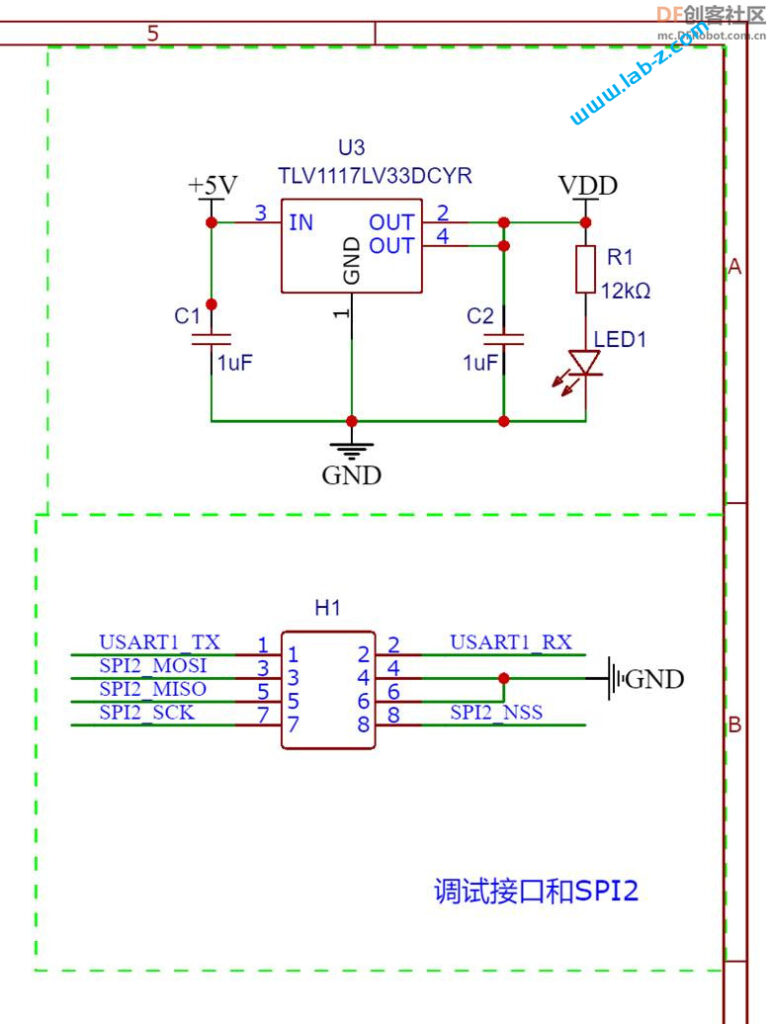
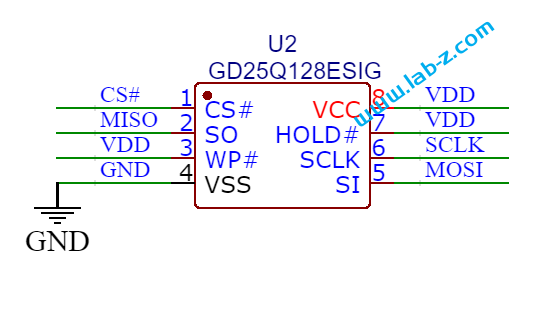
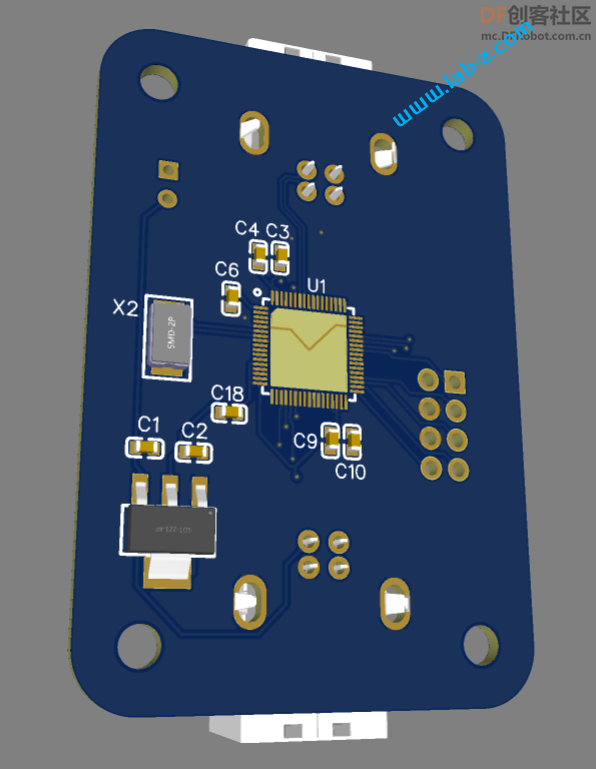
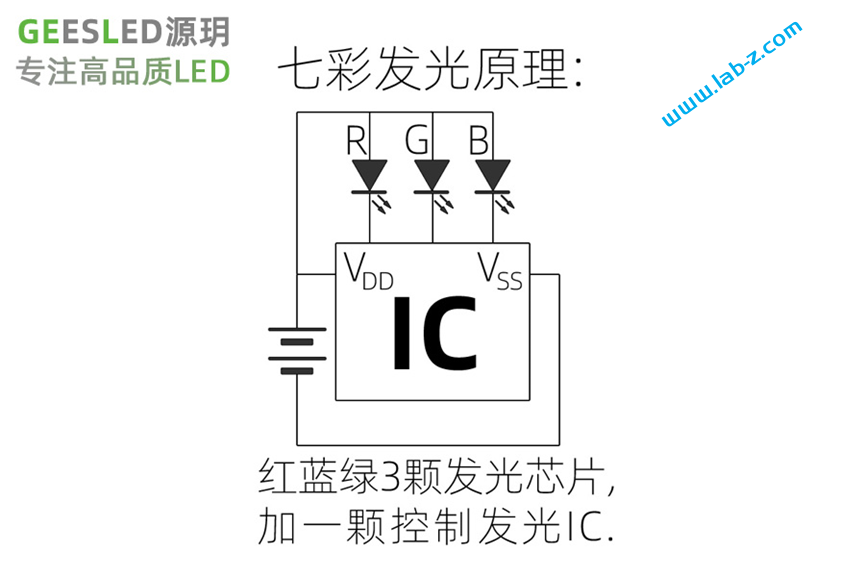
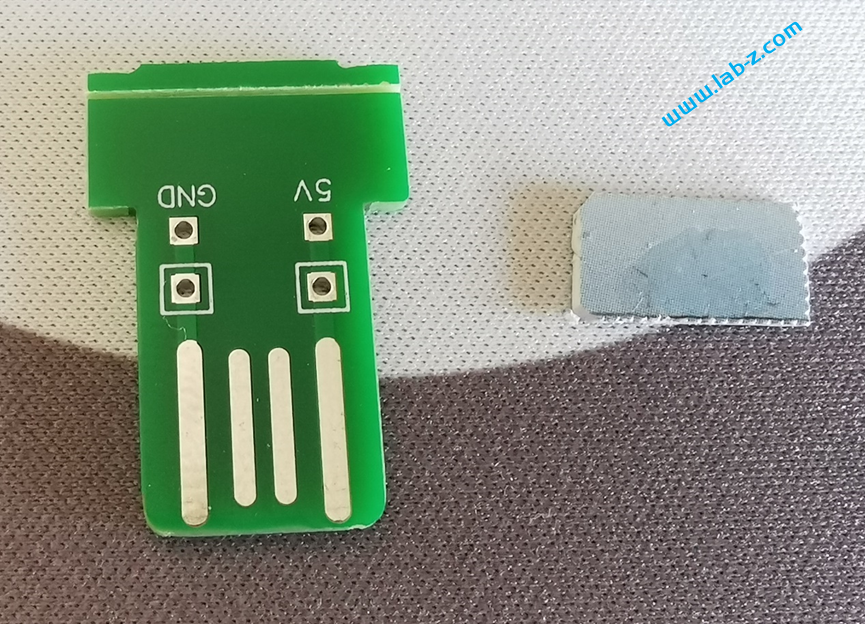
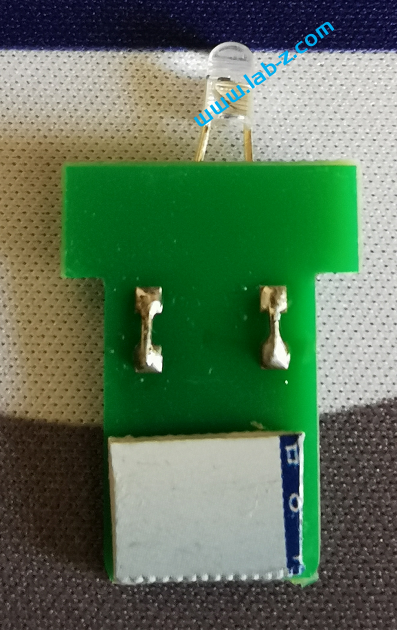
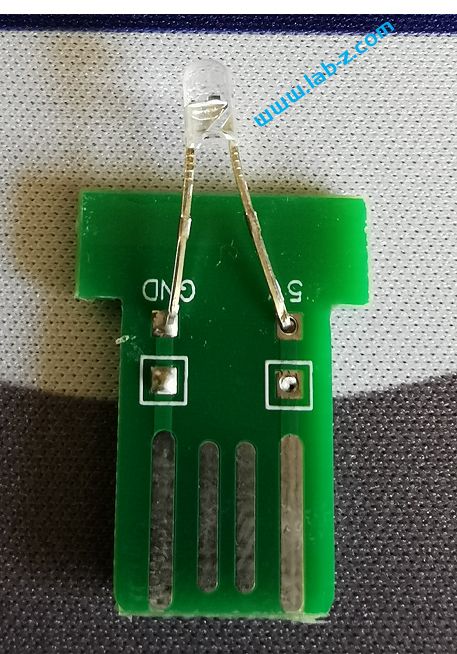
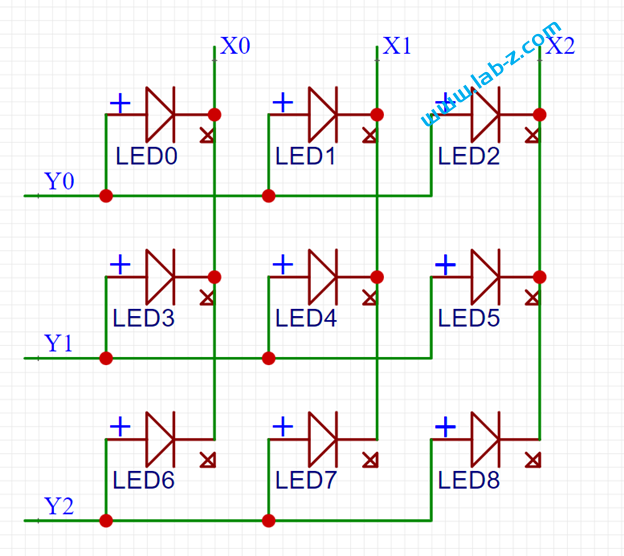
在开始之前,首先介绍LED 的静态驱动和动态驱动的概念。当我们在一个发光二极管两端加上一个电压的时候,发光二极管即可工作。理论上,如果驱动N个共阴极的LED那么需要N个提供正电压。这种带来一个问题,如果需要驱动大量的LED,那么就同样需要同样数量的引脚作为正极。对于单片机来说,会遇到IO引脚不够的问题。
可以看到这种电路,我们可以一次性点亮一行或者一列上的LED,但是如果要点亮的位于不同的行列就会出现问题。例如:我们希望在矩阵上点亮LED0和LED6, 那么需要Y0、Y2为高,X0 为低,这种情况比较简单;但是如果需要同时点亮LED0和 LED4 问题就变得麻烦。因为 LED0 要求Y0 为高X0为低才能点亮,LED4 要求Y1为高X1为低,但是Y1为高X0为低时LED3也会同时亮起。因此,这里需要引入一个分时点亮的方法,比如,先设置Y0 为高X0为低点亮LED0,再设置Y0为低熄灭LED0,设置Y1为高X1为低点亮LED4,只要点亮速度足够快眼睛无法分辨出他们不是同时点亮的。这就是所谓的“动态扫描”。
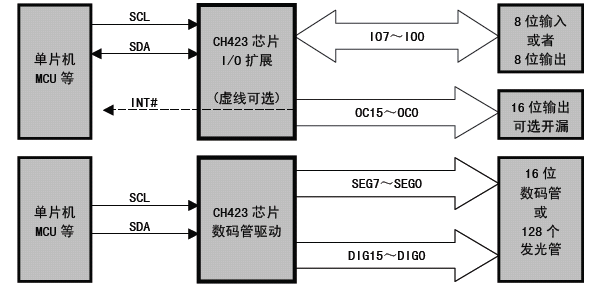
可以看出,这样的方法会使得程序复杂度上升,同样的,对于N 个灯需要根号N 个 IO。经过研究发现一个好玩的 IC: WCH 的 CH423。它是IC I/O 扩展芯片,功能如下【参考1】:
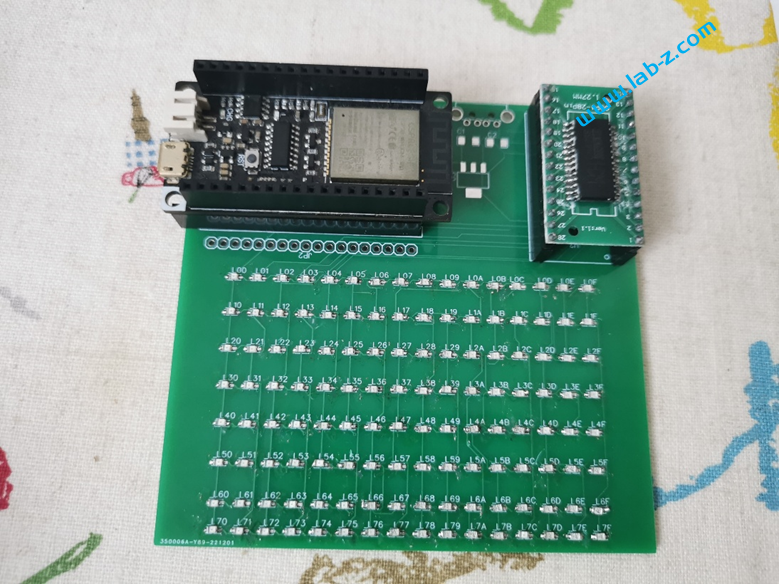
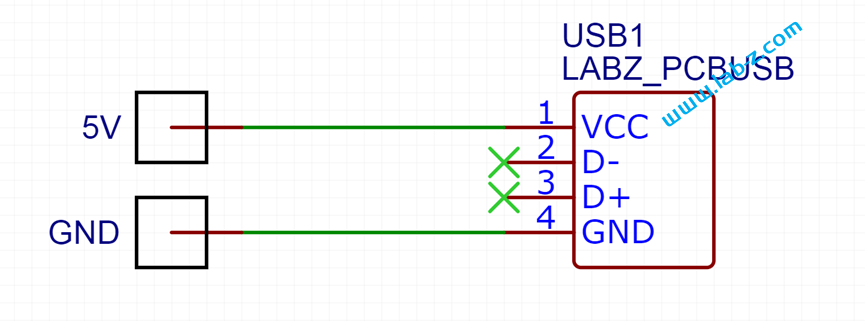
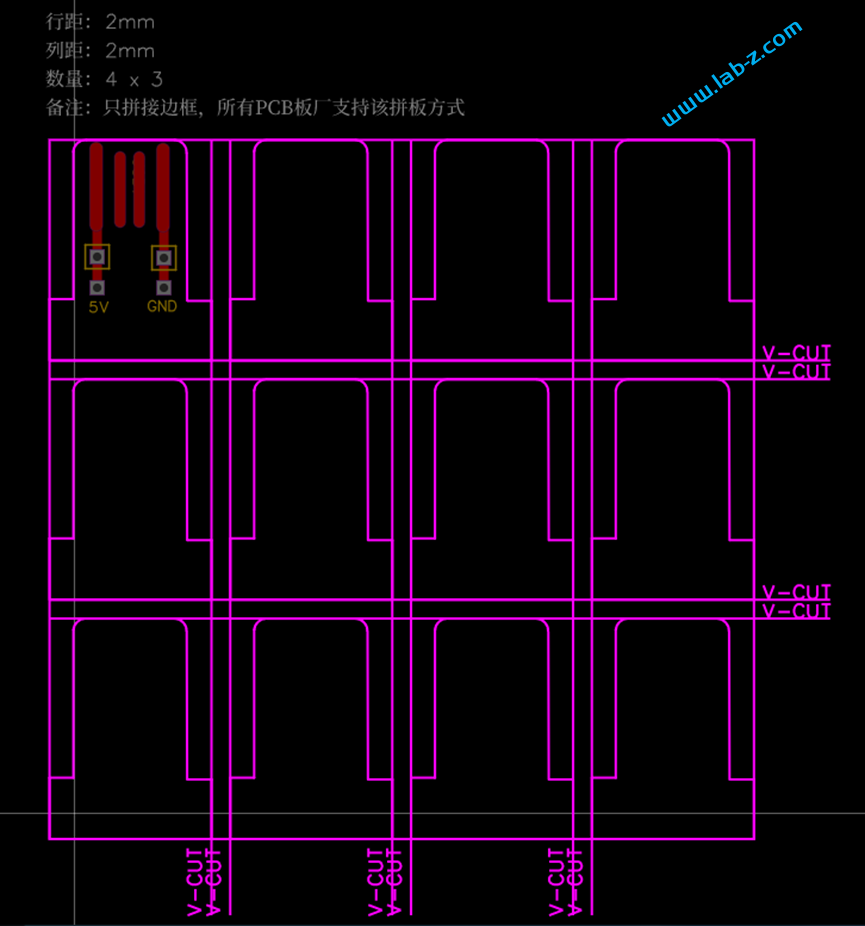
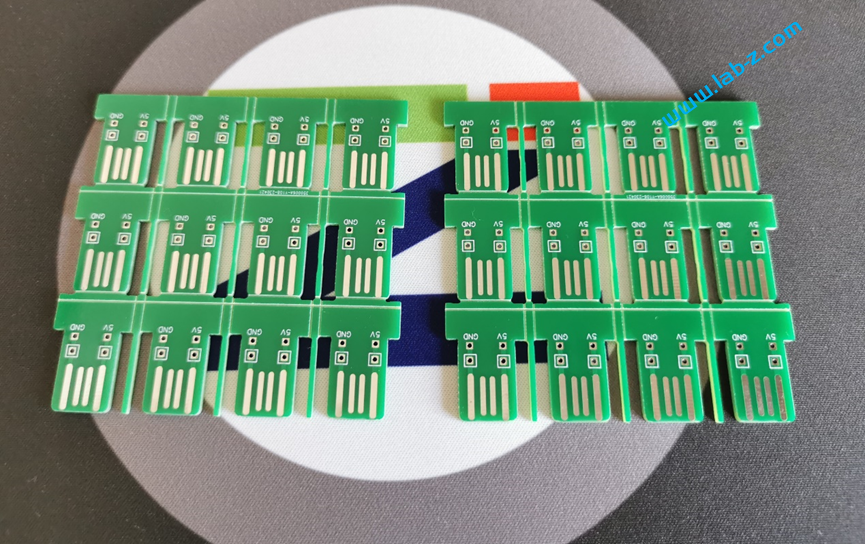
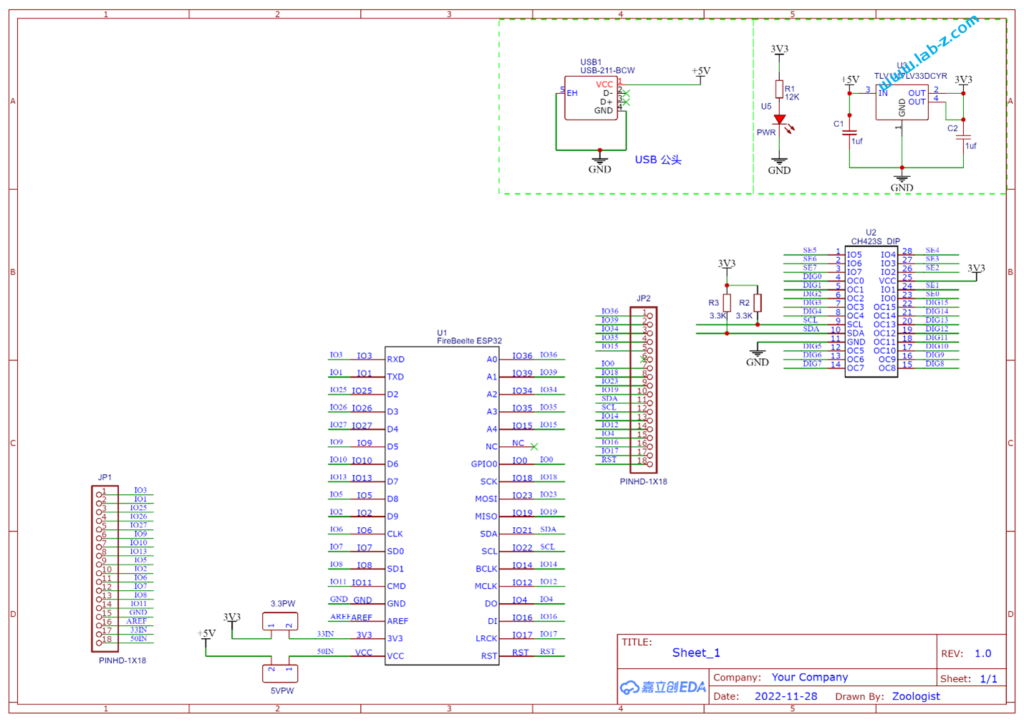
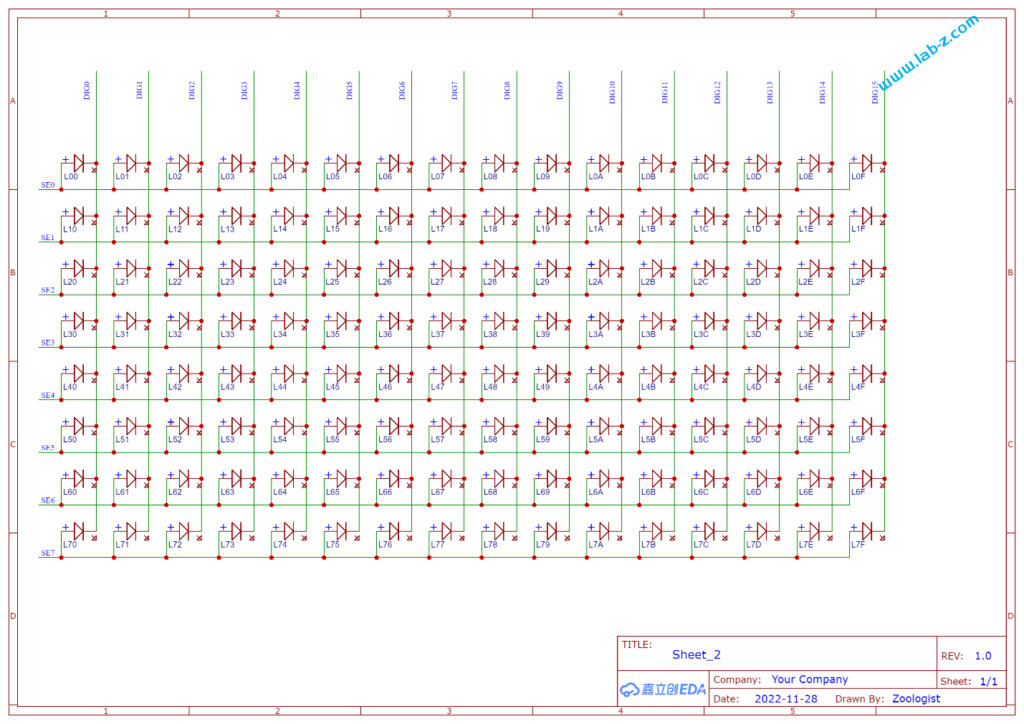
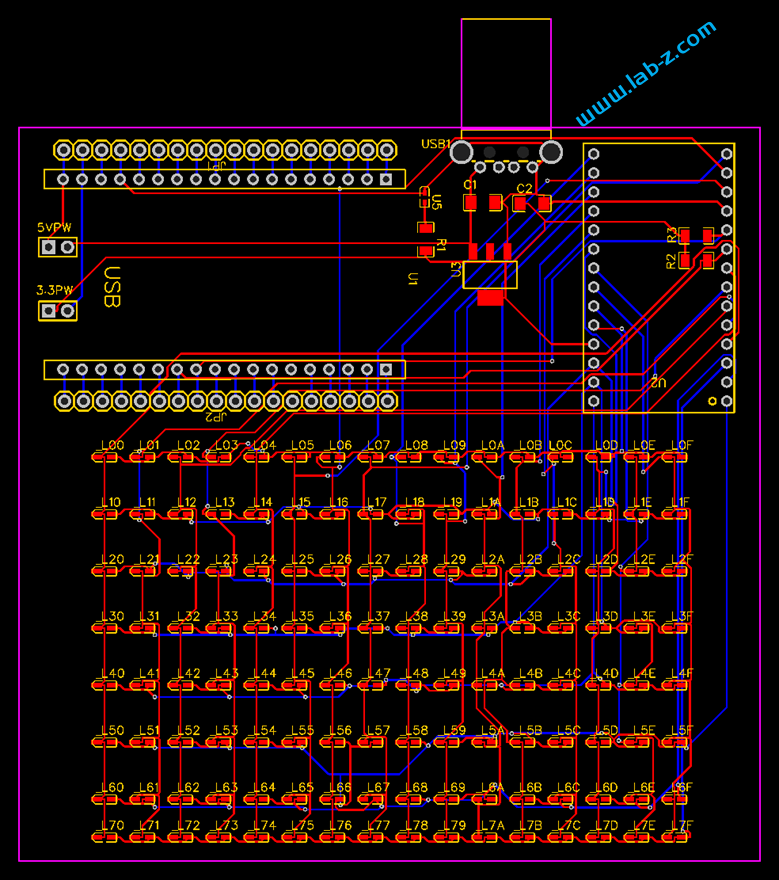
芯片是I2C 接口,控制线路非常简单:SCl和SDA就好了。CH423是SOP28封装,为了便于试验我从淘宝购买了一个SOP28转DIP的小PCB,焊接之后将CH423插入到PCB上。接下来是LED矩阵的设计:
其中 SE[N] 信号能够输出高低电平,DEG[M] 只用作吸收电流使用。对CH423 发送命令,告知我现在要做动态扫描使用,然后告知SE[N]和DEG[M] 的组合即可。例如:告知SE1 输出高,DIG0 吸收电流和SE7输出高,DIG15吸收电流,之后芯片本身会动态控制,肉眼看起来就是 L00和L7F 点亮【参考2】。
#include <Wire.h>
// CH423接口定义
#define CH423_I2C_ADDR1 0x20 // CH423的地址
#define CH423_I2C_MASK 0x3E // CH423的高字节命令掩码
#define CH423_SYSON1 0x0417 //开启自动扫描显示
unsigned char CH423_buf[16]; //定义16个数码管的数据映象缓存区
const unsigned char BCD_decode_tab[ 0x10 ] = { 0X3F, 0X06, 0X5B, 0X4F, 0X66, 0X6D, 0X7D, 0X07, 0X7F, 0X6F, 0X77, 0X7C, 0X58, 0X5E, 0X79, 0X71 };
void CH423_Write( uint32_t cmd ) // 写命令
{
Serial.print("Address ");
Serial.print(( unsigned char )(cmd >> 8), HEX);
Serial.print(" command ");
Serial.print(( unsigned char ) (cmd & 0xff), HEX);
Wire.beginTransmission (( unsigned char )(cmd >> 8));
Wire.write( ( unsigned char ) (cmd & 0xff) ); // 发送数据
// 结束总线
if (Wire.endTransmission() == 0) {
Serial.println(" I2C Success!");
} else {
Serial.println("I2C error!");
}
}
// 向CH423输出数据或者操作命令,自动建立数据映象
void CH423_buf_write( uint32_t cmd )
{
if ( cmd & 0x1000 )
{ // 加载数据的命令,需要备份数据到映象缓冲区
CH423_buf[ (unsigned char)( cmd >> 8 ) & 0x0F ] = (unsigned char)( cmd & 0xFF ); // 备份数据到相应的映象单元
}
CH423_Write( cmd ); // 发出
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin (115200);
Wire.begin (21, 22); // sda= GPIO_21 /scl= GPIO_22.
/* INTENS [00-11]
OD_EN 使能开漏
X_INT 0x08
DEC_H 0x04
DEC_L 0x02
IO_OE 0x01
*/
CH423_buf_write( 0x2417 );
/* OC_L_DAT OC7-OC0 电平控制
*/
CH423_buf_write( 0x2200 );
/* OC_H_DAT OC15-OC8 电平控制
*/
CH423_buf_write( 0x2300 );
// 初始化时保持全灭
uint32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
CH423_buf_write(((0x30 + i) << 8) + 0x00);
}
}
// 要显示的字符取模, DFRobot 字样
// 来自 https://www.zhetao.com/fontarray.html
const unsigned char bitmap_bit_bytes[] = {
0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b11111000, 0b11111100, 0b11111100, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b01000100, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b00000000, 0b11000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b01000010, 0b01001000, 0b01000010, 0b00000000, 0b01000000, 0b00000000, 0b00010000,
0b01000010, 0b01001000, 0b01000010, 0b00000000, 0b01000000, 0b00000000, 0b00010000,
0b01000010, 0b01111000, 0b01111100, 0b00111100, 0b01011000, 0b00111100, 0b01111100,
0b01000010, 0b01001000, 0b01001000, 0b01000010, 0b01100100, 0b01000010, 0b00010000,
0b01000010, 0b01001000, 0b01001000, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b00010000,
0b01000010, 0b01000000, 0b01000100, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b00010000,
0b01000010, 0b01000000, 0b01000100, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b00010000,
0b01000100, 0b01000000, 0b01000010, 0b01000010, 0b01100100, 0b01000010, 0b00010010,
0b11111000, 0b11100000, 0b11100011, 0b00111100, 0b01011000, 0b00111100, 0b00001100,
0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000, 0b00000000,
};
// 显示一个动画效果
uint16_t buf[8] = {
0b0100000000000000,
0b0010000000000000,
0b0001000000000000,
0b0000100000000000,
0b0000010000000000,
0b0000100000000000,
0b0001000000000000,
0b0010000000000000,
};
void loop() {
uint16_t i, j, m;
char c, v;
while (Serial.available()) {
c = Serial.read();
// 显示卡面定义的字符
if (c == '1') {
for (i = 0; i < 7 ; i++) { //一共有7个字符
for (j = 0; j < 16; j++) { // 每个字符有16个1Byte数据
CH423_buf_write( ((0x30 + j) << 8) + bitmap_bit_bytes[i + j * 7] );
}
delay(500);
}
}
// 随机点亮测试
if (c == '2') {
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
CH423_buf_write( ((0x30 + j) << 8) + random(0, 256) );
}
delay(500);
}
}
// 移动的动画效果
if (c == '3') {
for (m = 0; m < 32; m++) {
// 显示 buf 定义的图形
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
v = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if ((buf[j] & (1 << i)) == 0) {
v = v << 1;
}
else {
v = (v << 1) + 1;
}
}
CH423_buf_write( ((0x30 + i) << 8) + v );
}
// 移动 buf 字符
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if ((buf[i]&1)!=0) {buf[i]=buf[i]|0x8000;}
buf[i]=buf[i]>>1;
}
delay(100);
}
}
}
}