最近学习了一下 MIT App Inventor 2 ,这是一种非常简单的可以方便编写 Android APP 的程序。
原理很简单,首先设计自己的二维码(比如:字符串 men2 表示“门”;deng1表示灯),打印出来之后贴在物品上,然后用自己编写的APP去扫描这些二维码,播放事先录制好的声音。
工作的视频:
http://www.tudou.com/programs/view/-r_TY3ll7dc/?resourceId=0_06_02_99
本文提到的二维码和AIA工程文件下载
最近学习了一下 MIT App Inventor 2 ,这是一种非常简单的可以方便编写 Android APP 的程序。
原理很简单,首先设计自己的二维码(比如:字符串 men2 表示“门”;deng1表示灯),打印出来之后贴在物品上,然后用自己编写的APP去扫描这些二维码,播放事先录制好的声音。
工作的视频:
http://www.tudou.com/programs/view/-r_TY3ll7dc/?resourceId=0_06_02_99
本文提到的二维码和AIA工程文件下载
一些情况下,我们需要在 Shell 下面使用文件进行测试,这次编写一个工具,生成使用随机数填充的文件。为了校验方便,文件的末尾有一个 checksum,按照 32Bits 的 UINTN ,整个文件的和应该是 0 .
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/SimpleFileSystem.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
//copied from \StdLib\Include\stdlib.h
/** Expands to an integer constant expression that is the maximum value
returned by the rand function.
The value of the RAND_MAX macro shall be at least 32767.
**/
#define RAND_MAX 0x7fffffff
//Copied from \StdLib\LibC\StdLib\Rand.c
static UINT32 next = 1;
/** Compute a pseudo-random number.
*
* Compute x = (7^5 * x) mod (2^31 - 1)
* without overflowing 31 bits:
* (2^31 - 1) = 127773 * (7^5) + 2836
* From "Random number generators: good ones are hard to find",
* Park and Miller, Communications of the ACM, vol. 31, no. 10,
* October 1988, p. 1195.
**/
UINT32
rand()
{
INT32 hi, lo, x;
/* Can't be initialized with 0, so use another value. */
if (next == 0)
next = 123459876;
hi = next / 127773;
lo = next % 127773;
x = 16807 * lo - 2836 * hi;
if (x < 0)
x += 0x7fffffff;
return ((next = x) % ((UINT32)RAND_MAX + 1));
}
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
UINTN FileSize=0;
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *Root;
EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL *SimpleFileSystem;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *FileHandle=0;
UINTN *HandleBuffer;
UINT32 i,t,sum=0;
if (Argc>1) {
FileSize=StrDecimalToUintn(Argv[1])*1024;
//Print(L"%d",FileSize);
}
else
{
FileSize=1024*1024*10;
}
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(
&gEfiSimpleFileSystemProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID **)&SimpleFileSystem);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Cannot find EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = SimpleFileSystem->OpenVolume(SimpleFileSystem,&Root);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"OpenVolume error \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = Root -> Open(Root,
&FileHandle,
(CHAR16 *) L"ztest.bin",
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE | EFI_FILE_MODE_READ | EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE,
0);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status) || (FileHandle==0)) {
Print(L"Open error \r\n");
return Status;
}
HandleBuffer = AllocateZeroPool(FileSize);
if (HandleBuffer == NULL) {
Print(L"Not enough memory!\n");
return Status;
}
for (i=0;i<(FileSize-4)/4;i++)
{
t=rand();
*(HandleBuffer+i)=t;
sum=sum+t;
}
*(HandleBuffer+(FileSize-4)/4)=(UINT32)(0-sum);
Status = FileHandle -> Write(FileHandle, &FileSize, HandleBuffer);
Print(L"Write Done \r\n");
FreePool(HandleBuffer);
Status = FileHandle -> Close (FileHandle);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
除了生成文件的工具,还有一个用来校验文件的工具,他的作用是将文件全部内容相加,查看结果是否为0.
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
RETURN_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_INFO *FileInfo = NULL;
UINT32 *HandleBuffer=NULL;
UINTN ReadSize;
UINT32 i,sum=0;
//Check if there is a parameter
if (Argc == 1) {
Print(L"Usage: crctest [filename]\n");
return 0;
}
//Open the file given by the parameter
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(Argv[1], (SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ , 0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
//Get file size
FileInfo = ShellGetFileInfo( (SHELL_FILE_HANDLE)FileHandle);
//if the file size is not the multiple of 4, we don't check it!
if ((UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize % 4 !=0 ) {
Print(L"We can't check this file as the filesize is wrong!\n");
}
//Allocate a memory buffer
HandleBuffer = AllocateZeroPool((UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize);
if (HandleBuffer == NULL) {
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES); }
ReadSize=(UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize;
//Load the whole file to the buffer
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&ReadSize,HandleBuffer);
for (i=0;i< FileInfo-> FileSize / 4;i++)
{
sum=sum+*(HandleBuffer+i);
}
if (sum==0) {
Print(L"Pass!\n");
}
else
{
Print(L"Fail!\n");
}
FreePool(HandleBuffer);
FileHandle -> Close (FileHandle);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
完整的代码和 EFI 文件下载:
TestFileGen
Chker
EFI 在设计之初就考虑了多语言的支持,使用HII可以轻松的实现汉字的显示。本篇文章介绍获得汉字字形的其他方法,掌握这种方法之后可以在没有HII支持的情况下显示汉字。当然,程序只是为了演示原理,介绍如何读取16×16的汉字字形信息,没有转为图形。
比如:“宋”字查询到的区位码是4346 【参考3】,意思是区码为43,位码是46。计算这个字在字库中的方法是:((43-1)*94+(46-1))*32=6828。之后,在字库文件的 6828偏移处连续读取32个字节即可。
代码如下:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
#define FONT_SIZE (16)
#define HZ_INDEX(hz) ((hz[0] - 1) * 94 + (hz[1] -1))*32
#define DOTS_BYTES (FONT_SIZE * FONT_SIZE / 8)
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
RETURN_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_INFO *FileInfo = NULL;
EFI_HANDLE *HandleBuffer=NULL;
UINTN ReadSize;
UINTN i,j;
UINT8 HZChar[2] = {43,46};
CHAR8 *c;
CHAR8 k;
//Open the file given by the parameter
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(L"HZK16K.BIN",
(SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ ,
0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
//Get file size
FileInfo = ShellGetFileInfo( (SHELL_FILE_HANDLE)FileHandle);
//Allocate a memory buffer
HandleBuffer = AllocateZeroPool((UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize);
if (HandleBuffer == NULL) {
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES); }
ReadSize=(UINTN) FileInfo-> FileSize;
//Load the whole file to the buffer
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&ReadSize,HandleBuffer);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"ReadFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
for (i=0;i<DOTS_BYTES;i++)
{
c=((UINT8*)HandleBuffer)+HZ_INDEX(HZChar)+i;
k=*c;
for (j=0;j<8;j++)
{
if (0 == (k & 0x80))
{
Print(L" ");
}
else
{
Print(L"OO");
}
k=k<<1;
}
if ((i+1)%2==0) {Print(L"\n");}
}
FreePool(HandleBuffer);
ShellCloseFile((SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle);
}
运行结果(特别注意要把字库文件放在Fsnt0:这样的目录下):
完整的代码下载:
HZ
最后,关于【参考1】的代码多说两句。其中有unsigned char word[3] = “我”; 这样直接的定义,这是因为很久很久之前,为了编便于 PC处理汉字定义一个汉字由两个大于127的ASCII码组成。组成的规则是:区码+A0,位码+A0。比如,我在中文环境下定义一个“宋”,
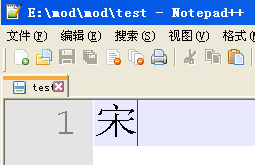
然后切换到英文环境下打开,看到的是2个ASCII码,
如果再切换到十六进制编辑,会看到 CB CE (前提是保存为 ANSI格式,如果你存为unicode,看到的又是另外的东西)
时代已经变了,对于 Windows 编程来说上述的知识都已经过时,如果你需要搞嵌入式开发,还是值得认真学习和理解。
另外,PC刚开始流行的时候,很长一段时间都有汉字不适合PC处理等等的言论,对于普通用户来说,汉字的输入也是很大的困扰。而最终的解决,我认为是人们强烈的交流的需求使得这样的问题很快被克服掉了。时至今日,我仍然能记得同一个寝室的胖子在他的 Nokia手机上,在十几个按键上运指如飞和各种MM聊得火热。很快,没人再认为汉字在PC的普及上是一个问题。
参考 :
1.https://blog.twofei.com/embedded/hzk.html HZK16汉字16*16点阵字库的使用及示例程序
2.http://blog.csdn.net/turingo/article/details/8191712 图灵狗的专栏
3.http://www.jscj.com/index/gb2312.php 汉字区位码查询系统 (具体)
==============================================================
2018年12月30日 补充: 在【参考1】的文章中提供了一个取得字模的代码,我在 Win10 下实验过,很好用:
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE* fphzk = NULL;
int i, j, k, offset;
int flag;
unsigned char buffer[32];
unsigned char word[5];
unsigned char key[8] = {
0x80,0x40,0x20,0x10,0x08,0x04,0x02,0x01
};
fphzk = fopen("hzk16", "rb");
if(fphzk == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "error hzk16\n");
return 1;
}
while(1){
printf("输入要生成字模的汉字(多个):");
for(;;){
fgets((char*)word, 3, stdin);
if(*word == '\n')
break;
offset = (94*(unsigned int)(word[0]-0xa0-1)+(word[1]-0xa0-1))*32;
fseek(fphzk, offset, SEEK_SET);
fread(buffer, 1, 32, fphzk);
for(k=0; k<16; k++){
for(j=0; j<2; j++){
for(i=0; i<8; i++){
flag = buffer[k*2+j]&key[i];
printf("%s", flag?"●":"○");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("uchar code key[32] = {");
for(k=0; k<31; k++){
printf("0x%02X,", buffer[k]);
}
printf("0x%02X};\n", buffer[31]);
printf("\n");
}
}
fclose(fphzk);
fphzk = NULL;
return 0;
}
如果你是英文的OS,需要先切换内码为 CP936
我们可以通过EFI_HII_FONT_PROTOCOL【参考1】 中的 GetGlyph来取得一些字符的字形定义。
GetGlyph 的原型可以在 \MdePkg\Include\Protocol\HiiFont.h 中找到:
/**
Convert the glyph for a single character into a bitmap.
@param This A pointer to the EFI_HII_FONT_PROTOCOL instance.
@param Char The character to retrieve.
@param StringInfo Points to the string font and color
information or NULL if the string should use
the default system font and color.
@param Blt This must point to a NULL on entry. A buffer will
be allocated to hold the output and the pointer
updated on exit. It is the caller's responsibility
to free this buffer.
@param Baseline The number of pixels from the bottom of the bitmap
to the baseline.
@retval EFI_SUCCESS The glyph bitmap created.
@retval EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES Unable to allocate the output buffer Blt.
@retval EFI_WARN_UNKNOWN_GLYPH The glyph was unknown and was
replaced with the glyph for
Unicode character code 0xFFFD.
@retval EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER Blt is NULL, or Width is NULL, or
Height is NULL
**/
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_HII_GET_GLYPH)(
IN CONST EFI_HII_FONT_PROTOCOL *This,
IN CONST CHAR16 Char,
IN CONST EFI_FONT_DISPLAY_INFO *StringInfo,
OUT EFI_IMAGE_OUTPUT **Blt,
OUT UINTN *Baseline OPTIONAL
);
其中 Char 是你要取对应字形的文字(特别注意是单个的CHAR16),StringInfo 为 NULL时取得的是系统默认的字体,输出结果在 Blt 中。最后一项含义我不清楚……
再看一下输出结果是 EFI_IMAGE_OUTPUT。它的定义在 \MdePkg\Include\Protocol\HiiImage.h中。其中含有一个Union的定义,在我们这里使用时,会按照 EFI_GRAPHICS_OUTPUT_BLT_PIXEL 给出。
最后写一个简单的测试程序如下,功能是取得“z”字符的字形。
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/HiiFont.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status = 0;
UINTN BaseLine;
UINTN i,j;
EFI_HII_FONT_PROTOCOL *HiiFont = 0;
EFI_IMAGE_OUTPUT *Blt=NULL;
CHAR8 *c,*p;
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol (&gEfiHiiFontProtocolGuid, NULL, (VOID **) &HiiFont);
if (Status!=EFI_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"Error when LocateProtocol gEfiHiiFontProtocolGuid. Code[%r]\n",Status);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
Status = HiiFont->GetGlyph (
HiiFont, //Protocol instance
L'Z', //Show char 'Z'
NULL, //Use the defualt system font and color
&Blt, //GLYPH information
&BaseLine); //I don't know
Print(L"This is [%d]x[%d]\n",Blt->Width,Blt->Height);
c=(CHAR8*) Blt->Image.Bitmap;
for (j=0;j<Blt->Height;j++)
{
p=c;
for (i=0;i<Blt->Width;i++)
{
Print(L"%2X",(*c)&0xFF);
c=c+4;
}
Print(L" ");
c=p+1;
for (i=0;i<Blt->Width;i++)
{
Print(L"%2X",(*c)&0xFF);
c=c+4;
}
Print(L" ");
c=p+2;
for (i=0;i<Blt->Width;i++)
{
Print(L"%2X",(*c)&0xFF);
c=c+4;
}
c=p+(Blt->Width*4);
Print(L"\n");
}
c=(CHAR8*) Blt->Image.Bitmap;
for (j=0;j<Blt->Height;j++)
{
for (i=0;i<Blt->Width;i++)
{
if (*c!=0) {
Print(L"*");
}
else
{
Print(L" ");
}
c=c+4;
}
Print(L"\n");
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果,首先输出的是 R G B 数组,隐隐约约能看到其中有一个形状
程序后面有一个判断,直接输出星号和空格,结果如下,这样就看到非常清楚了。
完整的代码下载
GetGlyph
唯一的问题是:我还不知道取得这个东西能有什么用途…….
参考:
1.UEFI spec 2.4 P1711
最近调试程序的时候遇到一个奇怪的 Warning ,查了一会才找到原因:
c:\edk\AppPkg\Applications\C4066\C4066.c(17) : warning C4066: characters beyond first in wide-character constant ignored
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
Print(L'[%d]',2015);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
错误产生的原因是:把双引号写成了单引号,编译器以为你要定义一个 CHAR16 的字符,所以要忽略一些东西。修改的方法是,改成双引号即可。
参考:
1.https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa748819(v=vs.60).aspx
Compiler Warning (level 3) C4066
Visual Studio 6.0
characters beyond first in wide-character constant ignored
The compiler processes only the first character of a wide-character constant.
串口是非常有效和廉价的Debug手段,在开发中,几乎所有的UEFI 主板都会支持串口,本文介绍如何在Shell下面实现 串口通讯。
与之相关的是 EFI_SERIAL_IO_PROTOCOL,这个 Protocol 的定义可以在 UEFI Spec【参考1】中看到:
代码如下:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/SerialIo.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
EFI_GUID gEfiSerialIoProtocolGuid = { 0xBB25CF6F, 0xF1D4, 0x11D2, { 0x9A, 0x0C, 0x00, 0x90, 0x27, 0x3F, 0xC1, 0xFD }};
EFI_STATUS
DumpSetting(
IN UINT64 BaudRate,
IN UINT32 ReceiveFifoDepth,
IN UINT32 Timeout,
IN EFI_PARITY_TYPE Parity,
IN UINT8 DataBits,
IN EFI_STOP_BITS_TYPE StopBits)
{
Print(L" Timeout: [%d]\n",Timeout);
Print(L" BaudRate:[%ld]\n",BaudRate);
Print(L" DataBits:[%d]\n",DataBits);
Print(L" Parity: [%d]\n",Parity);
Print(L" StopBits:[%d]\n",StopBits);
Print(L" ReceiveFifoDepth:[%d]\n",ReceiveFifoDepth);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN char **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_SERIAL_IO_PROTOCOL *Serial;
CHAR8 *Textbuf1 = "www.lab-z.com waiting.........\n";
CHAR8 *Textbuf2 = "Continue............\n";
CHAR8 *Textbuf3 = "12345678";
CHAR16 *Textbuf4 = L" ";
UINTN BufferSize;
EFI_TIME TimeStart,TimeEnd;
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(
&gEfiSerialIoProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID **)&Serial);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Cannot find EFI_SERIAL_IO_PROTOCOL \r\n");
return Status;
}
Print(L"Current Settings:\n");
DumpSetting(
Serial->Mode->BaudRate,
Serial->Mode->ReceiveFifoDepth,
Serial->Mode->Timeout,
Serial->Mode->Parity,
Serial->Mode->DataBits & 0xFF,
Serial->Mode->StopBits);
// Baudrate 115200,Data Bits=8,Parity=None,Stop Bits=1,Flow Type= None
Status=Serial->SetAttributes( Serial,
115200,
Serial->Mode->ReceiveFifoDepth,
Serial->Mode->Timeout,
NoParity,
8,
OneStopBit);
if (Status!=EFI_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"[%d], %r",Status,Status);
}
Print(L"New Settings:\n");
DumpSetting(
Serial->Mode->BaudRate,
Serial->Mode->ReceiveFifoDepth,
Serial->Mode->Timeout,
Serial->Mode->Parity,
Serial->Mode->DataBits & 0xFF,
Serial->Mode->StopBits);
BufferSize=AsciiStrLen(Textbuf1);
Serial->Write(Serial,&BufferSize,Textbuf1);
gRT->GetTime(&TimeStart,NULL);
TimeEnd=TimeStart;
while ((TimeEnd.Hour - TimeStart.Hour) * 60 * 60
+ (TimeEnd.Minute - TimeStart.Minute)*60
+ (TimeEnd.Second - TimeStart.Second) < 30)
{
BufferSize=AsciiStrLen(Textbuf3);
Status=Serial->Read(Serial,&BufferSize,Textbuf3);
if ((Status==EFI_SUCCESS) && (BufferSize!=0))
{
Print(L"read [%d] %s\n",BufferSize,AsciiStrToUnicodeStr(Textbuf3,Textbuf4));
}
gRT->GetTime(&TimeEnd,NULL);
}
BufferSize=AsciiStrLen(Textbuf2);
Serial->Write(Serial,&BufferSize,Textbuf2);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
上面程序的基本流程:首先检查一下串口设置,打印在屏幕上,然后设置为我们通常使用的 115200。最后测试用 Write从 Shell 下发送数据出来,再尝试用Read接收数据。
程序运行结果:
完整代码下载:
特别注意:Shell 使用 Read 只能接收固定长度的数据。比如: Read(Serial,8,Textbuf) 那么只能接收8个字符,如果你只输入了7个bytes,不会有反应;如果输入了9个bytes,那么只能收到前面8个。目前不清楚为什么有这样的限制。
另外,对于普通的串口,使用GetControl 获得的当前的状态中并没有当前串口的发送接收状态。定义的 EFI_SERIAL_INPUT_BUFFER_EMPTY和EFI_SERIAL_OUTPUT_BUFFER_EMPTY 应该是给存在对应线路的串口使用的,是一种硬件线路的标志。如果你只用了 TX RX GND , 这里的状态是没有意义的。
参考:
1. UEFI Spec 2.4 P476
UDK2015 发布已经有一段时间了,这几天正好有需要,所以研究了一下。安装和使用上与之前的版本没什么差别,都是解压 MyWorkSpace到需要的目录中,然后再放入 BaseTools(Windows).zip 中的内容。
但是,发布这个版本的人一定没有在 Windows XP 下次试过,编译BaseTool的工具也一定不是 VS2008。于是,按照上述方法配置后, Win32 下面的 GenFv.exe GetBootSector.exe 等等工具都无法运行,错误信息是“不是有效的 Win32 应用程序”。解决方法是:重新编译一次 C版本的工具,具体做法请参考之前的文章。
这里下载 UDK2015 还有我重新编译过的 BaseTools ,可以在 XP中运行
其中还有一个配置好的 VirtualBox 的虚拟机镜像,有需要的朋友可以直接下载到本地运行。
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eQNvkR4 密码:eks0
某些时候因为一些特殊的原因,使得我们不能直接使用U盘之类的存储设备,比如:不容许使用U盘,只能让你手工编辑文档然后按上机时间收费。但是,只要运行在Windows系统上,USB键盘还能使用,我们就有办法输入我们需要的代码进去。
先说一下原理,Windows自带了一个叫做“写字板”的程序,他定义了一种 RTF 格式的文件。在这种文件中,可以根据需要插入一些附件,RTF内容完全是可见的 ASCII字符组成。
比如,我在下面这个文档中插入了一个图片:
保存之后在用十六进制编辑工具打开看到的内容如下,可以看到全部都是可见的ASCII 字符(除了换行和回车):
如果我们在目标机器上从键盘输入这些 ASCII 字符,保存之后即可重建整个文件。
设计这样的设备要求能够模拟为USB键盘,我选择Arduino Pro Micro 外加一个SD卡读卡器和一张SD卡即可。
代码如下:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// On the Ethernet Shield, CS is pin 4. Note that even if it's not
// used as the CS pin, the hardware CS pin (10 on most Arduino boards,
// 53 on the Mega) must be left as an output or the SD library
// functions will not work.
const int chipSelect = 10;
int RUNMARK=false;
void setup()
{
// make sure that the default chip select pin is set to
// output, even if you don't use it:
pinMode(10, OUTPUT);
pinMode(3, INPUT_PULLUP);
Keyboard.begin();
// see if the card is present and can be initialized:
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
return;
}
}
void loop()
{
if ((digitalRead(3)==LOW)&&(RUNMARK==false)) {
// open the file. note that only one file can be open at a time,
// so you have to close this one before opening another.
File dataFile = SD.open("type.rtf");
// if the file is available, write to it:
if (dataFile) {
while (dataFile.available()) {
Keyboard.print(char(dataFile.read()));
delay(10);
}
dataFile.close();
}
Keyboard.end();
RUNMARK=true;
}
}
设计上特别之处在于:
设定Pin3为开关,更新程序之后,短接GND和Pin3即打开自动输入功能。在使用USB键盘鼠标模拟的时候,这是必须的,否则你会发现下一次刷写用于干扰会难以完成;
在发送字符的时候,还有一个Delay,这是多次实验得到的值,如果不放这个的话,输入1.8K 左右个字符之后,会停止,我比较怀疑是Arduino内存耗尽导致的。
工作的视频:
http://www.tudou.com/programs/view/GtsGFH8yRyA/?resourceId=0_06_02_99
最后:当然如果你没有我这个装置,有足够的耐心的话,手工敲入每个字符也是可以的。
最近在看书,上面讲中世纪的僧侣抄写《圣经》,为了防止出错,给每一个字母编上一个数字,先计算原文每行字母之和,再计算抄写之后每行字母之和这样能保证抄写结果和原文完全一致。不知道除了让人一遍遍看中文是否有这样的纠错办法?
最后鸣谢Windows专家,天杀同学~
前几天看吴军《数学之美》 P11 提到
当司马迁用近53万字记载了总过上千年历史的同时,远在中东的犹太人也用类似的篇幅记载了自创世纪以来,主要是摩西以来他们祖先的历史,这就是《圣经》中的《旧约》部分。《圣经》简洁的文风和中国的《史记》颇有相似之处。但是和史记这本由唯一作者写成的史书不同,《圣经》的写作持续了很多世纪,后世的人在做补充时,看到的是几百年前甚至上千年前原作的抄本,抄写的错误便在所难免,据说今天也只有牛津大学保留了一本没有任何错误的古本。虽然做事认真的犹太人要求在抄写《圣经》时,要虔诚并且打起十二分精神,尤其每写道上帝(GOD和Lord)这个词时要去洗手起到,但是抄写错误还是难以避免。于是犹太人发明了一种类似于我们今天计算机和通信中校验码的方法。他们把每一个希伯来字母对应一个数字,这样每行文字加起来便得到一个特殊的数字,这个数字便成为了这一行的校验码。同样,对于每一列也是这样处理,当犹太学者抄完一页《圣经》时,他们需要把每一行的文字加起来,看看新的校验码是否和原文的相同,然后对每一页进行同样的处理。如果这一页每一行和每一列的校验码和原文完全相同,说明这一页的抄写无误。如果某行的校验码和原文中的对应不上,则说明这一行至少有一个抄写错误。当然,错误的对应列的校验码也一定和原文对不上,这样可以很快找到出错的地方,这背后的原理我们今天的各种校验是相同的。
我们在 EDK2 的代码中能看到 Shell下部分命令的代码,这里介绍如何把这样的代码提取出来做成能够独立编译和运行的程序。简单起见,以 Stall 命令和 MV 命令为例。
经过试验,这些命令中使用到的大部分函数都可以在 ShellLib.h 中找到,我们要做的只是把这个文件copy一份到我们程序下面。
最后修改之后的程序如下:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include "ShellLib.h"
#define ASSERT(Expression)
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_PROBLEM[] = L"Error. The argument '%s' is incorrect.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_TOO_FEW[] = L"Error. Too few arguments specified.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_TOO_MANY[]= L"Error. Too many arguments specified.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_PROBLEM_VAL[] = L"Error. The argument '%s' has incorrect value.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_STALL_FAILED[] = L"Error. BootService Stall() failed with %r.\r\n";
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
LIST_ENTRY *Package;
CHAR16 *ProblemParam;
SHELL_STATUS ShellStatus;
UINT64 Intermediate;
//
// parse the command line
//
Status = ShellCommandLineParse (EmptyParamList, &Package, &ProblemParam, TRUE);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (Status == EFI_VOLUME_CORRUPTED && ProblemParam != NULL) {
Print(STR_GEN_PROBLEM,ProblemParam);
FreePool(ProblemParam);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else {
ASSERT(FALSE);
}
} else {
if (ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 2) != NULL) {
Print(STR_GEN_TOO_MANY);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else if (ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1) == NULL) {
Print(STR_GEN_TOO_FEW);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else {
Status = ShellConvertStringToUint64(
ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1), &Intermediate, FALSE, FALSE);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status) || ((UINT64)(UINTN)(Intermediate)) != Intermediate) {
Print(STR_GEN_PROBLEM_VAL, ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1));
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else {
Status = gBS->Stall((UINTN)Intermediate);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(STR_STALL_FAILED, Status);
ShellStatus = SHELL_DEVICE_ERROR;
}
}
}
ShellCommandLineFreeVarList (Package);
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
完整代码下载(特别注意,涉及到时钟的程序在NT32模拟环境中和实际环境中存在很大差别,不要在实际环境中使用为模拟环境编译的EFI文件)。
zStall
总结一下,如果想把一个命令改造为独立的程序,需要做下面的事情:
1. 增加 #define ASSERT(Expression) 这个定义,上面代码为了简单,我只是定义它为空
2. 拷贝 ShellLib.h 到你的代码目录下,然后用 “”直接使用
3. 改造程序中定义的字符串,这些字符串都是定义在 UNI 文件中。如果你没有多语言的需要,可以像我这样在代码中重新定义一次
4. 将所有的 ShellPrintHiiEx 都修改为 Print
下面再用 MV 命令的代码练习一下
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include <Library/BaseMemoryLib.h>
#include <Protocol/UnicodeCollation.h>
#include "ShellLib.h"
#define ASSERT(Expression)
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_PROBLEM[] = L"Error. The argument '%s' is incorrect.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_TOO_MANY[]= L"Error. Too many arguments specified.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_TOO_FEW[] = L"Error. Too few arguments specified.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_NO_CWD[] = L"Error. No current directory is specified.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_FILE_NF[] = L"Error. File '%s' was not found.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_ERR_FILE[]= L"Error. File '%s' error: %r\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_MV_INV_SUB[] = L"Error. Cannot move a directory into itself or its subdirectory.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_MV_INV_RO[] = L"Error. Cannot move a read-only File or Directory.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_MV_INV_CWD[] = L"Error. Cannot move current working directory or its subdirectory.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_MV_INV_FS[] = L"Error. Cannot move between file systems.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_NO_MEM[] = L"Error. Memory is not available.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_ERR_UK[] = L"Error: %r\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_MV_OUTPUT[] = L"Moving %s -> %s\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_RES_OK[] = L"- [ok]\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_MARG_ERROR[] = L"Error. The destination '%s' is ambigious.\r\n";
CONST CHAR16 STR_GEN_FILE_ERROR[] = L"Error. The destination is an existant file '%s'.\r\n";
//copy from \ShellPkg\Library\BasePathLib\BasePathLib.c
/**
Removes the last directory or file entry in a path by changing the last
L'\' to a CHAR_NULL.
@param[in, out] Path The pointer to the path to modify.
@retval FALSE Nothing was found to remove.
@retval TRUE A directory or file was removed.
**/
BOOLEAN
EFIAPI
PathRemoveLastItem(
IN OUT CHAR16 *Path
)
{
CHAR16 *Walker;
CHAR16 *LastSlash;
//
// get directory name from path... ('chop' off extra)
//
for ( Walker = Path, LastSlash = NULL
; Walker != NULL && *Walker != CHAR_NULL
; Walker++
){
if (*Walker == L'\\' && *(Walker + 1) != CHAR_NULL) {
LastSlash = Walker+1;
}
}
if (LastSlash != NULL) {
*LastSlash = CHAR_NULL;
return (TRUE);
}
return (FALSE);
}
/**
Function to take a destination path that might contain wildcards and verify
that there is only a single possible target (IE we cant have wildcards that
have 2 possible destination).
if the result is sucessful the caller must free *DestPathPointer.
@param[in] DestDir The original path to the destination.
@param[in, out] DestPathPointer A pointer to the callee allocated final path.
@param[in] Cwd A pointer to the current working directory.
@retval SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER The DestDir could not be resolved to a location.
@retval SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER The DestDir could be resolved to more than 1 location.
@retval SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER Cwd is required and is NULL.
@retval SHELL_SUCCESS The operation was sucessful.
**/
SHELL_STATUS
EFIAPI
GetDestinationLocation(
IN CONST CHAR16 *DestDir,
IN OUT CHAR16 **DestPathPointer,
IN CONST CHAR16 *Cwd
)
{
EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *DestList;
EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *Node;
CHAR16 *DestPath;
UINTN NewSize;
UINTN CurrentSize;
DestList = NULL;
DestPath = NULL;
if (StrStr(DestDir, L"\\") == DestDir) {
if (Cwd == NULL) {
return SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
}
DestPath = AllocateZeroPool(StrSize(Cwd));
if (DestPath == NULL) {
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
StrCpy(DestPath, Cwd);
while (PathRemoveLastItem(DestPath)) ;
//
// Append DestDir beyond '\' which may be present
//
CurrentSize = StrSize(DestPath);
StrnCatGrow(&DestPath, &CurrentSize, &DestDir[1], 0);
*DestPathPointer = DestPath;
return (SHELL_SUCCESS);
}
//
// get the destination path
//
ShellOpenFileMetaArg((CHAR16*)DestDir, EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|EFI_FILE_MODE_READ|EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE, &DestList);
if (DestList == NULL || IsListEmpty(&DestList->Link)) {
//
// Not existing... must be renaming
//
if (StrStr(DestDir, L":") == NULL) {
if (Cwd == NULL) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
return (SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER);
}
NewSize = StrSize(Cwd);
NewSize += StrSize(DestDir);
DestPath = AllocateZeroPool(NewSize);
if (DestPath == NULL) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
StrCpy(DestPath, Cwd);
if (DestPath[StrLen(DestPath)-1] != L'\\' && DestDir[0] != L'\\') {
StrCat(DestPath, L"\\");
} else if (DestPath[StrLen(DestPath)-1] == L'\\' && DestDir[0] == L'\\') {
((CHAR16*)DestPath)[StrLen(DestPath)-1] = CHAR_NULL;
}
StrCat(DestPath, DestDir);
} else {
ASSERT(DestPath == NULL);
DestPath = StrnCatGrow(&DestPath, NULL, DestDir, 0);
if (DestPath == NULL) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
}
} else {
Node = (EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO*)GetFirstNode(&DestList->Link);
//
// Make sure there is only 1 node in the list.
//
if (!IsNodeAtEnd(&DestList->Link, &Node->Link)) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
Print(STR_GEN_MARG_ERROR, DestDir);
return (SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER);
}
if (ShellIsDirectory(Node->FullName)==EFI_SUCCESS) {
DestPath = AllocateZeroPool(StrSize(Node->FullName)+sizeof(CHAR16));
if (DestPath == NULL) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES);
}
StrCpy(DestPath, Node->FullName);
StrCat(DestPath, L"\\");
} else {
//
// cant move onto another file.
//
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
Print(STR_GEN_FILE_ERROR,DestDir);
return (SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER);
}
}
*DestPathPointer = DestPath;
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&DestList);
return (SHELL_SUCCESS);
}
/**
Function to clean up paths.
- Single periods in the path are removed.
- Double periods in the path are removed along with a single parent directory.
- Forward slashes L'/' are converted to backward slashes L'\'.
This will be done inline and the existing buffer may be larger than required
upon completion.
@param[in] Path The pointer to the string containing the path.
@retval NULL An error occured.
@return Path in all other instances.
**/
CHAR16*
EFIAPI
PathCleanUpDirectories(
IN CHAR16 *Path
)
{
CHAR16 *TempString;
UINTN TempSize;
if (Path==NULL) {
return(NULL);
}
//
// Fix up the '/' vs '\'
//
for (TempString = Path ; TempString != NULL && *TempString != CHAR_NULL ; TempString++) {
if (*TempString == L'/') {
*TempString = L'\\';
}
}
//
// Fix up the ..
//
while ((TempString = StrStr(Path, L"\\..\\")) != NULL) {
*TempString = CHAR_NULL;
TempString += 4;
PathRemoveLastItem(Path);
TempSize = StrSize(TempString);
CopyMem(Path+StrLen(Path), TempString, TempSize);
}
if ((TempString = StrStr(Path, L"\\..")) != NULL && *(TempString + 3) == CHAR_NULL) {
*TempString = CHAR_NULL;
PathRemoveLastItem(Path);
}
//
// Fix up the .
//
while ((TempString = StrStr(Path, L"\\.\\")) != NULL) {
*TempString = CHAR_NULL;
TempString += 2;
TempSize = StrSize(TempString);
CopyMem(Path+StrLen(Path), TempString, TempSize);
}
if ((TempString = StrStr(Path, L"\\.")) != NULL && *(TempString + 2) == CHAR_NULL) {
*(TempString + 1) = CHAR_NULL;
}
return (Path);
}
STATIC EFI_UNICODE_COLLATION_PROTOCOL *mUnicodeCollation = NULL;
/**
Function to compare 2 strings without regard to case of the characters.
@param[in] Buffer1 Pointer to String to compare.
@param[in] Buffer2 Pointer to second String to compare.
@retval 0 Buffer1 equal to Buffer2.
@return < 0 Buffer1 is less than Buffer2.
@return > 0 Buffer1 is greater than Buffer2.
**/
INTN
EFIAPI
StringNoCaseCompare (
IN CONST VOID *Buffer1,
IN CONST VOID *Buffer2
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
if (mUnicodeCollation == NULL) {
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(
&gEfiUnicodeCollation2ProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID**)&mUnicodeCollation);
ASSERT(Status);
}
return (mUnicodeCollation->StriColl(
mUnicodeCollation,
*(CHAR16**)Buffer1,
*(CHAR16**)Buffer2));
}
/**
Function to validate that moving a specific file (FileName) to a specific
location (DestPath) is valid.
This function will verify that the destination is not a subdirectory of
FullName, that the Current working Directory is not being moved, and that
the directory is not read only.
if the move is invalid this function will report the error to StdOut.
@param FullName [in] The name of the file to move.
@param Cwd [in] The current working directory
@param DestPath [in] The target location to move to
@param Attribute[in] The Attribute of the file
@retval TRUE The move is valid
@retval FALSE The move is not
**/
BOOLEAN
EFIAPI
IsValidMove(
IN CONST CHAR16 *FullName,
IN CONST CHAR16 *Cwd,
IN CONST CHAR16 *DestPath,
IN CONST UINT64 Attribute
)
{
CHAR16 *Test;
CHAR16 *Test1;
CHAR16 *TestWalker;
INTN Result;
UINTN TempLen;
if (Cwd != NULL && StrCmp(FullName, Cwd) == 0) {
//
// Invalid move
//
Print(STR_MV_INV_CWD);
return (FALSE);
}
Test = NULL;
Test = StrnCatGrow(&Test, NULL, DestPath, 0);
TestWalker = Test;
ASSERT(TestWalker != NULL);
while(*TestWalker == L'\\') {
TestWalker++;
}
while(TestWalker != NULL && TestWalker[StrLen(TestWalker)-1] == L'\\') {
TestWalker[StrLen(TestWalker)-1] = CHAR_NULL;
}
ASSERT(TestWalker != NULL);
ASSERT(FullName != NULL);
if (StrStr(FullName, TestWalker) != 0) {
TempLen = StrLen(FullName);
if (StrStr(FullName, TestWalker) != FullName // not the first items... (could below it)
&& TempLen <= (StrLen(TestWalker) + 1)
&& StrStr(FullName+StrLen(TestWalker) + 1, L"\\") == NULL) {
//
// Invalid move
//
Print(STR_MV_INV_SUB);
FreePool(Test);
return (FALSE);
}
}
FreePool(Test);
if (StrStr(DestPath, FullName) != 0 && StrStr(DestPath, FullName) != DestPath) {
//
// Invalid move
//
Print(STR_MV_INV_SUB);
return (FALSE);
}
if ((Attribute & EFI_FILE_READ_ONLY) != 0) {
//
// invalid to move read only
//
Print(STR_MV_INV_RO);
return (FALSE);
}
Test = StrStr(FullName, L":");
Test1 = StrStr(DestPath, L":");
if (Test1 != NULL && Test != NULL) {
*Test = CHAR_NULL;
*Test1 = CHAR_NULL;
Result = StringNoCaseCompare(&FullName, &DestPath);
*Test = L':';
*Test1 = L':';
if (Result != 0) {
Print(STR_MV_INV_FS);
return (FALSE);
}
}
return (TRUE);
}
/**
function to take a list of files to move and a destination location and do
the verification and moving of those files to that location. This function
will report any errors to the user and continue to move the rest of the files.
@param[in] FileList A LIST_ENTRY* based list of files to move
@param[out] Resp pointer to response from question. Pass back on looped calling
@param[in] DestDir the destination location
@retval SHELL_SUCCESS the files were all moved.
@retval SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER a parameter was invalid
@retval SHELL_SECURITY_VIOLATION a security violation ocurred
@retval SHELL_WRITE_PROTECTED the destination was write protected
@retval SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES a memory allocation failed
**/
SHELL_STATUS
EFIAPI
ValidateAndMoveFiles(
IN CONST EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *FileList,
OUT VOID **Resp,
IN CONST CHAR16 *DestDir
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
CHAR16 *DestPath;
CONST CHAR16 *Cwd;
SHELL_STATUS ShellStatus;
CONST EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *Node;
EFI_FILE_INFO *NewFileInfo;
CHAR16 *TempLocation;
UINTN NewSize;
UINTN Length;
VOID *Response;
SHELL_FILE_HANDLE DestHandle;
CHAR16 STR_GEN_DEST_EXIST_OVR[] = L"Destination file already exists. Overwrite? Yes, No, All, Cancel ";
ASSERT(FileList != NULL);
ASSERT(DestDir != NULL);
DestPath = NULL;
Cwd = ShellGetCurrentDir(NULL);
Response = *Resp;
//
// Get and validate the destination location
//
ShellStatus = GetDestinationLocation(DestDir, &DestPath, Cwd);
if (ShellStatus != SHELL_SUCCESS) {
return (ShellStatus);
}
DestPath = PathCleanUpDirectories(DestPath);
//
// Go through the list of files and directories to move...
//
for (Node = (EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *)GetFirstNode(&FileList->Link)
; !IsNull(&FileList->Link, &Node->Link)
; Node = (EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *)GetNextNode(&FileList->Link, &Node->Link)
){
if (ShellGetExecutionBreakFlag()) {
break;
}
ASSERT(Node->FileName != NULL);
ASSERT(Node->FullName != NULL);
//
// skip the directory traversing stuff...
//
if (StrCmp(Node->FileName, L".") == 0 || StrCmp(Node->FileName, L"..") == 0) {
continue;
}
//
// Validate that the move is valid
//
if (!IsValidMove(Node->FullName, Cwd, DestPath, Node->Info->Attribute)) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
continue;
}
//
// Chop off map info from "DestPath"
//
if ((TempLocation = StrStr(DestPath, L":")) != NULL) {
CopyMem(DestPath, TempLocation+1, StrSize(TempLocation+1));
}
//
// construct the new file info block
//
NewSize = StrSize(DestPath);
NewSize += StrSize(Node->FileName) + SIZE_OF_EFI_FILE_INFO + sizeof(CHAR16);
NewFileInfo = AllocateZeroPool(NewSize);
if (NewFileInfo == NULL) {
Print(STR_GEN_NO_MEM);
ShellStatus = SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES;
} else {
CopyMem(NewFileInfo, Node->Info, SIZE_OF_EFI_FILE_INFO);
if (DestPath[0] != L'\\') {
StrCpy(NewFileInfo->FileName, L"\\");
StrCat(NewFileInfo->FileName, DestPath);
} else {
StrCpy(NewFileInfo->FileName, DestPath);
}
Length = StrLen(NewFileInfo->FileName);
if (Length > 0) {
Length--;
}
if (NewFileInfo->FileName[Length] == L'\\') {
if (Node->FileName[0] == L'\\') {
//
// Don't allow for double slashes. Eliminate one of them.
//
NewFileInfo->FileName[Length] = CHAR_NULL;
}
StrCat(NewFileInfo->FileName, Node->FileName);
}
NewFileInfo->Size = SIZE_OF_EFI_FILE_INFO + StrSize(NewFileInfo->FileName);
Print(STR_MV_OUTPUT, Node->FullName, NewFileInfo->FileName);
if (!EFI_ERROR(ShellFileExists(NewFileInfo->FileName))) {
if (Response == NULL) {
ShellPromptForResponse(ShellPromptResponseTypeYesNoAllCancel, STR_GEN_DEST_EXIST_OVR, &Response);
}
switch (*(SHELL_PROMPT_RESPONSE*)Response) {
case ShellPromptResponseNo:
FreePool(NewFileInfo);
continue;
case ShellPromptResponseCancel:
*Resp = Response;
//
// indicate to stop everything
//
FreePool(NewFileInfo);
FreePool(DestPath);
return (SHELL_ABORTED);
case ShellPromptResponseAll:
*Resp = Response;
break;
case ShellPromptResponseYes:
FreePool(Response);
break;
default:
FreePool(Response);
FreePool(NewFileInfo);
FreePool(DestPath);
return SHELL_ABORTED;
}
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(NewFileInfo->FileName, &DestHandle, EFI_FILE_MODE_READ|EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE, 0);
ShellDeleteFile(&DestHandle);
}
//
// Perform the move operation
//
Status = ShellSetFileInfo(Node->Handle, NewFileInfo);
//
// Free the info object we used...
//
FreePool(NewFileInfo);
//
// Check our result
//
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(STR_GEN_ERR_UK, Status);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
if (Status == EFI_SECURITY_VIOLATION) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_SECURITY_VIOLATION;
} else if (Status == EFI_WRITE_PROTECTED) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_WRITE_PROTECTED;
} else if (Status == EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES;
} else if (Status == EFI_DEVICE_ERROR) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_DEVICE_ERROR;
} else if (Status == EFI_ACCESS_DENIED) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_ACCESS_DENIED;
}
} else {
Print( L"%s", STR_GEN_RES_OK);
}
}
} // for loop
FreePool(DestPath);
return (ShellStatus);
}
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
LIST_ENTRY *Package;
CHAR16 *ProblemParam;
SHELL_STATUS ShellStatus;
UINTN ParamCount;
UINTN LoopCounter;
EFI_SHELL_FILE_INFO *FileList;
VOID *Response;
ProblemParam = NULL;
ShellStatus = SHELL_SUCCESS;
ParamCount = 0;
FileList = NULL;
Response = NULL;
//
// parse the command line
//
Status = ShellCommandLineParse (EmptyParamList, &Package, &ProblemParam, TRUE);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
if (Status == EFI_VOLUME_CORRUPTED && ProblemParam != NULL) {
Print(STR_GEN_PROBLEM , ProblemParam);
FreePool(ProblemParam);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else {
ASSERT(FALSE);
}
} else {
//
// check for "-?"
//
if (ShellCommandLineGetFlag(Package, L"-?")) {
ASSERT(FALSE);
}
switch (ParamCount = ShellCommandLineGetCount(Package)) {
case 0:
case 1:
//
// we have insufficient parameters
//
Print(STR_GEN_TOO_FEW);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
break;
case 2:
//
// must have valid CWD for single parameter...
//
if (ShellGetCurrentDir(NULL) == NULL){
Print(STR_GEN_NO_CWD);
ShellStatus = SHELL_INVALID_PARAMETER;
} else {
Status = ShellOpenFileMetaArg((CHAR16*)ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1), EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|EFI_FILE_MODE_READ, &FileList);
if (FileList == NULL || IsListEmpty(&FileList->Link) || EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(STR_GEN_FILE_NF, ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1));
ShellStatus = SHELL_NOT_FOUND;
} else {
//
// ValidateAndMoveFiles will report errors to the screen itself
//
ShellStatus = ValidateAndMoveFiles(FileList, &Response, ShellGetCurrentDir(NULL));
}
}
break;
default:
///@todo make sure this works with error half way through and continues...
for (ParamCount--, LoopCounter = 1 ; LoopCounter < ParamCount ; LoopCounter++) {
if (ShellGetExecutionBreakFlag()) {
break;
}
Status = ShellOpenFileMetaArg((CHAR16*)ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, LoopCounter), EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE|EFI_FILE_MODE_READ, &FileList);
if (FileList == NULL || IsListEmpty(&FileList->Link) || EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(STR_GEN_FILE_NF, ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, LoopCounter));
ShellStatus = SHELL_NOT_FOUND;
} else {
//
// ValidateAndMoveFiles will report errors to the screen itself
// Only change ShellStatus if it's sucessful
//
if (ShellStatus == SHELL_SUCCESS) {
ShellStatus = ValidateAndMoveFiles(FileList, &Response, ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, ParamCount));
} else {
ValidateAndMoveFiles(FileList, &Response, ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, ParamCount));
}
}
if (FileList != NULL && !IsListEmpty(&FileList->Link)) {
Status = ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&FileList);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status) && ShellStatus == SHELL_SUCCESS) {
ShellStatus = SHELL_ACCESS_DENIED;
Print(STR_GEN_ERR_FILE , ShellCommandLineGetRawValue(Package, 1), ShellStatus|MAX_BIT);
}
}
}
break;
} // switch on parameter count
if (FileList != NULL) {
ShellCloseFileMetaArg(&FileList);
}
//
// free the command line package
//
ShellCommandLineFreeVarList (Package);
}
SHELL_FREE_NON_NULL(Response);
if (ShellGetExecutionBreakFlag()) {
return (SHELL_ABORTED);
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
完整代码下载:
实验了一下之前买的一个 Micro SD Card的模块【参考1】
SD卡是工作在 3.3v电压下面的,这个板子最主要的作用是实现5v转3.3v。我使用的是 Arduino Micro Pro.线路接法如下:
| SD Card | Arduino Pro Micro |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | VCC(5V) |
| MISO | Pin14 |
| MOSI | Pin16 |
| SCK | Pin15 |
| CS | Pin10 |
测试代码在 文件 -> 示例 –> SD –>CardInfo
/*
SD card test
This example shows how use the utility libraries on which the'
SD library is based in order to get info about your SD card.
Very useful for testing a card when you're not sure whether its working or not.
The circuit:
* SD card attached to SPI bus as follows:
** MOSI - pin 11 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** MISO - pin 12 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** CLK - pin 13 on Arduino Uno/Duemilanove/Diecimila
** CS - depends on your SD card shield or module.
Pin 4 used here for consistency with other Arduino examples
created 28 Mar 2011
by Limor Fried
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe
*/
// include the SD library:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// set up variables using the SD utility library functions:
Sd2Card card;
SdVolume volume;
SdFile root;
// change this to match your SD shield or module;
// Arduino Ethernet shield: pin 4
// Adafruit SD shields and modules: pin 10
// Sparkfun SD shield: pin 8
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup()
{
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for Leonardo only
}
Serial.print("\nInitializing SD card...");
// On the Ethernet Shield, CS is pin 4. It's set as an output by default.
// Note that even if it's not used as the CS pin, the hardware SS pin
// (10 on most Arduino boards, 53 on the Mega) must be left as an output
// or the SD library functions will not work.
pinMode(10, OUTPUT); // change this to 53 on a mega
// we'll use the initialization code from the utility libraries
// since we're just testing if the card is working!
if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed. Things to check:");
Serial.println("* is a card is inserted?");
Serial.println("* Is your wiring correct?");
Serial.println("* did you change the chipSelect pin to match your shield or module?");
return;
} else {
Serial.println("Wiring is correct and a card is present.");
}
// print the type of card
Serial.print("\nCard type: ");
switch (card.type()) {
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1:
Serial.println("SD1");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2:
Serial.println("SD2");
break;
case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC:
Serial.println("SDHC");
break;
default:
Serial.println("Unknown");
}
// Now we will try to open the 'volume'/'partition' - it should be FAT16 or FAT32
if (!volume.init(card)) {
Serial.println("Could not find FAT16/FAT32 partition.\nMake sure you've formatted the card");
return;
}
// print the type and size of the first FAT-type volume
uint32_t volumesize;
Serial.print("\nVolume type is FAT");
Serial.println(volume.fatType(), DEC);
Serial.println();
volumesize = volume.blocksPerCluster(); // clusters are collections of blocks
volumesize *= volume.clusterCount(); // we'll have a lot of clusters
volumesize *= 512; // SD card blocks are always 512 bytes
Serial.print("Volume size (bytes): ");
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Kbytes): ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.print("Volume size (Mbytes): ");
volumesize /= 1024;
Serial.println(volumesize);
Serial.println("\nFiles found on the card (name, date and size in bytes): ");
root.openRoot(volume);
// list all files in the card with date and size
root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE);
}
void loop(void) {
}
运行结果
参考:
1. 淘宝店铺 赛宝电子
ArduinoSB配件 Micro SD卡模块 SPI接口 迷你TF卡读写(H5A2)