0xD2,0x56, 0xF0, 0xF2, 0x71,0xF4, 0x4C } };
EFI_GUID gEfiManagedNetworkProtocolGuid = {0x7AB33A91, 0xACE5,0x4326,
{ 0xB5, 0x72,0xE7, 0xEE, 0x33, 0xD3,0x9F, 0x16 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiArpServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xF44C00EE, 0x1F2C,0x4A00,
{ 0xAA, 0x9,0x1C, 0x9F, 0x3E, 0x8,0x0, 0xA3 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiArpProtocolGuid = {0xF4B427BB, 0xBA21,0x4F16,
{ 0xBC, 0x4E,0x43, 0xE4, 0x16, 0xAB,0x61, 0x9C } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDhcp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x9D9A39D8, 0xBD42,0x4A73,
{ 0xA4, 0xD5,0x8E, 0xE9, 0x4B, 0xE1,0x13, 0x80 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDhcp4ProtocolGuid = {0x8A219718, 0x4EF5,0x4761,
{ 0x91, 0xC8,0xC0, 0xF0, 0x4B, 0xDA,0x9E, 0x56 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTcp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x720665, 0x67EB,0x4A99,
{ 0xBA, 0xF7,0xD3, 0xC3, 0x3A, 0x1C,0x7C, 0xC9 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTcp4ProtocolGuid = {0x65530BC7, 0xA359,0x410F,
{ 0xB0, 0x10,0x5A, 0xAD, 0xC7, 0xEC,0x2B, 0x62 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xC51711E7, 0xB4BF,0x404A,
{ 0xBF, 0xB8,0xA, 0x4, 0x8E, 0xF1,0xFF, 0xE4 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp4ProtocolGuid = {0x41D94CD2, 0x35B6,0x455A,
{ 0x82, 0x58,0xD4, 0xE5, 0x13, 0x34,0xAA, 0xDD } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp4ConfigProtocolGuid = {0x3B95AA31, 0x3793,0x434B,
{ 0x86, 0x67,0xC8, 0x7, 0x8, 0x92,0xE0, 0x5E } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp4Config2ProtocolGuid = {0x5B446ED1, 0xE30B,0x4FAA,
{ 0x87, 0x1A,0x36, 0x54, 0xEC, 0xA3,0x60, 0x80 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUdp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x83F01464, 0x99BD,0x45E5,
{ 0xB3, 0x83,0xAF, 0x63, 0x5, 0xD8,0xE9, 0xE6 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUdp4ProtocolGuid = {0x3AD9DF29, 0x4501,0x478D,
{ 0xB1, 0xF8,0x7F, 0x7F, 0xE7, 0xE,0x50, 0xF3 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiMtftp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x2FE800BE, 0x8F01,0x4AA6,
{ 0x94, 0x6B,0xD7, 0x13, 0x88, 0xE1,0x83, 0x3F } };
EFI_GUID gEfiMtftp4ProtocolGuid = {0x78247C57, 0x63DB,0x4708,
{ 0x99, 0xC2,0xA8, 0xB4, 0xA9, 0xA6,0x1F, 0x6B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiAuthenticationInfoProtocolGuid = {0x7671D9D0, 0x53DB,0x4173,
{ 0xAA, 0x69,0x23, 0x27, 0xF2, 0x1F,0xB, 0xC7 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHashServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x42881C98, 0xA4F3,0x44B0,
{ 0xA3, 0x9D,0xDF, 0xA1, 0x86, 0x67,0xD8, 0xCD } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHashProtocolGuid = {0xC5184932, 0xDBA5,0x46DB,
{ 0xA5, 0xBA,0xCC, 0xB, 0xDA, 0x9C,0x14, 0x35 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiFontProtocolGuid = {0xE9CA4775, 0x8657,0x47FC,
{ 0x97, 0xE7,0x7E, 0xD6, 0x5A, 0x8,0x43, 0x24 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiStringProtocolGuid = {0xFD96974, 0x23AA,0x4CDC,
{ 0xB9, 0xCB,0x98, 0xD1, 0x77, 0x50,0x32, 0x2A } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiImageProtocolGuid = {0x31A6406A, 0x6BDF,0x4E46,
{ 0xB2, 0xA2,0xEB, 0xAA, 0x89, 0xC4,0x9, 0x20 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiConfigRoutingProtocolGuid = {0x587E72D7, 0xCC50,0x4F79,
{ 0x82, 0x9,0xCA, 0x29, 0x1F, 0xC1,0xA1, 0xF } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiConfigAccessProtocolGuid = {0x330D4706, 0xF2A0,0x4E4F,
{ 0xA3, 0x69,0xB6, 0x6F, 0xA8, 0xD5,0x43, 0x85 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiFormBrowser2ProtocolGuid = {0xB9D4C360, 0xBCFB,0x4F9B,
{ 0x92, 0x98,0x53, 0xC1, 0x36, 0x98,0x22, 0x58 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDeviceIoProtocolGuid = {0xAF6AC311, 0x84C3,0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x3C,0x0, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69,0x72, 0x3B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUgaDrawProtocolGuid = {0x982C298B, 0xF4FA,0x41CB,
{ 0xB8, 0x38,0x77, 0xAA, 0x68, 0x8F,0xB8, 0x39 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUgaIoProtocolGuid = {0x61A4D49E, 0x6F68,0x4F1B,
{ 0xB9, 0x22,0xA8, 0x6E, 0xED, 0xB,0x7, 0xA2 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDriverConfigurationProtocolGuid = {0x107A772B, 0xD5E1,0x11D4,
{ 0x9A, 0x46,0x0, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F,0xC1, 0x4D } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDriverConfiguration2ProtocolGuid = {0xBFD7DC1D, 0x24F1,0x40D9,
{ 0x82, 0xE7,0x2E, 0x9, 0xBB, 0x6B,0x4E, 0xBE } };
EFI_GUID gEfiSimpleTextInputExProtocolGuid = {0xDD9E7534, 0x7762,0x4698,
{ 0x8C, 0x14,0xF5, 0x85, 0x17, 0xA6,0x25, 0xAA } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp6ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xEC835DD3, 0xFE0F,0x617B,
{ 0xA6, 0x21,0xB3, 0x50, 0xC3, 0xE1,0x33, 0x88 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp6ProtocolGuid = {0x2C8759D5, 0x5C2D,0x66EF,
{ 0x92, 0x5F,0xB6, 0x6C, 0x10, 0x19,0x57, 0xE2 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIp6ConfigProtocolGuid = {0x937FE521, 0x95AE,0x4D1A,
{ 0x89, 0x29,0x48, 0xBC, 0xD9, 0xA,0xD3, 0x1A } };
EFI_GUID gEfiMtftp6ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xD9760FF3, 0x3CCA,0x4267,
{ 0x80, 0xF9,0x75, 0x27, 0xFA, 0xFA,0x42, 0x23 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiMtftp6ProtocolGuid = {0xBF0A78BA, 0xEC29,0x49CF,
{ 0xA1, 0xC9,0x7A, 0xE5, 0x4E, 0xAB,0x6A, 0x51 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDhcp6ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x9FB9A8A1, 0x2F4A,0x43A6,
{ 0x88, 0x9C,0xD0, 0xF7, 0xB6, 0xC4,0x7A, 0xD5 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDhcp6ProtocolGuid = {0x87C8BAD7, 0x595,0x4053,
{ 0x82, 0x97,0xDE, 0xDE, 0x39, 0x5F,0x5D, 0x5B } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUdp6ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0x66ED4721, 0x3C98,0x4D3E,
{ 0x81, 0xE3,0xD0, 0x3D, 0xD3, 0x9A,0x72, 0x54 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUdp6ProtocolGuid = {0x4F948815, 0xB4B9,0x43CB,
{ 0x8A, 0x33,0x90, 0xE0, 0x60, 0xB3,0x49, 0x55 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTcp6ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xEC20EB79, 0x6C1A,0x4664,
{ 0x9A, 0xD,0xD2, 0xE4, 0xCC, 0x16,0xD6, 0x64 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTcp6ProtocolGuid = {0x46E44855, 0xBD60,0x4AB7,
{ 0xAB, 0xD,0xA6, 0x79, 0xB9, 0x44,0x7D, 0x77 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiVlanConfigProtocolGuid = {0x9E23D768, 0xD2F3,0x4366,
{ 0x9F, 0xC3,0x3A, 0x7A, 0xBA, 0x86,0x43, 0x74 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEapProtocolGuid = {0x5D9F96DB, 0xE731,0x4CAA,
{ 0xA0, 0xD,0x72, 0xE1, 0x87, 0xCD,0x77, 0x62 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiEapManagementProtocolGuid = {0xBB62E663, 0x625D,0x40B2,
{ 0xA0, 0x88,0xBB, 0xE8, 0x36, 0x23,0xA2, 0x45 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiFtp4ServiceBindingProtocolGuid = {0xFAAECB1, 0x226E,0x4782,
{ 0xAA, 0xCE,0x7D, 0xB9, 0xBC, 0xBF,0x4D, 0xAF } };
EFI_GUID gEfiFtp4ProtocolGuid = {0xEB338826, 0x681B,0x4295,
{ 0xB3, 0x56,0x2B, 0x36, 0x4C, 0x75,0x7B, 0x9 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIpSecConfigProtocolGuid = {0xCE5E5929, 0xC7A3,0x4602,
{ 0xAD, 0x9E,0xC9, 0xDA, 0xF9, 0x4E,0xBF, 0xCF } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDriverHealthProtocolGuid = {0x2A534210, 0x9280,0x41D8,
{ 0xAE, 0x79,0xCA, 0xDA, 0x1, 0xA2,0xB1, 0x27 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDeferredImageLoadProtocolGuid = {0x15853D7C, 0x3DDF,0x43E0,
{ 0xA1, 0xCB,0xEB, 0xF8, 0x5B, 0x8F,0x87, 0x2C } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUserCredentialProtocolGuid = {0x71EE5E94, 0x65B9,0x45D5,
{ 0x82, 0x1A,0x3A, 0x4D, 0x86, 0xCF,0xE6, 0xBE } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUserManagerProtocolGuid = {0x6FD5B00C, 0xD426,0x4283,
{ 0x98, 0x87,0x6C, 0xF5, 0xCF, 0x1C,0xB1, 0xFE } };
EFI_GUID gEfiAtaPassThruProtocolGuid = {0x1D3DE7F0, 0x807,0x424F,
{ 0xAA, 0x69,0x11, 0xA5, 0x4E, 0x19,0xA4, 0x6F } };
EFI_GUID gEfiFirmwareManagementProtocolGuid = {0x86C77A67, 0xB97,0x4633,
{ 0xA1, 0x87,0x49, 0x10, 0x4D, 0x6,0x85, 0xC7 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIpSecProtocolGuid = {0xDFB386F7, 0xE100,0x43AD,
{ 0x9C, 0x9A,0xED, 0x90, 0xD0, 0x8A,0x5E, 0x12 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIpSec2ProtocolGuid = {0xA3979E64, 0xACE8,0x4DDC,
{ 0xBC, 0x7,0x4D, 0x66, 0xB8, 0xFD,0x9, 0x77 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiKmsProtocolGuid = {0xEC3A978D, 0x7C4E,0x48FA,
{ 0x9A, 0xBE,0x6A, 0xD9, 0x1C, 0xC8,0xF8, 0x11 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiBlockIo2ProtocolGuid = {0xA77B2472, 0xE282,0x4E9F,
{ 0xA2, 0x45,0xC2, 0xC0, 0xE2, 0x7B,0xBC, 0xC1 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiStorageSecurityCommandProtocolGuid = {0xC88B0B6D, 0xDFC,0x49A7,
{ 0x9C, 0xB4,0x49, 0x7, 0x4B, 0x4C,0x3A, 0x78 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiUserCredential2ProtocolGuid = {0xE98ADB03, 0xB8B9,0x4AF8,
{ 0xBA, 0x20,0x26, 0xE9, 0x11, 0x4C,0xBC, 0xE5 } };
EFI_GUID gPcdProtocolGuid = {0x11B34006, 0xD85B,0x4D0A,
{ 0xA2, 0x90,0xD5, 0xA5, 0x71, 0x31,0xE, 0xF7 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiTcgProtocolGuid = {0xF541796D, 0xA62E,0x4954,
{ 0xA7, 0x75,0x95, 0x84, 0xF6, 0x1B,0x9C, 0xDD } };
EFI_GUID gEfiHiiPackageListProtocolGuid = {0x6A1EE763, 0xD47A,0x43B4,
{ 0xAA, 0xBE,0xEF, 0x1D, 0xE2, 0xAB,0x56, 0xFC } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDriverFamilyOverrideProtocolGuid = {0xB1EE129E, 0xDA36,0x4181,
{ 0x91, 0xF8,0x4, 0xA4, 0x92, 0x37,0x66, 0xA7 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiIdeControllerInitProtocolGuid = {0xA1E37052, 0x80D9,0x4E65,
{ 0xA3, 0x17,0x3E, 0x9A, 0x55, 0xC4,0x3E, 0xC9 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDiskIo2ProtocolGuid = {0x151C8EAE, 0x7F2C,0x472C,
{ 0x9E, 0x54,0x98, 0x28, 0x19, 0x4F,0x6A, 0x88 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiAdapterInformationProtocolGuid = {0xE5DD1403, 0xD622,0xC24E,
{ 0x84, 0x88,0xC7, 0x1B, 0x17, 0xF5,0xE8, 0x2 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiShellDynamicCommandProtocolGuid = {0x3C7200E9, 0x5F,0x4EA4,
{ 0x87, 0xDE,0xA3, 0xDF, 0xAC, 0x8A,0x27, 0xC3 } };
EFI_GUID gEfiDiskInfoProtocolGuid = {0xD432A67F, 0x14DC,0x484B,
{ 0xB3, 0xBB,0x3F, 0x2, 0x91, 0x84,0x93, 0x27 } };