修改 Processing IDE 字体的方法和之前提到的“Arduino IDE 修改字体大小”【参考1】的方法相同,也是在
File -> Perferences 下面的 Editor font size中。
1.http://www.lab-z.com/arduino-ide-%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E5%AD%97%E4%BD%93%E5%A4%A7%E5%B0%8F/ Arduino IDE 修改字体大小
最近发现一个挺有意思的功能,Print 使用 %r 参数可以直接输出错误信息的含义。这样的话,我们可以直接取得错误信息,省去不少麻烦。例如,下面的代码
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
Print(L"%r\n",EFI_SUCCESS);
Print(L"%r\n",RETURN_WARN_WRITE_FAILURE);
Print(L"%r\n",RETURN_COMPROMISED_DATA);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
我们再仔细研究一下 %r 的具体实现。
查看 PrintR 编译生成的 printf.map ,可以看到 _Print 是链接到 UefiLibPrint.obj 中。用这个文件名,我们确定是在 \MdePkg\Library\UefiLib\UefiLibPrint.c 这个文件中
0001:000000ce _ShellCEntryLib 0000032e f UefiShellCEntryLib:UefiShellCEntryLib.obj
0001:00000140 _InternalPrint 000003a0 f UefiLib:UefiLibPrint.obj
0001:0000018b _Print 000003eb f UefiLib:UefiLibPrint.obj
0001:000001a8 _ShellFindSE2 00000408 f UefiShellLib:UefiShellLib.obj
0001:000002d8 _ShellLibConstructorWorker 00000538 f UefiShellLib:UefiShellLib.obj
0001:0000048d _ShellLibDestructor 000006ed f UefiShellLib:UefiShellLib.obj
0001:00000535 _ShellOpenFileByDevicePath 00000795 f UefiShellLib:UefiShellLib.obj
Print 函数:
/**
Prints a formatted Unicode string to the console output device specified by
ConOut defined in the EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE.
This function prints a formatted Unicode string to the console output device
specified by ConOut in EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE and returns the number of Unicode
characters that printed to ConOut. If the length of the formatted Unicode
string is greater than PcdUefiLibMaxPrintBufferSize, then only the first
PcdUefiLibMaxPrintBufferSize characters are sent to ConOut.
If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Format is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If gST->ConOut is NULL, then ASSERT().
@param Format A Null-terminated Unicode format string.
@param ... A Variable argument list whose contents are accessed based
on the format string specified by Format.
@return The number of Unicode characters printed to ConOut.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
Print (
IN CONST CHAR16 *Format,
...
)
{
VA_LIST Marker;
UINTN Return;
VA_START (Marker, Format);
Return = InternalPrint (Format, gST->ConOut, Marker);
VA_END (Marker);
return Return;
}
InternalPrint 函数在同一个文件中
/**
Internal function which prints a formatted Unicode string to the console output device
specified by Console
This function prints a formatted Unicode string to the console output device
specified by Console and returns the number of Unicode characters that printed
to it. If the length of the formatted Unicode string is greater than PcdUefiLibMaxPrintBufferSize,
then only the first PcdUefiLibMaxPrintBufferSize characters are sent to Console.
If Format is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Format is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
@param Format A Null-terminated Unicode format string.
@param Console The output console.
@param Marker A VA_LIST marker for the variable argument list.
@return The number of Unicode characters in the produced
output buffer, not including the Null-terminator.
**/
UINTN
InternalPrint (
IN CONST CHAR16 *Format,
IN EFI_SIMPLE_TEXT_OUTPUT_PROTOCOL *Console,
IN VA_LIST Marker
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
UINTN Return;
CHAR16 *Buffer;
UINTN BufferSize;
ASSERT (Format != NULL);
ASSERT (((UINTN) Format & BIT0) == 0);
ASSERT (Console != NULL);
BufferSize = (PcdGet32 (PcdUefiLibMaxPrintBufferSize) + 1) * sizeof (CHAR16);
Buffer = (CHAR16 *) AllocatePool(BufferSize);
ASSERT (Buffer != NULL);
Return = UnicodeVSPrint (Buffer, BufferSize, Format, Marker);
if (Console != NULL && Return > 0) {
//
// To be extra safe make sure Console has been initialized
//
Status = Console->OutputString (Console, Buffer);
if (EFI_ERROR (Status)) {
Return = 0;
}
}
FreePool (Buffer);
return Return;
}
处理输出的核心是 UnicodeVSPrint 函数
/**
Produces a Null-terminated Unicode string in an output buffer based on
a Null-terminated Unicode format string and a VA_LIST argument list
Produces a Null-terminated Unicode string in the output buffer specified by StartOfBuffer
and BufferSize.
The Unicode string is produced by parsing the format string specified by FormatString.
Arguments are pulled from the variable argument list specified by Marker based on the
contents of the format string.
The number of Unicode characters in the produced output buffer is returned not including
the Null-terminator.
If BufferSize is 0 or 1, then no output buffer is produced and 0 is returned.
If BufferSize > 1 and StartOfBuffer is NULL, then ASSERT().
If BufferSize > 1 and StartOfBuffer is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If BufferSize > 1 and FormatString is NULL, then ASSERT().
If BufferSize > 1 and FormatString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and FormatString contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then
ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and produced Null-terminated Unicode string
contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the
Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param StartOfBuffer A pointer to the output buffer for the produced Null-terminated
Unicode string.
@param BufferSize The size, in bytes, of the output buffer specified by StartOfBuffer.
@param FormatString A Null-terminated Unicode format string.
@param Marker VA_LIST marker for the variable argument list.
@return The number of Unicode characters in the produced output buffer not including the
Null-terminator.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
UnicodeVSPrint (
OUT CHAR16 *StartOfBuffer,
IN UINTN BufferSize,
IN CONST CHAR16 *FormatString,
IN VA_LIST Marker
)
{
ASSERT_UNICODE_BUFFER (StartOfBuffer);
ASSERT_UNICODE_BUFFER (FormatString);
return BasePrintLibSPrintMarker ((CHAR8 *)StartOfBuffer, BufferSize >> 1, FORMAT_UNICODE | OUTPUT_UNICODE, (CHAR8 *)FormatString, Marker, NULL);
}
BasePrintLibSPrintMarker 函数在 \MdePkg\Library\BasePrintLib\PrintLib.c
/**
Worker function that produces a Null-terminated string in an output buffer
based on a Null-terminated format string and a VA_LIST argument list.
VSPrint function to process format and place the results in Buffer. Since a
VA_LIST is used this routine allows the nesting of Vararg routines. Thus
this is the main print working routine.
If COUNT_ONLY_NO_PRINT is set in Flags, Buffer will not be modified at all.
@param[out] Buffer The character buffer to print the results of the
parsing of Format into.
@param[in] BufferSize The maximum number of characters to put into
buffer.
@param[in] Flags Initial flags value.
Can only have FORMAT_UNICODE, OUTPUT_UNICODE,
and COUNT_ONLY_NO_PRINT set.
@param[in] Format A Null-terminated format string.
@param[in] VaListMarker VA_LIST style variable argument list consumed by
processing Format.
@param[in] BaseListMarker BASE_LIST style variable argument list consumed
by processing Format.
@return The number of characters printed not including the Null-terminator.
If COUNT_ONLY_NO_PRINT was set returns the same, but without any
modification to Buffer.
**/
UINTN
BasePrintLibSPrintMarker (
OUT CHAR8 *Buffer,
IN UINTN BufferSize,
IN UINTN Flags,
IN CONST CHAR8 *Format,
IN VA_LIST VaListMarker, OPTIONAL
IN BASE_LIST BaseListMarker OPTIONAL
)
处理 %r 的代码如下
case 'r':
if (BaseListMarker == NULL) {
Status = VA_ARG (VaListMarker, RETURN_STATUS);
} else {
Status = BASE_ARG (BaseListMarker, RETURN_STATUS);
}
ArgumentString = ValueBuffer;
if (RETURN_ERROR (Status)) {
//
// Clear error bit
//
Index = Status & ~MAX_BIT;
if (Index > 0 && Index <= ERROR_STATUS_NUMBER) {
ArgumentString = mStatusString [Index + WARNING_STATUS_NUMBER];
}
} else {
Index = Status;
if (Index <= WARNING_STATUS_NUMBER) {
ArgumentString = mStatusString [Index];
}
}
if (ArgumentString == ValueBuffer) {
BasePrintLibSPrint ((CHAR8 *) ValueBuffer, MAXIMUM_VALUE_CHARACTERS, 0, "%08X", Status);
}
break;
核心就是查 mStatusString 表,在 \MdePkg\Library\BasePrintLib\PrintLibInternal.c 中有定义
GLOBAL_REMOVE_IF_UNREFERENCED CONST CHAR8 *mStatusString[] = {
"Success", // RETURN_SUCCESS = 0
"Warning Unknown Glyph", // RETURN_WARN_UNKNOWN_GLYPH = 1
"Warning Delete Failure", // RETURN_WARN_DELETE_FAILURE = 2
"Warning Write Failure", // RETURN_WARN_WRITE_FAILURE = 3
"Warning Buffer Too Small", // RETURN_WARN_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL = 4
"Warning Stale Data", // RETURN_WARN_STALE_DATA = 5
"Load Error", // RETURN_LOAD_ERROR = 1 | MAX_BIT
"Invalid Parameter", // RETURN_INVALID_PARAMETER = 2 | MAX_BIT
"Unsupported", // RETURN_UNSUPPORTED = 3 | MAX_BIT
"Bad Buffer Size", // RETURN_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE = 4 | MAX_BIT
"Buffer Too Small", // RETURN_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL, = 5 | MAX_BIT
"Not Ready", // RETURN_NOT_READY = 6 | MAX_BIT
"Device Error", // RETURN_DEVICE_ERROR = 7 | MAX_BIT
"Write Protected", // RETURN_WRITE_PROTECTED = 8 | MAX_BIT
"Out of Resources", // RETURN_OUT_OF_RESOURCES = 9 | MAX_BIT
"Volume Corrupt", // RETURN_VOLUME_CORRUPTED = 10 | MAX_BIT
"Volume Full", // RETURN_VOLUME_FULL = 11 | MAX_BIT
"No Media", // RETURN_NO_MEDIA = 12 | MAX_BIT
"Media changed", // RETURN_MEDIA_CHANGED = 13 | MAX_BIT
"Not Found", // RETURN_NOT_FOUND = 14 | MAX_BIT
"Access Denied", // RETURN_ACCESS_DENIED = 15 | MAX_BIT
"No Response", // RETURN_NO_RESPONSE = 16 | MAX_BIT
"No mapping", // RETURN_NO_MAPPING = 17 | MAX_BIT
"Time out", // RETURN_TIMEOUT = 18 | MAX_BIT
"Not started", // RETURN_NOT_STARTED = 19 | MAX_BIT
"Already started", // RETURN_ALREADY_STARTED = 20 | MAX_BIT
"Aborted", // RETURN_ABORTED = 21 | MAX_BIT
"ICMP Error", // RETURN_ICMP_ERROR = 22 | MAX_BIT
"TFTP Error", // RETURN_TFTP_ERROR = 23 | MAX_BIT
"Protocol Error", // RETURN_PROTOCOL_ERROR = 24 | MAX_BIT
"Incompatible Version", // RETURN_INCOMPATIBLE_VERSION = 25 | MAX_BIT
"Security Violation", // RETURN_SECURITY_VIOLATION = 26 | MAX_BIT
"CRC Error", // RETURN_CRC_ERROR = 27 | MAX_BIT
"End of Media", // RETURN_END_OF_MEDIA = 28 | MAX_BIT
"Reserved (29)", // RESERVED = 29 | MAX_BIT
"Reserved (30)", // RESERVED = 30 | MAX_BIT
"End of File", // RETURN_END_OF_FILE = 31 | MAX_BIT
"Invalid Language", // RETURN_INVALID_LANGUAGE = 32 | MAX_BIT
"Compromised Data" // RETURN_COMPROMISED_DATA = 33 | MAX_BIT
};
具体的实现就是这样。
继续介绍 EFI 下面的常用字符串函数
\MdePkg\Include\Library\BaseLib.h
1.StrStr 函数作用:在字符串中查找另外的字符串
/** Returns the first occurrence of a Null-terminated Unicode sub-string in a Null-terminated Unicode string. This function scans the contents of the Null-terminated Unicode string specified by String and returns the first occurrence of SearchString. If SearchString is not found in String, then NULL is returned. If the length of SearchString is zero, then String is returned. If String is NULL, then ASSERT(). If String is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If SearchString is NULL, then ASSERT(). If SearchString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and SearchString or String contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param SearchString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string to search for. @retval NULL If the SearchString does not appear in String. @return others If there is a match. **/ CHAR16 * EFIAPI StrStr ( IN CONST CHAR16 *String, IN CONST CHAR16 *SearchString );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 *s2=L"COM";
CHAR16 *s3=L"com";
CHAR16 s4[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrStr(s4,s1);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
Result=StrStr(s4,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
Result=StrStr(s4,s3);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
2.StrDecimalToUintn 作用:把字符串转换为数字
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode decimal string to a value of
type UINTN.
This function returns a value of type UINTN by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a decimal number. The format
of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces] [decimal digits].
The valid decimal digit character is in the range [0-9]. The
function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or
tab characters, before [decimal digits]. The running zero in the
beginning of [decimal digits] will be ignored. Then, the function
stops at the first character that is a not a valid decimal character
or a Null-terminator, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then 0 is returned.
If String has no pad spaces or valid decimal digits,
then 0 is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according
to the range defined by UINTN, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains
more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including
the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
StrDecimalToUintn (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
实例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100";
CHAR16 *s2=L"77F";
CHAR16 *s3=L"77f";
CHAR16 *s4=L"77z";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s3);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s4);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
具体实现的代码可以在下面找到:
\MdePkg\Library\BaseLib\String.c
while (InternalIsDecimalDigitCharacter (*String)) {
//
// If the number represented by String overflows according
// to the range defined by UINTN, then ASSERT().
//
ASSERT (Result <= ((((UINTN) ~0) - (*String - L'0')) / 10));
Result = Result * 10 + (*String - L'0');
String++;
}
/**
Check if a Unicode character is a decimal character.
This internal function checks if a Unicode character is a
decimal character. The valid decimal character is from
L'0' to L'9'.
@param Char The character to check against.
@retval TRUE If the Char is a decmial character.
@retval FALSE If the Char is not a decmial character.
**/
BOOLEAN
EFIAPI
InternalIsDecimalDigitCharacter (
IN CHAR16 Char
)
{
return (BOOLEAN) (Char >= L'0' && Char <= L'9');
}
从上面可以看到:最后一个字符会被忽略,所以你写 77f 或者 77z都能得到同样的结果
再测试一下具体取值的大小
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100000000";
CHAR16 *s2=L"987654321Z";
CHAR16 *s3=L"2147483647"; // == 7FFFFFFF
CHAR16 *s4=L"2147483648"; // == 80000000
CHAR16 *s5=L"-1";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s3);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s4);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUintn(s5);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
3.StrDecimalToUint64 函数用途:将字符串转换为数值,和前面的函数相比,可用范围更大
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode decimal string to a value of
type UINT64.
This function returns a value of type UINT64 by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a decimal number. The format
of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces] [decimal digits].
The valid decimal digit character is in the range [0-9]. The
function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or
tab characters, before [decimal digits]. The running zero in the
beginning of [decimal digits] will be ignored. Then, the function
stops at the first character that is a not a valid decimal character
or a Null-terminator, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then 0 is returned.
If String has no pad spaces or valid decimal digits,
then 0 is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according
to the range defined by UINT64, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains
more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including
the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINT64
EFIAPI
StrDecimalToUint64 (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
实例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"100000000";
CHAR16 *s2=L"9876543210000Z";
CHAR16 *s3=L"2147483647"; // == 7FFFFFFF
CHAR16 *s4=L"2147483648"; // == 80000000
CHAR16 *s5=L"-1";
UINT64 Result;
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s1);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s2);
Print(L"\n%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s2);
Print(L"%LX\n\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s3);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s4);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
Result=StrDecimalToUint64(s5);
Print(L"%Ld\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
4.StrHexToUintn 函数作用:将字符串按照十六进制处理转换为数值
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode hexadecimal string to a value of type UINTN.
This function returns a value of type UINTN by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a hexadecimal number.
The format of the input Unicode string String is:
[spaces][zeros][x][hexadecimal digits].
The valid hexadecimal digit character is in the range [0-9], [a-f] and [A-F].
The prefix "0x" is optional. Both "x" and "X" is allowed in "0x" prefix.
If "x" appears in the input string, it must be prefixed with at least one 0.
The function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or tab characters,
before [zeros], [x] or [hexadecimal digit]. The running zero before [x] or
[hexadecimal digit] will be ignored. Then, the decoding starts after [x] or the
first valid hexadecimal digit. Then, the function stops at the first character
that is a not a valid hexadecimal character or NULL, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then zero is returned.
If String has no leading pad spaces, leading zeros or valid hexadecimal digits,
then zero is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according to the range defined by
UINTN, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator,
then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINTN
EFIAPI
StrHexToUintn (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"0x234";
CHAR16 *s2=L"1024";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrHexToUintn(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrHexToUintn(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
5.StrHexToUint64 函数作用:把字符串按照十六进制处理转化为数值
/**
Convert a Null-terminated Unicode hexadecimal string to a value of type UINT64.
This function returns a value of type UINT64 by interpreting the contents
of the Unicode string specified by String as a hexadecimal number.
The format of the input Unicode string String is
[spaces][zeros][x][hexadecimal digits].
The valid hexadecimal digit character is in the range [0-9], [a-f] and [A-F].
The prefix "0x" is optional. Both "x" and "X" is allowed in "0x" prefix.
If "x" appears in the input string, it must be prefixed with at least one 0.
The function will ignore the pad space, which includes spaces or tab characters,
before [zeros], [x] or [hexadecimal digit]. The running zero before [x] or
[hexadecimal digit] will be ignored. Then, the decoding starts after [x] or the
first valid hexadecimal digit. Then, the function stops at the first character that is
a not a valid hexadecimal character or NULL, whichever one comes first.
If String is NULL, then ASSERT().
If String is not aligned in a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If String has only pad spaces, then zero is returned.
If String has no leading pad spaces, leading zeros or valid hexadecimal digits,
then zero is returned.
If the number represented by String overflows according to the range defined by
UINT64, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator,
then ASSERT().
@param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@retval Value translated from String.
**/
UINT64
EFIAPI
StrHexToUint64 (
IN CONST CHAR16 *String
);
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"0x234";
CHAR16 *s2=L"0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF";
UINT64 Result;
Result=StrHexToUint64(s1);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
Result=StrHexToUint64(s2);
Print(L"%ld\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
6.UnicodeStrToAsciiStr 函数作用:将Unicode的字符串转换为 ASCII的字符串
/** Convert a Null-terminated Unicode string to a Null-terminated ASCII string and returns the ASCII string. This function converts the content of the Unicode string Source to the ASCII string Destination by copying the lower 8 bits of each Unicode character. It returns Destination. The caller is responsible to make sure Destination points to a buffer with size equal or greater than ((StrLen (Source) + 1) * sizeof (CHAR8)) in bytes. If any Unicode characters in Source contain non-zero value in the upper 8 bits, then ASSERT(). If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Source is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated ASCII string. @return Destination. **/ CHAR8 * EFIAPI UnicodeStrToAsciiStr ( IN CONST CHAR16 *Source, OUT CHAR8 *Destination );
示例代码
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"www.lab-z.com";
CHAR8 *s2=" ";
CHAR8 *Result;
Result=UnicodeStrToAsciiStr(s1,s2);
Print(L"%a\n",s2);
Print(L"%a\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
7.AsciiStrToUnicodeStr 函数作用:将 ASCII的字符串转换为 Unicode的字符串
/** Convert one Null-terminated ASCII string to a Null-terminated Unicode string and returns the Unicode string. This function converts the contents of the ASCII string Source to the Unicode string Destination, and returns Destination. The function terminates the Unicode string Destination by appending a Null-terminator character at the end. The caller is responsible to make sure Destination points to a buffer with size equal or greater than ((AsciiStrLen (Source) + 1) * sizeof (CHAR16)) in bytes. If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumAsciiStringLength ASCII characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength ASCII characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated ASCII string. @param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @return Destination. **/ CHAR16 * EFIAPI AsciiStrToUnicodeStr ( IN CONST CHAR8 *Source, OUT CHAR16 *Destination );
示例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR8 *s1="www.lab-z.com";
CHAR16 *s2=L" ";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=AsciiStrToUnicodeStr (s1,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",s2);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果和前面的相同。
本文介绍如何使用 Arduino 打造一个设备,能够将你的USB键盘转化为蓝牙键盘。
键盘可以算作PC上最古老的设备了,他的出现使得人类可以用非常简单的方法与电脑进行交互。同样的,由于各种历史原因,键盘也是PC上最复杂,兼容性问题最多的设备之一(类似的还有硬盘,不过从IDE到SATA的进化过程中,标准明确,兼容性问题少多了)。
网上流传着一篇DIY USB键盘转换为无线的文章,非常不幸的是,那篇文章是错误的,很明显的错误是作者认为键盘是单向传输,而实际上传输是双向的。比如,USB每次通讯都需要HOST和SLAVE的参与,即便是PS2键盘的通讯也同样如此。此外,大小写键之类切换是主机端进行控制的。
硬件部分Arduino UNO , USB Host Shield 和 HID 蓝牙芯片。强调一下这里使用的是 HID 蓝牙芯片,并非普通的蓝牙串口透传芯片【特别注意是“蓝牙键盘芯片”也不是“蓝牙条码模块”】。关于这个模块可以参考我在【参考1】中的实验。
硬件连接很简单,USB HOST Shield插在 Arduino上,然后VCC/GND/TX/RX将Arduino 和 HID蓝牙模块连接在一起。
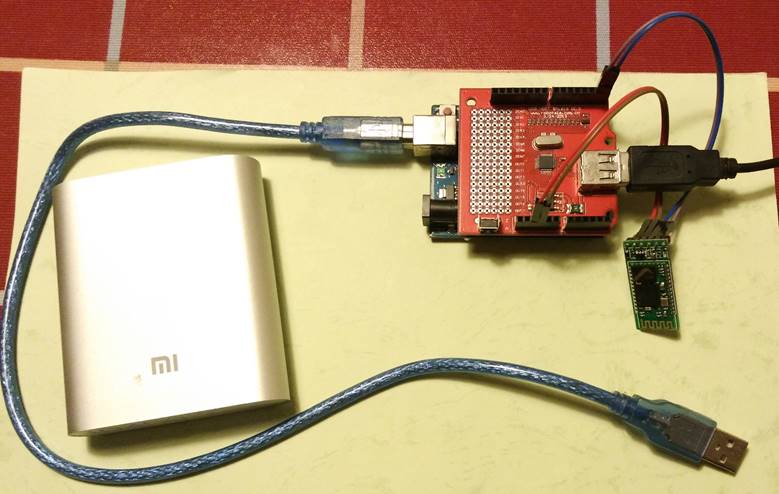
原理:首先,为了通用性和编程简单,我们用USB HOST发送命令把键盘切换到 Boot Protocol 模式下。这样即使不同的键盘,每次发出来的数据也都是统一的格式。然后,我们直接读取缓冲数据就可以解析出按键信息了。最后,将取下来的按键信息(Scan Code)按照HID蓝牙模块的格式要求通过串口送到模块上,主机端就收到了。
上述连接就可以正常工作了,但是为了美观和提高可靠性,我找到之前买的一个面包板Shield。
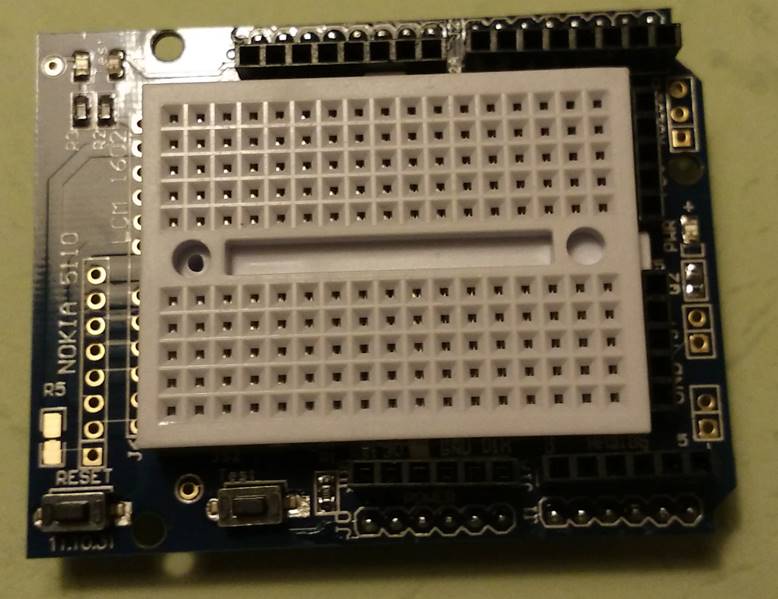
插好之后就是这样
具体代码:
/* MAX3421E USB Host controller LCD/keyboard demonstration */
//#include <Spi.h>
#include "Max3421e.h"
#include "Usb.h"
/* keyboard data taken from configuration descriptor */
#define KBD_ADDR 1
#define KBD_EP 1
#define KBD_IF 0
#define EP_MAXPKTSIZE 8
#define EP_POLL 0x0a
/**/
//******************************************************************************
// macros to identify special charaters(other than Digits and Alphabets)
//******************************************************************************
#define BANG (0x1E)
#define AT (0x1F)
#define POUND (0x20)
#define DOLLAR (0x21)
#define PERCENT (0x22)
#define CAP (0x23)
#define AND (0x24)
#define STAR (0x25)
#define OPENBKT (0x26)
#define CLOSEBKT (0x27)
#define RETURN (0x28)
#define ESCAPE (0x29)
#define BACKSPACE (0x2A)
#define TAB (0x2B)
#define SPACE (0x2C)
#define HYPHEN (0x2D)
#define EQUAL (0x2E)
#define SQBKTOPEN (0x2F)
#define SQBKTCLOSE (0x30)
#define BACKSLASH (0x31)
#define SEMICOLON (0x33)
#define INVCOMMA (0x34)
#define TILDE (0x35)
#define COMMA (0x36)
#define PERIOD (0x37)
#define FRONTSLASH (0x38)
#define DELETE (0x4c)
/**/
/* Modifier masks. One for both modifiers */
#define SHIFT 0x22
#define CTRL 0x11
#define ALT 0x44
#define GUI 0x88
/**/
/* "Sticky keys */
#define CAPSLOCK (0x39)
#define NUMLOCK (0x53)
#define SCROLLLOCK (0x47)
/* Sticky keys output report bitmasks */
#define bmNUMLOCK 0x01
#define bmCAPSLOCK 0x02
#define bmSCROLLLOCK 0x04
/**/
EP_RECORD ep_record[ 2 ]; //endpoint record structure for the keyboard
char buf[ 8 ] = { 0 }; //keyboard buffer
char old_buf[ 8 ] = { 0 }; //last poll
/* Sticky key state */
bool numLock = false;
bool capsLock = false;
bool scrollLock = false;
bool line = false;
void setup();
void loop();
MAX3421E Max;
USB Usb;
void setup() {
Serial.begin( 9600 );
Serial.println("Start");
Max.powerOn();
delay( 200 );
}
void loop() {
Max.Task();
Usb.Task();
if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_CONFIGURING ) { //wait for addressing state
kbd_init();
Usb.setUsbTaskState( USB_STATE_RUNNING );
}
if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_RUNNING ) { //poll the keyboard
kbd_poll();
}
}
/* Initialize keyboard */
void kbd_init( void )
{
byte rcode = 0; //return code
/**/
/* Initialize data structures */
ep_record[ 0 ] = *( Usb.getDevTableEntry( 0,0 )); //copy endpoint 0 parameters
ep_record[ 1 ].MaxPktSize = EP_MAXPKTSIZE;
ep_record[ 1 ].Interval = EP_POLL;
ep_record[ 1 ].sndToggle = bmSNDTOG0;
ep_record[ 1 ].rcvToggle = bmRCVTOG0;
Usb.setDevTableEntry( 1, ep_record ); //plug kbd.endpoint parameters to devtable
/* Configure device */
rcode = Usb.setConf( KBD_ADDR, 0, 1 );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Error attempting to configure keyboard. Return code :");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while(1); //stop
}
/* Set boot protocol */
rcode = Usb.setProto( KBD_ADDR, 0, 0, 0 );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Error attempting to configure boot protocol. Return code :");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while( 1 ); //stop
}
delay(2000);
Serial.println("Keyboard initialized");
}
/* Poll keyboard and print result */
/* buffer starts at position 2, 0 is modifier key state and 1 is irrelevant */
void kbd_poll( void )
{
char i;
boolean samemark=true;
static char leds = 0;
byte rcode = 0; //return code
/* poll keyboard */
rcode = Usb.inTransfer( KBD_ADDR, KBD_EP, 8, buf );
if( rcode != 0 ) {
return;
}//if ( rcode..
for( i = 2; i < 8; i++ ) {
if( buf[ i ] == 0 ) { //end of non-empty space
break;
}
if( buf_compare( buf[ i ] ) == false ) { //if new key
switch( buf[ i ] ) {
case CAPSLOCK:
capsLock =! capsLock;
leds = ( capsLock ) ? leds |= bmCAPSLOCK : leds &= ~bmCAPSLOCK; // set or clear bit 1 of LED report byte
break;
case NUMLOCK:
numLock =! numLock;
leds = ( numLock ) ? leds |= bmNUMLOCK : leds &= ~bmNUMLOCK; // set or clear bit 0 of LED report byte
break;
case SCROLLLOCK:
scrollLock =! scrollLock;
leds = ( scrollLock ) ? leds |= bmSCROLLLOCK : leds &= ~bmSCROLLLOCK; // set or clear bit 2 of LED report byte
Serial.write(0x0c); //BYTE1
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE2
Serial.write(0xA1); //BYTE3
Serial.write(0x01); //BYTE4
Serial.write(00); //BYTE5
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE6
Serial.write(0x1e); //BYTE7
Serial.write(0); //BYTE8
Serial.write(0); //BYTE9
Serial.write(0); //BYTE10
Serial.write(0); //BYTE11
Serial.write(0); //BYTE12
delay(500);
Serial.write(0x0c); //BYTE1
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE2
Serial.write(0xA1); //BYTE3
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE4
Serial.write(0); //BYTE5
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE6
Serial.write(0); //BYTE7
Serial.write(0); //BYTE8
Serial.write(0); //BYTE9
Serial.write(0); //BYTE10
Serial.write(0); //BYTE11
Serial.write(0); //BYTE12
break;
case DELETE:
line = false;
break;
case RETURN:
line =! line;
break;
//default:
//Serial.print(HIDtoA( buf[ i ], buf[ 0 ] ));
// break;
}//switch( buf[ i ...
rcode = Usb.setReport( KBD_ADDR, 0, 1, KBD_IF, 0x02, 0, &leds );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Set report error: ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
}//if( rcode ...
}//if( buf_compare( buf[ i ] ) == false ...
}//for( i = 2...
i=0;
while (i<8)
{
if (old_buf[i]!=buf[i]) { i=12; }
i++;
}
if (i==13) {
// for (i=0;i<8;i++) {
// Serial.print(buf[ i ],HEX);
// Serial.print(']');
// }
// Serial.println(' ');
Serial.write(0x0c); //BYTE1
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE2
Serial.write(0xA1); //BYTE3
Serial.write(0x01); //BYTE4
//Labz_Debug Serial.write(buf[1]); //BYTE5
Serial.write(buf[0]); //BYTE5 //Labz_Debug
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE6
Serial.write(buf[2]); //BYTE7
Serial.write(buf[3]); //BYTE8
Serial.write(buf[4]); //BYTE9
Serial.write(buf[5]); //BYTE10
Serial.write(buf[6]); //BYTE11
Serial.write(buf[7]); //BYTE12
}
//Labz_Debug for( i = 2; i < 8; i++ ) { //copy new buffer to old
for( i = 0; i < 8; i++ ) { //copy new buffer to old //Labz_Debug
old_buf[ i ] = buf[ i ];
}
}
/* compare byte against bytes in old buffer */
bool buf_compare( byte data )
{
char i;
for( i = 2; i < 8; i++ ) {
if( old_buf[ i ] == data ) {
return( true );
}
}
return( false );
}
我在处理SCROLLLOCK 键的地方插入了一个测试代码,理论上按下这个键的时候,主机还会收到 1 这个字符,这样是为了测试工作是否正常。
我在 x86 台式机上实测过,工作正常;小米4手机上实测过,工作正常; iPad 上是测过,工作也正常。
在iPad上工作的视频在下面:
完整代码下载
特别注意:
1. 因为我们使用的是最简单的Boot Protocol,所以如果你的键盘上有音量键之类的有可能失效;
2. 我不确定是否所有的键盘都会支持 Boot Protocol ,从之前玩USB鼠标的经验来看,确实有可能;
3. 供电部分没有经过优化,不知道电力消耗如何,不确定一个充电宝能够工作的时间;
最后讲一个小故事:有一次我去实验室,发现他们在折腾键盘。那是一款带着音量控制功能的键盘。系统测试的时候发现,按一下键盘音量键之后,屏幕上显示的音量会跳2格。从原理上说,按下那个键之后,键盘发出特定的Scan Code,系统中还有个专门响应这个Scan Code的程序然后在屏幕上绘制音量指示方块。蛮有意思的一件事情是:很多人认为大公司有操控供应商的能力,供应商在大厂面前会唯唯诺诺,这也是高层会有的想法,问题是底层人员未必吃这一套。每次想起这个事情,我都要想起敏感字关于矛盾的辩证法的论证。这个事情就是双方的下层在不停的扯,更准确的说,是键盘厂商,软件开发商和我们在一起纠缠,键盘厂商说同样的键盘在其他人家用起来没问题,软件开发商说我的软件在之前的机型上一直用,我们的人说,少扯淡,赶紧解决,前后一个多月都没有搞定…….那时候,组里刚买了一个usb逻辑分析仪,我用着感觉很好玩。于是,我就用逻辑分析仪测试了一下键盘,测试的结果是,键盘发出来的 Scan Code没有问题,每次按键都是一个Press一个Release,所以真相肯定是写上位机程序的软件厂商搞错了什么。截图附带着数据包一起丢给三方。这是最底层的传输,如果依然嘴硬,那只能落下笑柄而已。然后很快软件厂商就服软自己去修改了。只是说说我经历的事情,如果非要说出一些道理的话这个故事是为了说明:USB逻辑分析仪很有用……
就是这样.
=========================2017年5月11日更新=========================
有朋友说 Win ,Shift,Alt 都不工作,今天正好有空研究了一下,是我的代码有问题。解析出来的USB 键盘按键信息中 Buf[0] 是这些Key 的标志位,我没有正确Pass给模块。因此,修正下面2处代码,一个是发送,一个是每次保存当前的按键状态的位置:
Serial.write(0x0c); //BYTE1
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE2
Serial.write(0xA1); //BYTE3
Serial.write(0x01); //BYTE4
Serial.write(buf[0]); //BYTE5
Serial.write(0x00); //BYTE6
Serial.write(buf[2]); //BYTE7
Serial.write(buf[3]); //BYTE8
Serial.write(buf[4]); //BYTE9
Serial.write(buf[5]); //BYTE10
Serial.write(buf[6]); //BYTE11
Serial.write(buf[7]); //BYTE12
}
for( i = 0; i < 8; i++ ) { //copy new buffer to old
old_buf[ i ] = buf[ i ];
}
修改后可以正常工作的代码:
参考:
1. http://www.lab-z.com/btkeyboard/ 蓝牙键盘模块的实验
这里介绍一下常用的处理字符串的函数。这篇介绍 StrCpy/StrnCpy StrSize StrLen StrCmp/StrnCmp StrCat/StrnCat 。这些函数都是给 Unicode16 字符串设计的( CHAR16 定义的, 或者 L“www.lab-z.com” 这样定义的)。同样还有一组带有 Ascii 前缀的函数是给普通的字符串使用的。
函数定义原型可以在 \MdePkg\Include\Library\BaseLib.h 这个文件中找到
1.StrCpy (D<-S) 作用:将 Source 定义的字符串拷贝到 Destination 定义的字符串中(覆盖之)
// // String Services // /** Copies one Null-terminated Unicode string to another Null-terminated Unicode string and returns the new Unicode string. This function copies the contents of the Unicode string Source to the Unicode string Destination, and returns Destination. If Source and Destination overlap, then the results are undefined. If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @return Destination. **/ CHAR16 * EFIAPI StrCpy ( OUT CHAR16 *Destination, IN CONST CHAR16 *Source );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 *s2=L".LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrCpy(s1,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",s1);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
换一种字符串定义方式
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 s1[20]=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 s2[20]=L".LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrCpy(s1,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",s1);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果和上面的相同。
2.StrnCpy 作用:将 Source 定义的字符串中,前n个拷贝到 Destination 定义的字符串中(覆盖之)
/** Copies up to a specified length from one Null-terminated Unicode string to another Null-terminated Unicode string and returns the new Unicode string. This function copies the contents of the Unicode string Source to the Unicode string Destination, and returns Destination. At most, Length Unicode characters are copied from Source to Destination. If Length is 0, then Destination is returned unmodified. If Length is greater that the number of Unicode characters in Source, then Destination is padded with Null Unicode characters. If Source and Destination overlap, then the results are undefined. If Length > 0 and Destination is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and Source is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Length is greater than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Length The maximum number of Unicode characters to copy. @return Destination. **/ CHAR16 * EFIAPI StrnCpy ( OUT CHAR16 *Destination, IN CONST CHAR16 *Source, IN UINTN Length );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 *s2=L".LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrnCpy(s1,s2,4);
Print(L"%s\n",s1);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
3.StrLen 作用:返回字符串中字符的个数,注意:数量不包括结尾的 NULL。
/** Returns the length of a Null-terminated Unicode string. This function returns the number of Unicode characters in the Null-terminated Unicode string specified by String. If String is NULL, then ASSERT(). If String is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param String Pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @return The length of String. **/ UINTN EFIAPI StrLen ( IN CONST CHAR16 *String );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 s2[20]=L".LAB-Z.COM";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrLen(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrLen(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
4. StrSize 作用:返回字符串占用的内存字节数,注意:包括 NULL。
/** Returns the size of a Null-terminated Unicode string in bytes, including the Null terminator. This function returns the size, in bytes, of the Null-terminated Unicode string specified by String. If String is NULL, then ASSERT(). If String is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and String contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param String The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @return The size of String. **/ UINTN EFIAPI StrSize ( IN CONST CHAR16 *String );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW";
CHAR16 s2[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrSize(s1);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrSize(s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
定义的字符串实际上是: “www\0” ,每个字符都是 CHAR16, 算下来需要占用 8个字节。
5. StrCmp 作用:比较字符串是否相同。相同的话返回 0
/** Compares two Null-terminated Unicode strings, and returns the difference between the first mismatched Unicode characters. This function compares the Null-terminated Unicode string FirstString to the Null-terminated Unicode string SecondString. If FirstString is identical to SecondString, then 0 is returned. Otherwise, the value returned is the first mismatched Unicode character in SecondString subtracted from the first mismatched Unicode character in FirstString. If FirstString is NULL, then ASSERT(). If FirstString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If SecondString is NULL, then ASSERT(). If SecondString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and FirstString contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and SecondString contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param FirstString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param SecondString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @retval 0 FirstString is identical to SecondString. @return others FirstString is not identical to SecondString. **/ INTN EFIAPI StrCmp ( IN CONST CHAR16 *FirstString, IN CONST CHAR16 *SecondString );
实例代码:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW";
CHAR16 s2[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 s3[40]=L"LAB-Z";
CHAR16 s4[40]=L"MAB-Z";
UINTN Result;
Result=StrCmp(s1,s2);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrCmp(s2,s3);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrCmp(s3,s4);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
6. StrnCmp 作用:和上面的比较函数类似,只是这个函数只比较指定的前n个字符
/** Compares up to a specified length the contents of two Null-terminated Unicode strings, and returns the difference between the first mismatched Unicode characters. This function compares the Null-terminated Unicode string FirstString to the Null-terminated Unicode string SecondString. At most, Length Unicode characters will be compared. If Length is 0, then 0 is returned. If FirstString is identical to SecondString, then 0 is returned. Otherwise, the value returned is the first mismatched Unicode character in SecondString subtracted from the first mismatched Unicode character in FirstString. If Length > 0 and FirstString is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and FirstString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and SecondString is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Length > 0 and SecondString is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Length is greater than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and FirstString contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and SecondString contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param FirstString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param SecondString The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Length The maximum number of Unicode characters to compare. @retval 0 FirstString is identical to SecondString. @return others FirstString is not identical to SecondString. **/ INTN EFIAPI StrnCmp ( IN CONST CHAR16 *FirstString, IN CONST CHAR16 *SecondString, IN UINTN Length );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW";
CHAR16 s2[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 s3[40]=L"LAB-Z";
CHAR16 s4[40]=L"MAB-Z";
Result=StrnCmp(s1,s2,7);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrnCmp(s2,s3,5);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
Result=StrnCmp(s3,s4,5);
Print(L"%d\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
7. StrCat 作用:将 Source 字符串的内容拼接到 Destination 字符串上。
/** Concatenates one Null-terminated Unicode string to another Null-terminated Unicode string, and returns the concatenated Unicode string. This function concatenates two Null-terminated Unicode strings. The contents of Null-terminated Unicode string Source are concatenated to the end of Null-terminated Unicode string Destination. The Null-terminated concatenated Unicode String is returned. If Source and Destination overlap, then the results are undefined. If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source is NULL, then ASSERT(). If Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT(). If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Destination contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and concatenating Destination and Source results in a Unicode string with more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT(). @param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string. @return Destination. **/ CHAR16 * EFIAPI StrCat ( IN OUT CHAR16 *Destination, IN CONST CHAR16 *Source );
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 s2[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrCat(s1,s2);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
8.StrnCat 作用:将 Source 字符串前面n个字符的内容拼接到 Destination 字符串上。
/**
Concatenates up to a specified length one Null-terminated Unicode to the end
of another Null-terminated Unicode string, and returns the concatenated
Unicode string.
This function concatenates two Null-terminated Unicode strings. The contents
of Null-terminated Unicode string Source are concatenated to the end of
Null-terminated Unicode string Destination, and Destination is returned. At
most, Length Unicode characters are concatenated from Source to the end of
Destination, and Destination is always Null-terminated. If Length is 0, then
Destination is returned unmodified. If Source and Destination overlap, then
the results are undefined.
If Destination is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Length > 0 and Destination is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If Length > 0 and Source is NULL, then ASSERT().
If Length > 0 and Source is not aligned on a 16-bit boundary, then ASSERT().
If Source and Destination overlap, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Length is greater than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Destination contains more
than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the
Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and Source contains more than
PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength Unicode characters, not including the
Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
If PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength is not zero, and concatenating Destination
and Source results in a Unicode string with more than PcdMaximumUnicodeStringLength
Unicode characters, not including the Null-terminator, then ASSERT().
@param Destination The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@param Source The pointer to a Null-terminated Unicode string.
@param Length The maximum number of Unicode characters to concatenate from
Source.
@return Destination.
**/
CHAR16 *
EFIAPI
StrnCat (
IN OUT CHAR16 *Destination,
IN CONST CHAR16 *Source,
IN UINTN Length
);
实例:
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
CHAR16 *s1=L"WWW.";
CHAR16 s2[40]=L"LAB-Z.COM";
CHAR16 *Result;
Result=StrnCat(s1,s2,3);
Print(L"%s\n",Result);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果
本文参考 《UEFI 原理与编程》。
之前介绍过两种Arduino 模拟键盘的方法,一种是普通的Uno加上电阻之类的元件;一种是使用自带 USB 功能的 Arduino ,比如 Leonardo ,内部集成了USB Slave控制器。 这里再介绍蓝牙方案。
我们最常见的就是蓝牙透传模块,用蓝牙搜索安装之后能在系统中模拟出来一个串口,上位机直接按照串口方式即可进行通讯。这次介绍一款蓝牙键盘模块(实际上是键盘鼠标模块)。
外观和普通蓝牙透传模块一样(蓝牙芯片真正有用的都是内部Firmware)
用法非常类似,在蓝牙中搜索连接之后系统中会出现键盘设备。
然后数据是从串口送到蓝牙设备中的。根据说明我用 Arduino 编写了一个简单的测试程序,每隔5秒发送 “1” 字符。
输入 1:
按下数据 1 数据包为: 0C 00 A1 01 00 00 1E 00 00 00 00 00
按键弹起: 0C 00 A1 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
程序如下:
char KeyPress[]={0x0C,0x00,0xA1,0x01,0x00,0x00,0x1E,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00};
char KeyRelease[]={0x0C,0x00,0xA1,0x01,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00};
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial1.begin(9600); //设置串口波特率
}
void loop() {
for (byte i=0;i<sizeof(KeyPress);i++)
{
Serial1.write(KeyPress[i]);
}
for (byte i=0;i<sizeof(KeyRelease);i++)
{
Serial1.write(KeyRelease[i]);
}
delay(5000);
}
测试结果,每隔5秒我的电脑上就可以收到一个 1 的输入。
更多的好玩还在研究中。有模拟键盘需要的朋友不妨考虑这样的蓝牙模块,顺便说一下,这种模块在35元左右,比普通透传模块贵多了(通常20左右)。当然,你可以看看国外类似的产品,Adafruit出品的“EZ-Key BT HID Keyboard Controller纸模块”价格在180元,感觉就不那么贵了……
==================================================================
2016年3月13日 更新
我一直以为在文章中放出来过购买链接,昨天有朋友问检查了一下才发现我忘记了。这个模块的购买链接是 https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z09.2.0.0.V7mzul&id=521222818182&_u=dkf8s9fbec
卖家名字是 “重庆翔码电子工厂店”。买的时候你不妨问一下卖家,说你要做蓝牙HID设备,这个和普通常用的蓝牙串口透传模块之类的是不同的。
再放一下这个模块的说明书:BTHID
特别注意:之前我一直以为蓝牙键盘模块和蓝牙扫描枪模块是同一个东西,结果有朋友买成了“蓝牙扫描枪模块”,结果无法使用。他们之间的差别在于,键盘模块可以发送 shift/alt/ctrl 等等。蓝牙扫描枪模块只能发送可见的 ascii。
所以一定要询问清楚(估计是当时我和卖家说了,然后虽然拍下的是蓝牙扫描枪模块,但是给我的是蓝牙键盘模块)。
之前一直在使用攀藤 G1 ,前面提到 G1 都坏掉了郁闷无比。然后入手了一个 G3 。之所以还选择攀藤的产品最主要是考虑尽可能的复用之前的代码……
下面图是 G1 和 G3 外观,可以看出 G3 要小一点:
数据上和G1稍微有些差别,主要是送出来的数据短了一些。
下面是串口实际获得的数据
具体解读(来自说明书)
最后修改一下之前给 G1 写的 APP 即可
完整的代码
G3Ver1source
编译后的程序
Project2
前面实现了HP 鼠标数据的读取,下面继续研究 DELL 的鼠标。还是首先运行取得描述符的程序,结果如下:
Start
Device addressed… Requesting device descriptor.
Device descriptor:
Descriptor Length: 12
USB version: 1.10
Class: 00 Use class information in the Interface Descriptor
Subclass: 00
Protocol: 00
Max.packet size: 08
Vendor ID: 2188
Product ID: 0AE1
Revision ID: 0100
Mfg.string index: 00
Prod.string index: 01 Length: 38 Contents: USB OPTICAL MOUSE
Serial number index: 00
Number of conf.: 01
Configuration number 0
Total configuration length: 34 bytes
Configuration descriptor:
Total length: 0022
Number of interfaces: 01
Configuration value: 01
Configuration string: 00
Attributes: A0 Remote Wakeup
Max.power: 32 100ma
Interface descriptor:
Interface number: 00
Alternate setting: 00
Endpoints: 01
Class: 03 HID (Human Interface Device)
Subclass: 01
Protocol: 02
Interface string: 00
HID descriptor:
Descriptor length: 09 9 bytes
HID version: 1.11
Country Code: 0 Not Supported
Class Descriptors: 1
Class Descriptor Type: 22 Report
Class Descriptor Length:66 bytes
HID report descriptor:
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Usage Page Generic Desktop Controls Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Data: 02
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Collection Application (mouse, keyboard) Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report ID Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Collection Physical (group of axes) Data: 00
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Usage Page Button Data: 09
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Minimum Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Maximum Data: 03
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Logical Minimum Data: 00
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Logical Maximum Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Count Data: 03
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Size Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Input Data,Variable,Absolute,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile(Ignore for Input), Data: 02
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Count Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Size Data: 05
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Input Constant,Array,Absolute,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile(Ignore for Input), Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Usage Page Generic Desktop Controls Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Data: 30
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Data: 31
Length: 2 Type: Global Tag: Logical Minimum Data: 00 Data: F8
Length: 2 Type: Global Tag: Logical Maximum Data: FF Data: 07
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Size Data: 0C
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Count Data: 02
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Input Data,Variable,Relative,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile(Ignore for Input), Data: 06
Length: 1 Type: Local Tag: Usage Data: 38
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Logical Minimum Data: 81
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Logical Maximum Data: 7F
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Size Data: 08
Length: 1 Type: Global Tag: Report Count Data: 01
Length: 1 Type: Main Tag: Input Data,Variable,Relative,No Wrap,Linear,Preferred State,No Null Position,Non-volatile(Ignore for Input), Data: 06
Length: 0 Type: Main Tag: End Collection
Length: 0 Type: Main Tag: End Collection
Endpoint descriptor:
Endpoint address: 01 Direction: IN
Attributes: 03 Transfer type: Interrupt
Max.packet size: 0006
Polling interval: 0A 10 ms
同样,尝试之前的 Get_Report 方式的程序,得到的却是不停的输出的错误信息:
Setup packet error: 7
Mouse Poll Error: 7
没有办法直接了解这个错误编号的含义,最后只能用逻辑分析仪分析产生问题的原因:
可以看到当发送Get_Report之后,Device 会返回STALL 。
对比之前能够正常工作的 HP 鼠标,收到 Get_Report 后,会返回 ACK 还会继续通讯。
查看资料上说,返回STALL有可能是因为设备不支持该指令…… Windows的设备经常会出现这样的情况:可以正常工作,但是未必完整的 follow 工业标准。
上面的方法行不通,只能用中断方式来获取数据。我去掉了切换 Boot Protocol 的代码
/* Mouse communication via interrupt endpoint */
/* Assumes EP1 as interrupt IN ep */
#include "max3421e.h"
#include "usb.h"
#define DEVADDR 1
#define CONFVALUE 1
#define EP_MAXPKTSIZE 5
EP_RECORD ep_record[ 2 ]; //endpoint record structure for the mouse
void setup();
void loop();
MAX3421E Max;
USB Usb;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin( 115200 );
Serial.println("Start");
Max.powerOn();
delay( 200 );
}
void loop()
{
byte rcode;
Max.Task();
Usb.Task();
if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_CONFIGURING ) {
mouse1_init();
}//if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_CONFIGURING...
if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_RUNNING ) { //poll the keyboard
rcode = mouse1_poll();
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Mouse Poll Error: ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
}//if( rcode...
}//if( Usb.getUsbTaskState() == USB_STATE_RUNNING...
}
/* Initialize mouse */
void mouse1_init( void )
{
byte rcode = 0; //return code
byte tmpdata;
byte* byte_ptr = &tmpdata;
/**/
ep_record[ 0 ] = *( Usb.getDevTableEntry( 0,0 )); //copy endpoint 0 parameters
ep_record[ 1 ].MaxPktSize = EP_MAXPKTSIZE;
ep_record[ 1 ].sndToggle = bmSNDTOG0;
ep_record[ 1 ].rcvToggle = bmRCVTOG0;
Usb.setDevTableEntry( 1, ep_record ); //plug kbd.endpoint parameters to devtable
/* Configure device */
rcode = Usb.setConf( DEVADDR, 0, CONFVALUE );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Error configuring mouse. Return code : ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while(1); //stop
}//if( rcode...
rcode = Usb.setIdle( DEVADDR, 0, 0, 0, tmpdata );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Set Idle error. Return code : ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while(1); //stop
}
rcode = Usb.getIdle( DEVADDR, 0, 0, 0, (char *)byte_ptr );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Get Idle error. Return code : ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while(1); //stop
}
Serial.print("Idle Rate: ");
Serial.print(( tmpdata * 4 ), DEC ); //rate is returned in multiples of 4ms
Serial.println(" ms");
tmpdata = 0;
rcode = Usb.setIdle( DEVADDR, 0, 0, 0, tmpdata );
if( rcode ) {
Serial.print("Set Idle error. Return code : ");
Serial.println( rcode, HEX );
while(1); //stop
}
Usb.setUsbTaskState( USB_STATE_RUNNING );
return;
}
/* Poll mouse via interrupt endpoint and print result */
/* assumes EP1 as interrupt endpoint */
byte mouse1_poll( void )
{
byte rcode,i;
char buf[ 6 ] = { 0 }; //mouse report buffer
unsigned long int libuf[ sizeof(buf) ];
unsigned long int x;
unsigned long int y;
/* poll mouse */
rcode = Usb.inTransfer( DEVADDR, 1, sizeof(buf), buf, 1 ); //
if( rcode ) { //error
if( rcode == 0x04 ) { //NAK
rcode = 0;
}
return( rcode );
}
/* print buffer */
if( buf[ 1 ] & 0x01 ) {
Serial.println("Button1 pressed ");
}
if( buf[ 1 ] & 0x02 ) {
Serial.println("Button2 pressed ");
}
if( buf[ 1 ] & 0x04 ) {
Serial.println("Button3 pressed ");
}
for (int i=0;i<sizeof(buf);i++) {
libuf[i]=(buf[i]) & 0xff;
}
/*
Serial.print(libuf[0],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(libuf[1],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(libuf[2],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(libuf[3],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(libuf[4],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(libuf[5],HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println("");
*/
Serial.print("X-axis: ");
x=((libuf[3] & 0xF)<<8)+(libuf[2] & 0xFF );
if (x & 0x800) {
Serial.print("-");
x = ((~x) & 0x7FF) +1;
}
Serial.print(x, HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Y-axis: ");
y=(((libuf[3]>>4) & 0xF) +((libuf[4] & 0xFF )<<4));
if (y & 0x800) {
Serial.print("-");
y = ((~y) & 0x7FF) +1;
}
Serial.print(y, HEX); Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Wheel: ");
Serial.println(buf [5] & 0xFF, HEX);
return( rcode );
}
和前面那个程序相比,这个特别之处在于返回值多了 Report_ID ,对于我们处理数据来说,只是有效数据从 Buf[1] 开始,其他地方并无特别。
运行结果
完整代码下载
基本上,鼠标的玩法就是这些。可以用鼠标做很多好玩的东西。
根据网上搜到的结果,在【参考1】下载了 controlP5 的库,然后使用下面的程序
import controlP5.*;
ControlP5 cp5;
String[] textfieldNames = {"tf1", "tf2", "tf3", "tf4", "tf5"};
void setup() {
size(700,400);
PFont font = createFont("arial",20);
cp5 = new ControlP5(this);
int y = 20;
int spacing = 60;
for(String name: textfieldNames){
cp5.addTextfield(name)
.setPosition(20,y)
.setSize(100,40)
.setFont(font)
.setFocus(true)
.setColor(color(255,0,0))
;
y += spacing;
}
textFont(font);
}
void draw() {
background(0);
}
void controlEvent(ControlEvent theEvent) {
if(theEvent.isAssignableFrom(Textfield.class)) {
println("controlEvent: accessing a string from controller '"
+theEvent.getName()+"': "
+theEvent.getStringValue()
);
}
}
运行结果
1. http://www.sojamo.de/libraries/controlP5/
前面介绍了 MD5 的实现,这里介绍一下 SHA-1 算法的实现。具体代码来自【参考1】。
和之前 MD5 程序有一些差别在于这个程序不是一次性将所有文件都放入内存中,而是放入一部分,计算一部分,再用中间结果继续计算下一部分。这样,再大的文件也可以正常处理。
#include <Uefi.h>
#include <Library/UefiLib.h>
#include <Library/ShellCEntryLib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <Protocol/EfiShell.h>
#include <Library/ShellLib.h>
#include <Library/MemoryAllocationLib.h>
#include "sha1.h"
#define BUFFERSIZE 2048
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
extern EFI_SHELL_PROTOCOL *gEfiShellProtocol;
int
EFIAPI
main (
IN int Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_FILE_HANDLE FileHandle;
RETURN_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_INFO *FileInfo = NULL;
EFI_HANDLE *HandleBuffer=NULL;
UINTN ReadSize=BUFFERSIZE;
SHA1Context sha;
//Check if there is a parameter
if (Argc == 1) {
Print(L"Usage: crctest [filename]\n");
return 0;
}
//Open the file given by the parameter
Status = ShellOpenFileByName(Argv[1], (SHELL_FILE_HANDLE *)&FileHandle,
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ , 0);
if(Status != RETURN_SUCCESS) {
Print(L"OpenFile failed!\n");
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
//Get file size
FileInfo = ShellGetFileInfo( (SHELL_FILE_HANDLE)FileHandle);
/*
* Reset the SHA-1 context and process input
*/
SHA1Reset(&sha);
//Allocate a memory buffer
HandleBuffer = AllocateZeroPool(BUFFERSIZE);
if (HandleBuffer == NULL) {
return (SHELL_OUT_OF_RESOURCES); }
while (BUFFERSIZE == ReadSize)
{
ReadSize=BUFFERSIZE;
//Load the whole file to the buffer
Status = ShellReadFile(FileHandle,&ReadSize,HandleBuffer);
SHA1Input(&sha,(unsigned char *) HandleBuffer, ReadSize);
}
//Output
Print(L"File Name: %s\n",Argv[1]);
Print(L"File Size: %d\n",(UINTN)FileInfo-> FileSize);
if (!SHA1Result(&sha))
{
Print(L"sha: could not compute message digest\n");
}
else
{
Print(L"%08X %08X %08X %08X %08X\n",
sha.Message_Digest[0],
sha.Message_Digest[1],
sha.Message_Digest[2],
sha.Message_Digest[3],
sha.Message_Digest[4]);
}
FreePool(HandleBuffer);
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
完整的代码下载:
参考:
1.https://www.packetizer.com/